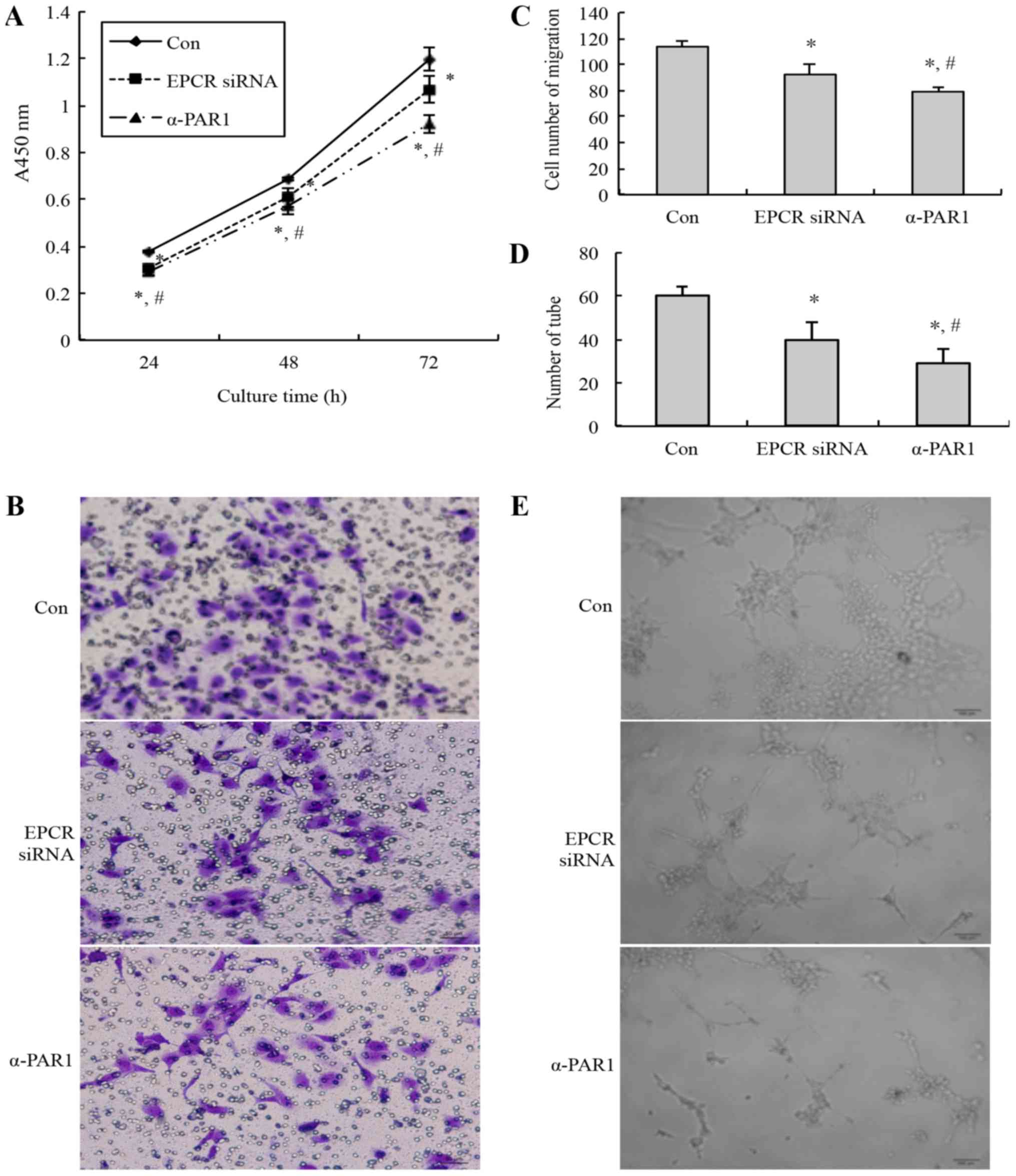
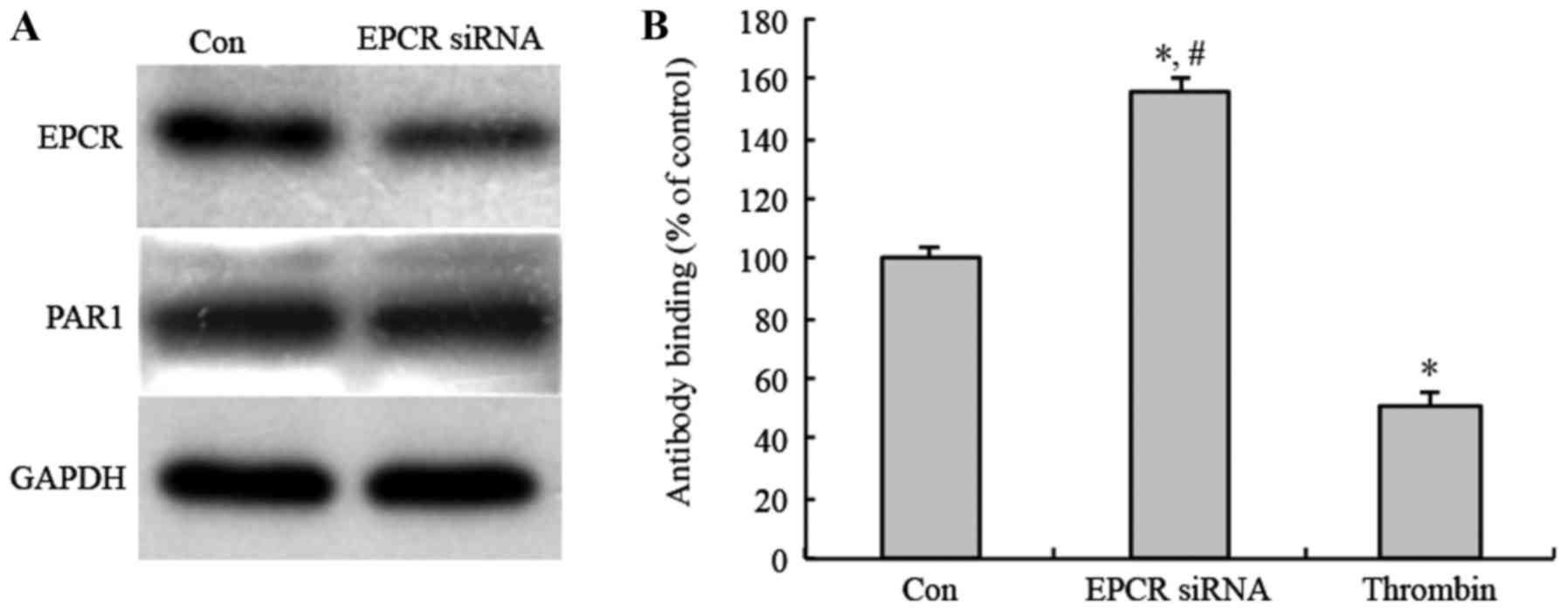
|
1
|
Liu CC, Shen Z, Kung HF and Lin MC: Cancer
gene therapy targeting angiogenesis: An updated review. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:6941–6948. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thiyagarajan M, Cheng T and Zlokovic BV:
Endothelial cell protein C receptor: Role beyond endothelium? Circ
Res. 100:155–157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Crawley JT: Multiple roles of the
endothelial cell protein C receptor. J Thromb Haemost. 5:1813–1816.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mohan Rao LV, Esmon CT and Pendurthi UR:
Endothelial cell protein C receptor: A multiliganded and
multifunctional receptor. Blood. 124:1553–1562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Riewald M, Petrovan RJ, Donner A and Ruf
W: Activated protein C signals through the thrombin receptor PAR1
in endothelial cells. J Endotoxin Res. 9:317–321. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uchiba M, Okajima K, Oike Y, Ito Y,
Fukudome K, Isobe H and Suda T: Activated protein C induces
endothelial cell proliferation by mitogen-activated protein kinase
activation in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. Circ Res. 95:34–41.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shua F, Kobayashia H, Fukudomeb K,
Tsuneyoshib N, Kimotob M and Teraoa T: Activated protein C
suppresses tissue factor expression on U937 cells in the
endothelial protein C receptor-dependent manner. FEBS Lett.
477:208–212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Keshava S, Sahoo S, Tucker TA, Idell S,
Rao LV and Pendurthi UR: Endothelial cell protein C receptor
opposes mesothelioma growth driven by tissue factor. Cancer Res.
73:3963–3973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ducros E, Mirshahi S, Azzazene D,
Camilleri-Broët S, Mery E, Al Farsi H, Althawadi H, Besbess S,
Chidiac J, Pujade-Lauraine E, et al: Endothelial protein C receptor
expressed by ovarian cancer cells as a possible biomarker of cancer
onset. Int J Oncol. 41:433–440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Antón I, Molina E, Luis-Ravelo D, Zandueta
C, Valencia K, Ormazabal C, Martínez-Canarias S, Perurena N,
Pajares MJ, Agorreta J, et al: Receptor of activated protein C
promotes metastasis and correlates with clinical outcome in lung
adenocarcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 186:96–105. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heng W, Mu CY, Chen C, Huang JA and Wang
ZY: Endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) is expressed by lung
carcinoma and correlated with clinical parameters. Clin Lab.
59:375–380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gramling MW, Beaulieu LM and Church FC:
Activated protein C enhances cell motility of endothelial cells and
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by intracellular signal
transduction. Exp Cell Res. 316:314–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perurena N, Zandueta C, Martínez-Canarias
S, Moreno H, Vicent S, Almeida AS, Guruceaga E, Gomis RR,
Santisteban M, Egeblad M, et al: EPCR promotes breast cancer
progression by altering SPOCK1/testican 1-mediated 3D growth. J
Hematol Oncol. 10:232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Q, Liu Q, Wang T, Yang H, Han Z and
Zhang P: Endothelial cell protein C receptor promotes MGC803
gastric cancer cells proliferation and migration by activating
ERK1/2. Med Oncol. 32:1622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jang HK, Kin BS, Han J, Yoon JK, Lee JR,
Jeong GJ and Shin JY: Therapeutic angiogenesis using tumor
cell-conditioned medium. Biotechnol Prog. 32:456–464. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu LN, Xu BN, Cai J, Yang JB and Lin N:
Tumor-associated fibroblast-conditioned medium promotes tumor cell
proliferation and angiogenesis. Genet Mol Res. 12:5863–5871. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang T and Jiang CL: Tumor conditioned
medium regulates the proliferation, adhesion and migration of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 63:256–260.
2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu T, Jabbes M, Nedrow-Byers JR, Wu LY,
Bryan JN and Berkman CE: Detection of prostate-specific membrane
antigen on HUVECs in response to breast tumor-conditioned medium.
Int J Oncol. 38:1349–1355. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koizumi S, Gu C, Amano S, Yamamoto S,
Ihara H, Tokuyama T and Namba H: Migration of mouse-induced
pluripotent stem cells to glioma-conditioned medium is mediated by
tumor-associated specific growth factors. Oncol Lett. 2:283–288.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng Y, Li J and Geng M: The glycan
profile of endothelial cells in the present of tumor-conditioned
medium and potential roles of beta-1,6-GlcNAc branching on HUVEC
conformation. Mol Cell Biochem. 340:143–152. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Falahat R, Wiranowska M, Gallant ND,
Toomey R, Hill R and Alcantar N: A cell ELISA for the
quantification of MUC1 mucin (CD227) expressed by cancer cells of
epithelial and neuroectodermal origin. Cell Immunol. 298:96–103.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Niessen F, Furlan-Freguia C, Fernández JA,
Mosnier LO, Castellino FJ, Weiler H, Rosen H, Griffin JH and Ruf W:
Endogenous EPCR/aPC-PAR1 signaling prevents inflammation-induced
vascular leakage and lethality. Blood. 113:2859–2866. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sundaram J, Keshava S, Gopalakrishnan R,
Esmon CT, Pendurthi UR and Rao LV: Factor VIIa binding to
endothelial cell protein C receptor protects vascular barrier
integrity in vivo. J Thromb Haemost. 12:690–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mosnier LO and Griffin JH: Inhibition of
staurosporine-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells by activated
protein C requires protease-activated receptor-1 and endothelial
cell protein C receptor. Biochem J. 373:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hun Lee J, Won S and Stein DG:
Progesterone attenuates thrombin-induced endothelial barrier
disruption in the brain endothelial cell line bEnd.3: The role of
tight junction proteins and the endothelial protein C receptor.
Brain Res. 1613:73–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sen P, Sahoo S, Pendurthi UR and Rao LV:
Zinc modulates the interaction of protein C and activated protein C
with endothelial cell protein C receptor. J Biol Chem.
285:20410–20420. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|