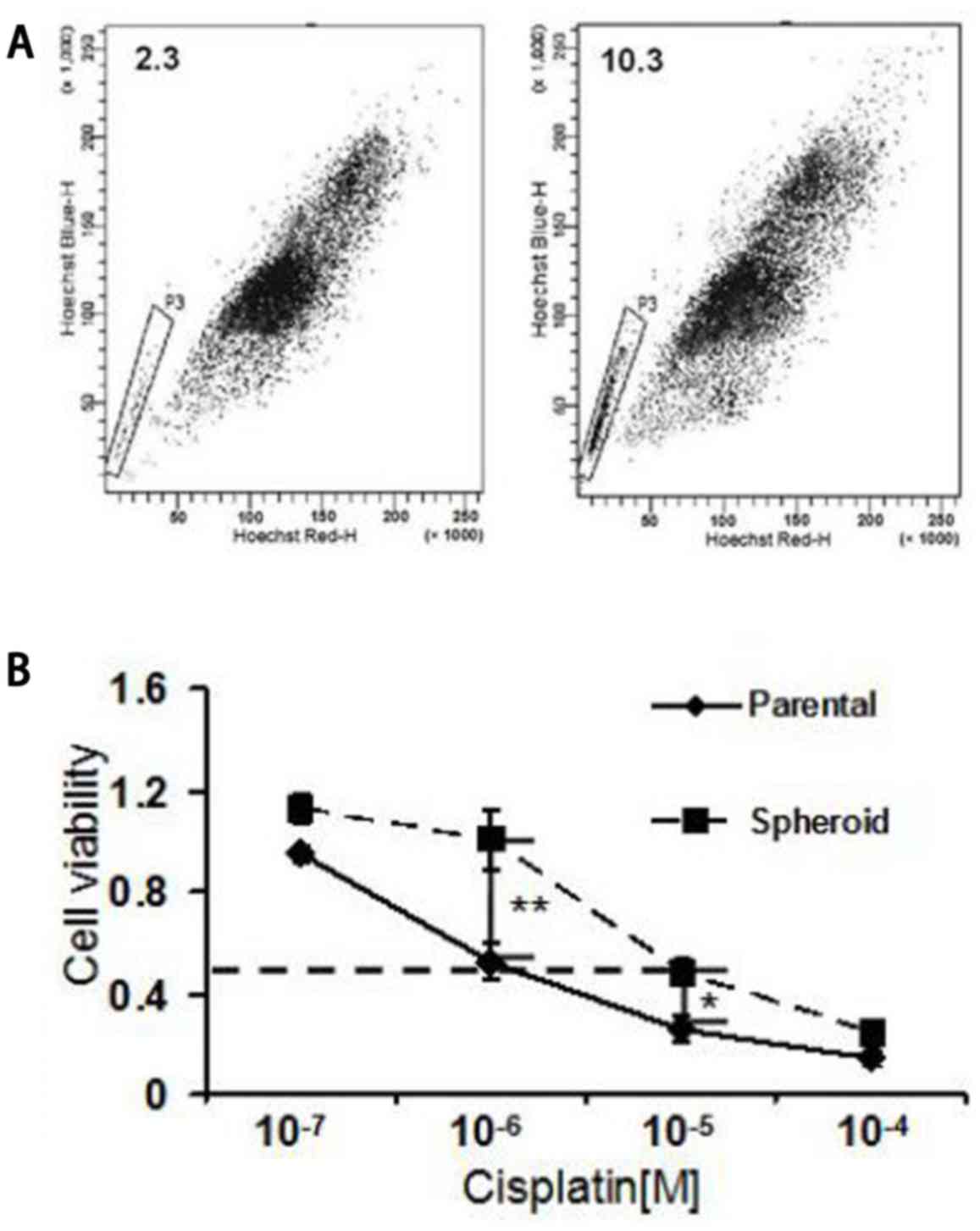
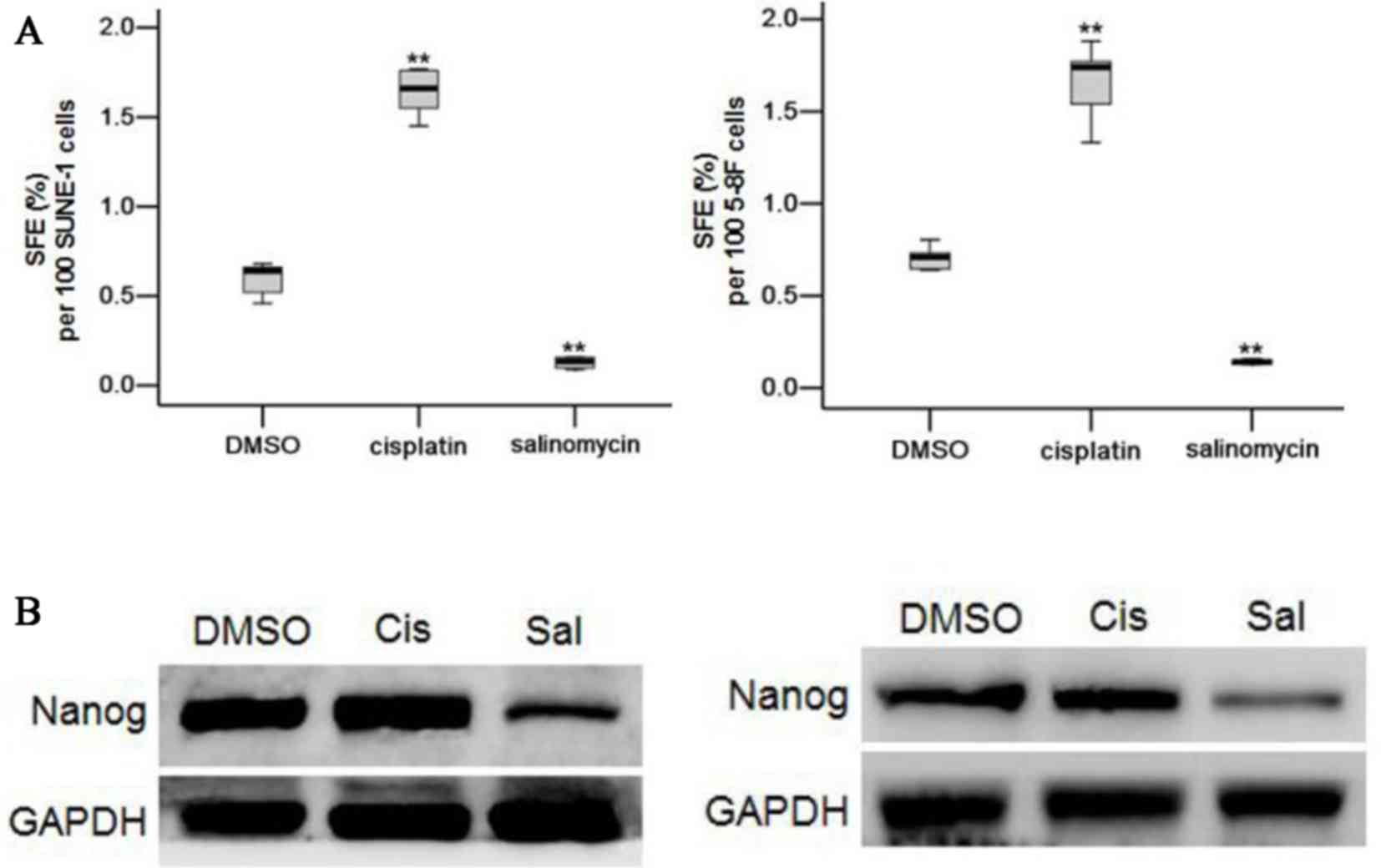
|
1
|
Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT and Chan AT:
Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current practice and future
perspective. J Clin Oncol. 33:3356–3364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tan WL, Tan EH, Lim DW, Ng QS, Tan DS,
Jain A and Ang MK: Advances in systemic treatment for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin Clin Oncol. 5:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sze H, Blanchard P, Ng WT, Pignon JP and
Lee AW: Chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma-current
recommendation and controversies. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am.
29:1107–1122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li JG, Venigalla P, Leeman JE, LaPlant Q,
Setton J, Sherman E, Tsai J, McBride S, Riaz N and Lee N: Patterns
of nodal failure after intensity modulated radiotherapy for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 127:377–382. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Greve B, Kelsch R, Spaniol K, Eich HT and
Götte M: Flow cytometry in cancer stem cell analysis and
separation. Cytometry A. 81:284–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dalerba P, Cho RW and Clarke MF: Cancer
stem cells: Models and concepts. Annu Rev Med. 58:267–284. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mathieu J, Zhang Z, Zhou W, Wang AJ,
Heddleston JM, Pinna CM, Hubaud A, Stadler B, Choi M, Bar M, et al:
HIF induces human embryonic stem cell markers in cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 71:4640–4652. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu A, Luo W, Zhang Q, Yang Z, Zhang G, Li
S and Yao K: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1, a functional marker for
identifying cancer stem cells in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cancer Lett. 330:181–189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo D, Xu BL, Zhang XH and Dong MM: Cancer
stem-like side population cells in the human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cell line cne-2 possess epithelial mesenchymal transition
properties in association with metastasis. Oncol Rep. 28:241–247.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bez A, Corsini E, Curti D, Biggiogera M,
Colombo A, Nicosia RF, Pagano SF and Parati EA: Neurosphere and
neurosphere-forming cells: Morphological and ultrastructural
characterization. Brain Res. 993:18–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi X, Gipp J and Bushman W:
Anchorage-independent culture maintains prostate stem cells. Dev
Biol. 312:396–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee CH, Yu CC, Wang BY and Chang WW:
Tumorsphere as an effective in vitro platform for screening
anti-cancer stem cell drugs. Oncotarget. 7:1215–1226.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson
KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ and Wicha MS: In vitro propagation and
transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Genes Dev. 17:1253–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lan X, Wu YZ, Wang Y, Wu FR, Zang CB, Tang
C, Cao S and Li SL: CD133 silencing inhibits stemness properties
and enhances chemoradiosensitivity in CD133-positive liver cancer
stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:315–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang CF, Peng LX, Huang TJ, Yang GD, Chu
QQ, Liang YY, Cao X, Xie P, Zheng LS, Huang HB, et al: Cancer
stem-like cell characteristics induced by EB virus-encoded LMP1
contribute to radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
suppressing the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway. Cancer Lett.
344:260–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou S, Wang F, Wong ET, Fonkem E, Hsieh
TC, Wu JM and Wu E: Salinomycin: A novel anti-cancer agent with
known anti-coccidial activities. Curr Med Chem. 20:4095–4101. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fu YZ, Yan YY, He M, Xiao QH, Yao WF, Zhao
L, Wu HZ, Yu ZJ, Zhou MY, Lv MT, et al: Salinomycin induces
selective cytotoxicity to MCF-7 mammosphere cells through targeting
the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:912–922. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Y: Effects of salinomycin on cancer
stem cell in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Med Chem.
7:106–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G,
Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA and Daidone M:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu F, Sim AC, Li C, Li Y, Zhao X, Wang DY
and Loh KS: Identification of a subpopulation of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells with cancer stem-like cell properties by high
aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Laryngoscope. 123:1903–1911. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McIntosh K, Balch C and Tiwari AK:
Tackling multidrug resistance mediated by efflux transporters in
tumor-initiating cells. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 12:633–644.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boesch M, Zeimet AG, Fiegl H, Wolf B,
Huber J, Klocker H, Gastl G, Sopper S and Wolf D: High prevalence
of side population in human cancer cell lines. Oncoscience.
3:85–87. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu S, Zhang R, Liu F, Wang H, Wu J and
Wang Y: Notch inhibition suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
depleting cancer stem-like side population cells. Oncol Rep.
28:561–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pan JJ, Ng WT, Zong JF, Lee SW, Choi HC,
Chan LL, Lin SJ, Guo QJ, Sze HC, Chen YB, et al: Prognostic
nomogram for refining the prognostication of the proposed 8th
edition of the AJCC/UICC staging system for nasopharyngeal cancer
in the era of intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Cancer.
122:3307–3315. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Tian Y, Song F, Fu C, Han B and
Wang Y: Salinomycin inhibits the growth of colorectal carcinoma by
targeting tumor stem cells. Oncol Rep. 34:2469–2476. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang B, Hu Y, Xiong RH, Pan YF, Xu QL,
Kong XY, Cai R, Chen QQ, Tang HY and Jiang W: Matched analysis of
induction chemotherapy plus chemoradiotherapy versus induction
chemotherapy plus radiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicenter study. Oncotarget.
8:14078–14088. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu C, Chen YP and Ma J: Clinical trials in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma-past, present and future. Chin Clin Oncol.
5:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hirschhaeuser F, Menne H, Dittfeld C, West
J, Mueller-Klieser W and Kunz-Schughart LA: Multicellular tumor
spheroids: An underestimated tool is catching up again. J
Biotechnol. 148:3–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gou S, Liu T, Wang C, Yin T, Li K, Yang M
and Zhou J: Establishment of clonal colony-forming assay for
propagation of pancreatic cancer cells with stem cell properties.
Pancreas. 34:429–435. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu W, Gao Q, Chen K, Xue X, Li M, Chen Q,
Zhu G and Gao Y: Hiwi facilitates chemoresistance as a cancer stem
cell marker in cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:1853–1860. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pranatharthi A, Ross C and Srivastava S:
Cancer stem cells and radioresistance: Rho/ROCK pathway plea
attention. Stem Cells Int. 2016:57857862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
De Bacco F, D'Ambrosio A, Casanova E,
Orzan F, Neggia R, Albano R, Verginelli F, Cominelli M, Poliani PL,
Luraghi P, et al: MET inhibition overcomes radiation resistance of
glioblastoma stem-like cells. EMBO Mol Med. 8:550–568. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan YH, Sze H, Chan C and
Lam TH: The battle against nasopharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol.
104:272–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang J, Zhang K, Wu J, Shi J, Xue J, Li J,
Chen J, Zhu Y, Wei J, He J and Liu X: Wnt5a increases properties of
lung cancer stem cells and resistance to cisplatin through
activation of Wnt5a/PKC signaling pathway. Stem Cells Int.
2016:16908962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|