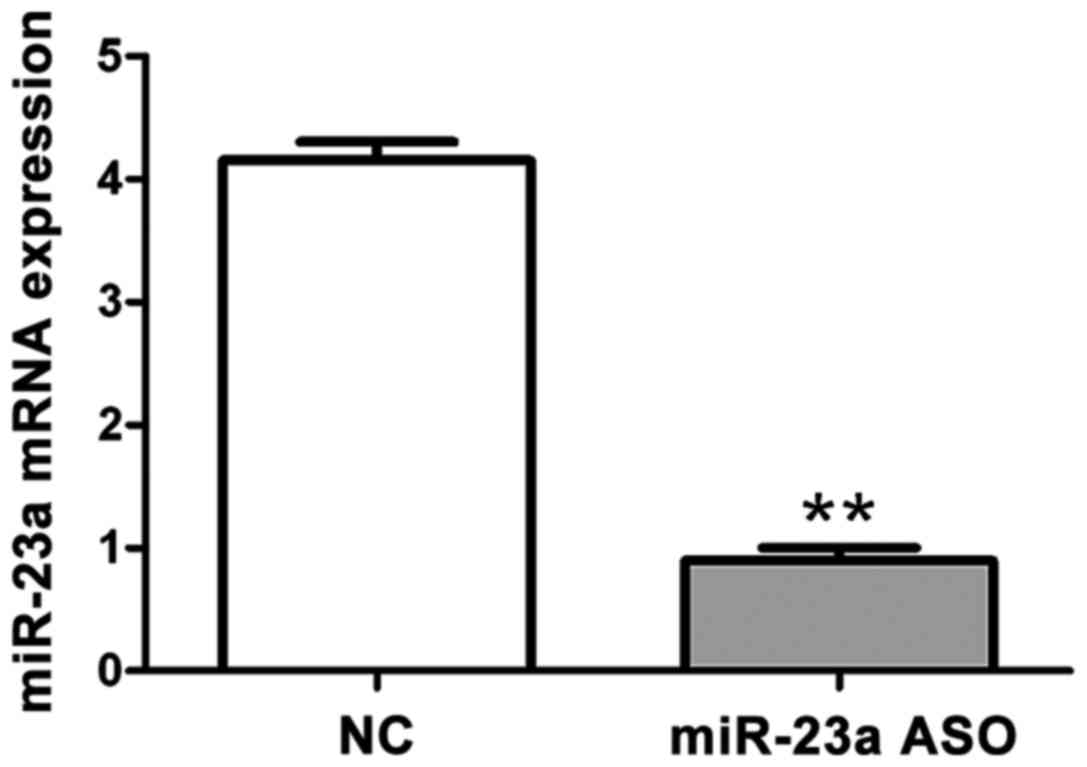
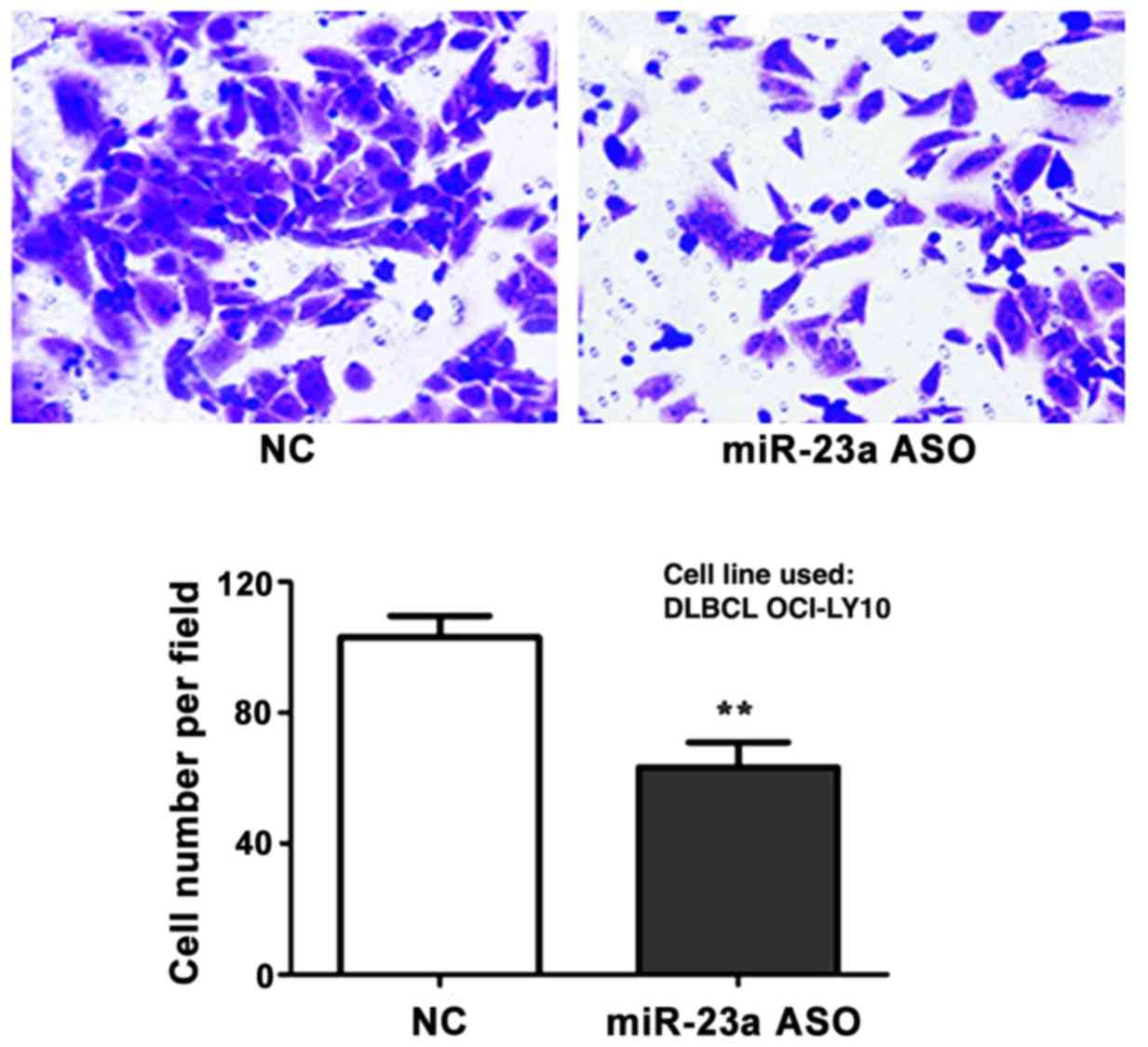
|
1
|
Vaidya R and Witzig TE: Prognostic factors
for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the R(X)CHOP era. Ann Oncol.
25:2124–2133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith A, Howell D, Patmore R, Jack A and
Roman E: Incidence of haematological malignancy by sub-type: A
report from the Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br J
Cancer. 105:1684–1692. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC,
Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E,
Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, et al: Confirmation of the molecular
classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by
immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 103:275–282.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shankland KR, Armitage JO and Hancock BW:
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet. 380:848–857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghielmini M, Vitolo U, Kimby E, Montoto S,
Walewski J, Pfreundschuh M, Federico M, Hoskin P, McNamara C,
Caligaris-Cappio F, et al: Panel Members of the 1st ESMO Consensus
Conference on Malignant Lymphoma: ESMO Guidelines consensus
conference on malignant lymphoma 2011 part 1: Diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL) and chronic lymphocytic
leukemia (CLL). Ann Oncol. 24:561–576. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Essadi I, Ismaili N, Tazi E, Elmajjaoui S,
Saidi A, Ichou M and Errihani H: Primary lymphoma of the head and
neck: Two case reports and review of the literature. Cases J.
1:4262008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board: Adult
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ): Health Professional
VersionPDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. National Cancer
Institute (US); Bethesda: 2002
|
|
8
|
Dogan A, Bagdi E, Munson P and Isaacson
PG: CD10 and BCL-6 expression in paraffin sections of normal
lymphoid tissue and B-cell lymphomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 24:846–852.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chhabra R, Dubey R and Saini N:
Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the
miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol
Cancer. 9:2322010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chhabra R, Adlakha YK, Hariharan M, Scaria
V and Saini N: Upregulation of miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster induces
caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in human embryonic
kidney cells. PLoS One. 4:e58482009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kong KY, Owens KS, Rogers JH, Mullenix J,
Velu CS, Grimes HL and Dahl R: MIR-23A microRNA cluster inhibits
B-cell development. Exp Hematol. 38(629–640): e12010.
|
|
12
|
Schetter AJ, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Mathé
EA, Yuen ST, Hawkes JE, Croce CM, Leung SY and Harris CC:
Association of inflammation-related and microRNA gene expression
with cancer-specific mortality of colon adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:5878–5887. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang WL, Yang C, Han XL, Wang R, Huang Y,
Zi YM and Li JD: MicroRNA-23a expression in paraffin-embedded
specimen correlates with overall survival of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma. Med Oncol. 31:9192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du P, Ye L, Li H, Yang Y and Jiang WG: The
tumour suppressive role of metastasis suppressor-1, MTSS1, in human
kidney cancer, a possible connection with the SHH pathway. J Exp
Ther Oncol. 10:91–99. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jahid S, Sun J, Edwards RA, Dizon D,
Panarelli NC, Milsom JW, Sikandar SS, Gümüs ZH and Lipkin SM:
miR-23a promotes the transition from indolent to invasive
colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2:540–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell
RB and Cohen SM: bantam encodes a developmentally regulated
microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the
proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell. 113:25–36. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, Lin S,
Park JK, Dai Z, Liu CG, Schmittgen TD, Reinhold WC, Croce CM, et
al: MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du T and Zamore PD: microPrimer: The
biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development. 132:4645–4652.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rao SA, Santosh V and Somasundaram K:
Genome-wide expression profiling identifies deregulated miRNAs in
malignant astrocytoma. Mod Pathol. 23:1404–1417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Deng D, Wang L, Chen Y, Li B, Xue L, Shao
N, Wang Q, Xia X, Yang Y and Zhi F: MicroRNA-124-3p regulates cell
proliferation, invasion, apoptosis, and bioenergetics by
targetingPIM1 in astrocytoma. Cancer Sci. 107:899–907. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu X, Chen D, Cui Y, Li Z and Huang J:
Targeting microRNA-23a to inhibit glioma cell invasion via HOXD10.
Sci Rep. 3:34232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee SH, Kerff F, Chereau D, Ferron F, Klug
A and Dominguez R: Structural basis for the actin-binding function
of missing-in-metastasis. Structure. 15:145–155. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee YG, Macoska JA, Korenchuk S and Pienta
KJ: MIM, a potential metastasis suppressor gene in bladder cancer.
Neoplasia. 4:291–294. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Gong T, Li
M, Sun L, Ji G, Shi Y, Han Z, et al: miRNA-223 promotes gastric
cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor
EPB41L3. Mol Cancer Res. 9:824–833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Z, Wei W and Sarkar FH: miR-23a, a
critical regulator of ‘migR’ ation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Discov. 2:489–491. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gottardo F, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Calin GA,
Fassan M, Bassi P, Sevignani C, Byrne D, Negrini M, Pagano F, et
al: Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol Oncol.
25:387–392. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Parr C and Jiang WG: Metastasis suppressor
1 (MTSS1) demonstrates prognostic value and anti-metastatic
properties in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 45:1673–1683. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|