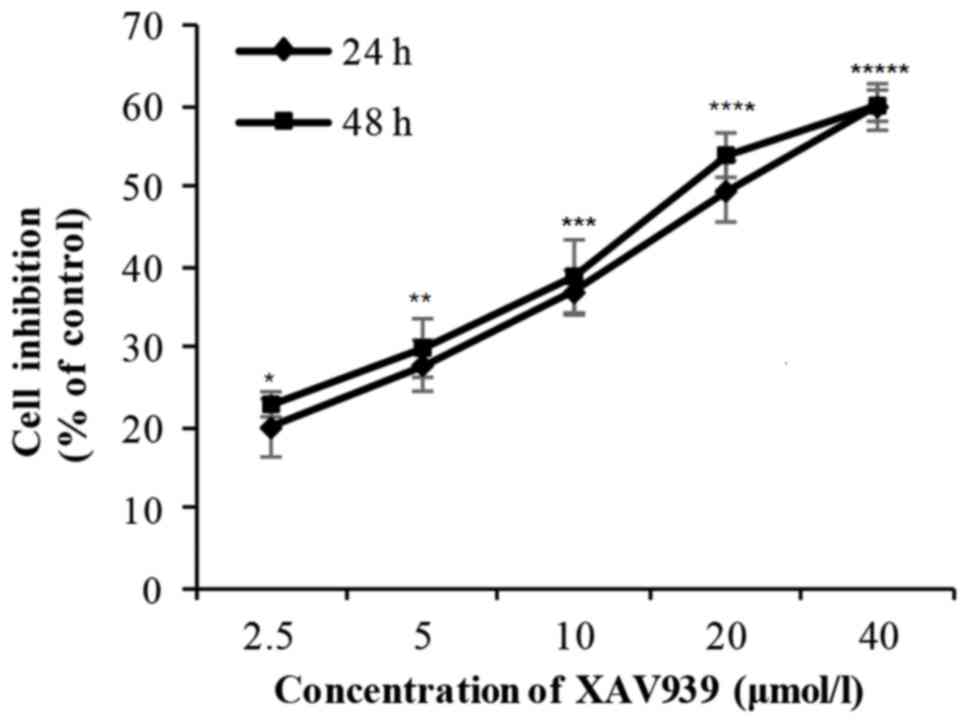
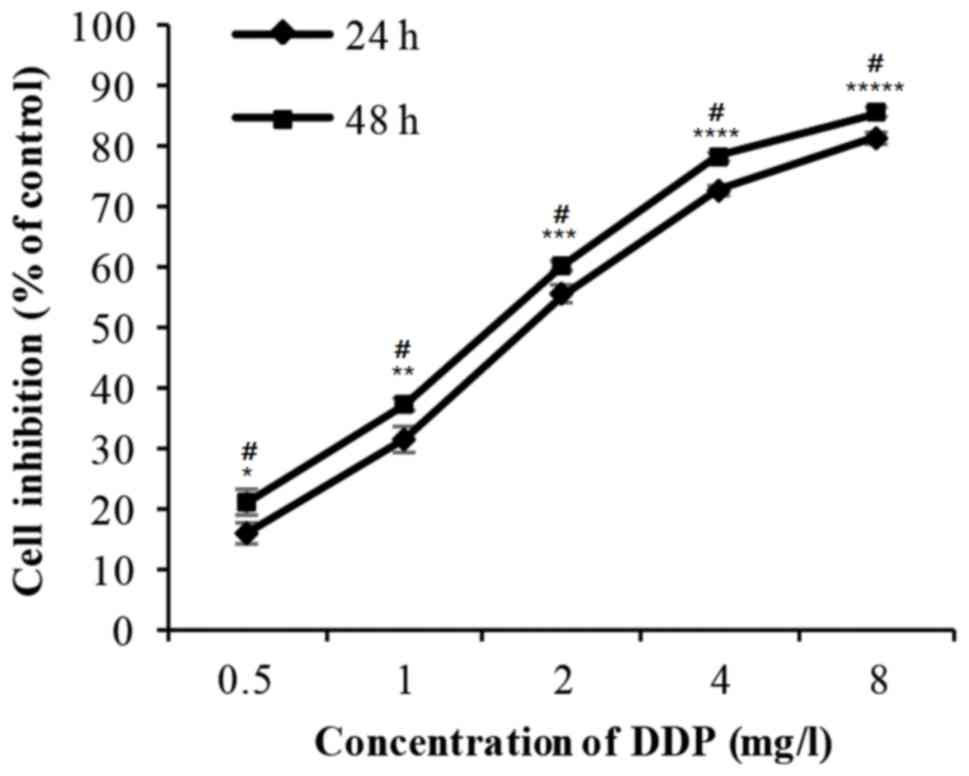
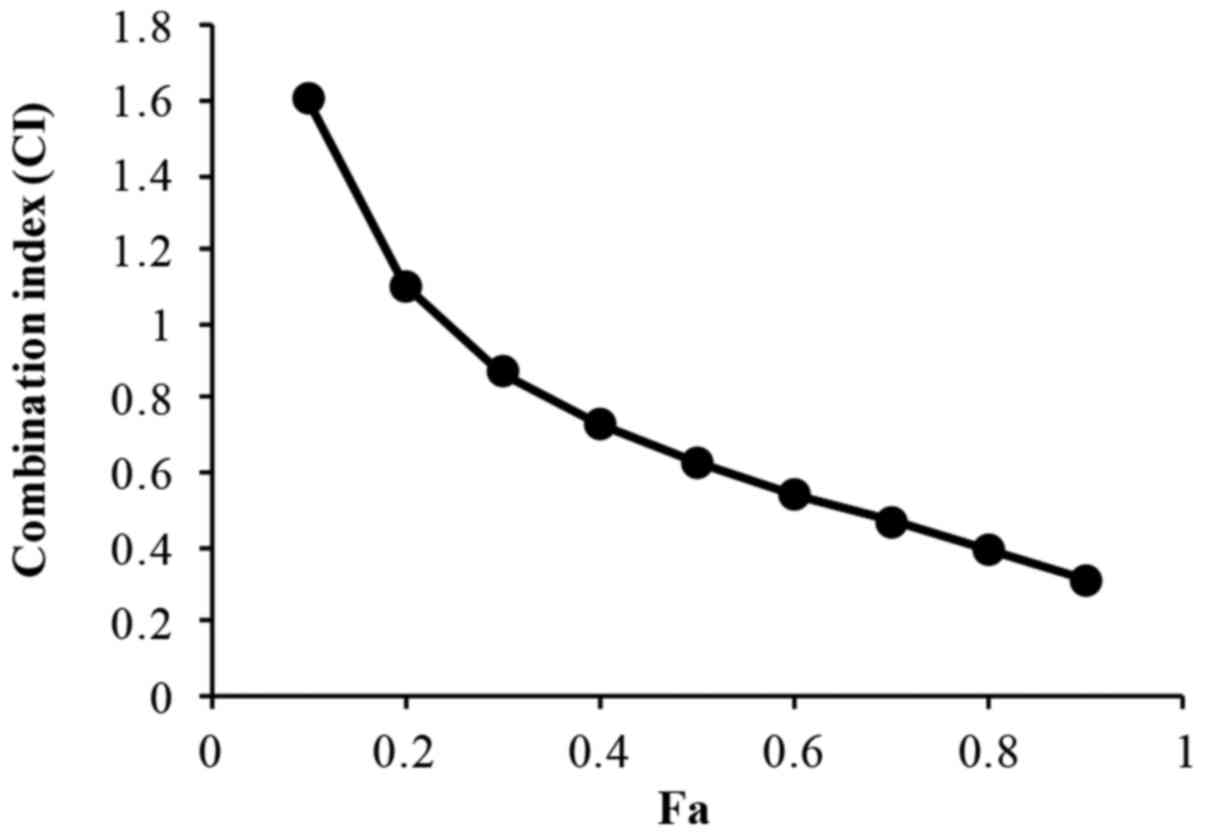
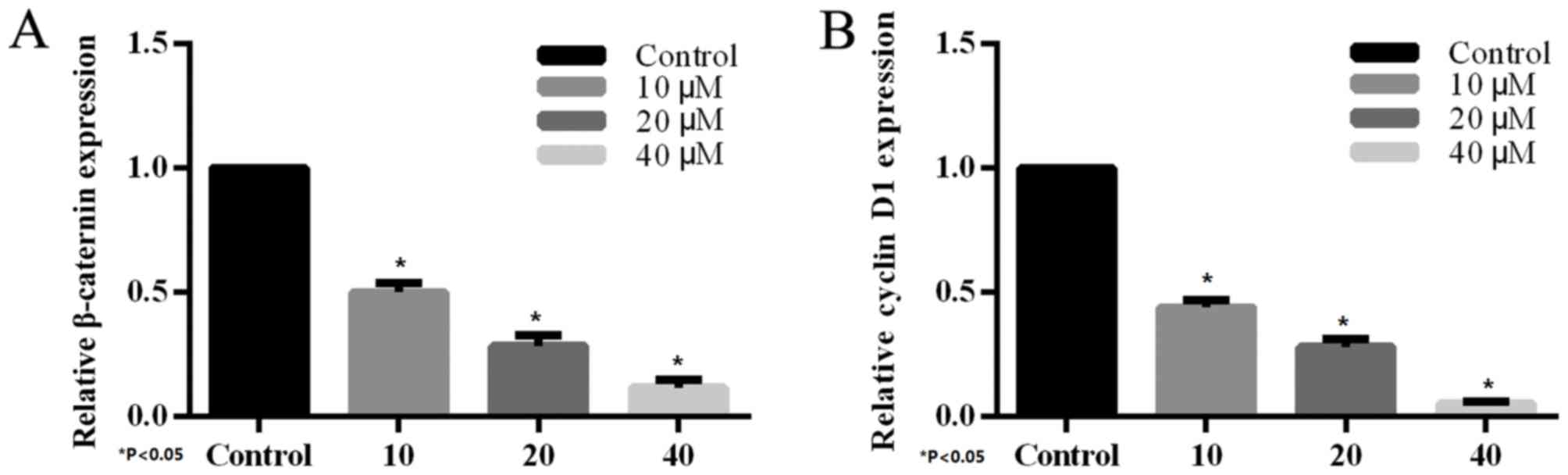
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Byers LA and Rudin CM: Small cell lung
cancer: Where do we go from here? Cancer. 121:664–672. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling in cancer. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0080522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Snow GE, Kasper AC, Busch AM, Schwarz E,
Ewings KE, Bee T, Spinella MJ, Dmitrovsky E and Freemantle SJ: Wnt
pathway reprogramming during human embryonal carcinoma
differentiation and potential for therapeutic targeting. BMC
Cancer. 9:3832009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
You L, He B, Xu Z, Uematsu K, Mazieres J,
Mikami I, Reguart N, Moody TW, Kitajewski J, McCormick F and
Jablons DM: Inhibition of Wnt-2-mediated signaling induces
programmed cell death in non-small-cell lung cancer cells.
Oncogene. 23:6170–6174. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pacheco-Pinedo EC, Durham AC, Stewart KM,
Goss AM, Lu MM, Demayo FJ and Morrisey EE: Wnt/β-catenin signaling
accelerates mouse lung tumorigenesis by imposing an embryonic
distal progenitor phenotype on lung epithelium. J Clin Invest.
121:1935–1945. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Zhang XH, Kim JY,
Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Gerald WL and Massagué J: WNT/TCF signaling
through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis.
Cell. 138:51–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund
JN and Costantini F: Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the
transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling
pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 22:1172–1183. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rousset R, Mack JA, Wharton KA Jr, Axelrod
JD, Cadigan KM, Fish MP, Nusse R and Scott MP: Naked cuticle
targets dishevelled to antagonize Wnt signal transduction. Genes
Dev. 15:658–671. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A,
Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner
S, et al: Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt
signalling. Nature. 461:614–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gelmini S, Poggesi M, Distante V, Bianchi
S, Simi L, Luconi M, Raggi CC, Cataliotti L, Pazzagli M and Orlando
C: Tankyrase, a positive regulator of telomere elongation, is over
expressed in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 216:81–87. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gelmini S, Poggesi M, Pinzani P, Mannurita
SC, Cianchi F, Valanzano R and Orlando C: Distribution of
Tankyrase-1 mRNA expression in colon cancer and its prospective
correlation with progression stage. Oncol Rep. 16:1261–1266.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gelmini S, Quattrone S, Malentacchi F,
Villari D, Travaglini F, Giannarini G, Della Melina A, Pazzagli M,
Nicita G, Selli C and Orlando C: Tankyrase-1 mRNA expression in
bladder cancer and paired urine sediment: Preliminary experience.
Clin Chem Lab Med. 45:862–866. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
MacNamara B, Wang W, Chen Z, Hou M, Mazur
J, Gruber A and Porwit-MacDonald A: Telomerase activity in relation
to pro- and anti-apoptotic protein expression in high grade
non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Haematologica. 86:386–393. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klapper W, Krams M, Qian W, Janssen D and
Parwaresch R: Telomerase activity in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas
is regulated by hTERT transcription and correlated with
telomere-binding protein expression but uncoupled from
proliferation. Br J Cancer. 89:713–719. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bao R, Christova T, Song S, Angers S, Yan
X and Attisano L: Inhibition of tankyrases induces Axin
stabilization and blocks Wnt signalling in breast cancer cells.
PLoS One. 7:e486702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Waaler J, Machon O, Tumova L, Dinh H,
Korinek V, Wilson SR, Paulsen JE, Pedersen NM, Eide TJ, Machonova
O, et al: A novel tankyrase inhibitor decreases canonical Wnt
signaling in colon carcinoma cells and reduces tumor growth in
conditional APC mutant mice. Cancer Res. 72:2822–2832. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Busch AM, Johnson KC, Stan RV, Sanglikar
A, Ahmed Y, Dmitrovsky E and Freemantle SJ: Evidence for tankyrases
as antineoplastic targets in lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:2112013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sharma RP and Chopra VL: Effect of the
Wingless (wg1) mutation on wing and haltere development in
Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 48:461–465. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nusse R, van Ooyen A, Cox D, Fung YK and
Varmus H: Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary
oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature. 307:131–136. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Siegfried E and Perrimon N: Drosophila
wingless: A paradigm for the function and mechanism of Wnt
signaling. Bioessays. 16:395–404. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moon RT: Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Sci
STKE. 2005:cm12005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Wnt signalling
and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:387–398. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Holland JD, Klaus A, Garratt AN and
Birchmeier W: Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 25:254–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dang CV: c-Myc target genes involved in
cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 19:1–11.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I,
Albanese C, D'Amico M, Pestell R and Ben-Ze'ev A: The cyclin D1
gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:5522–5527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|