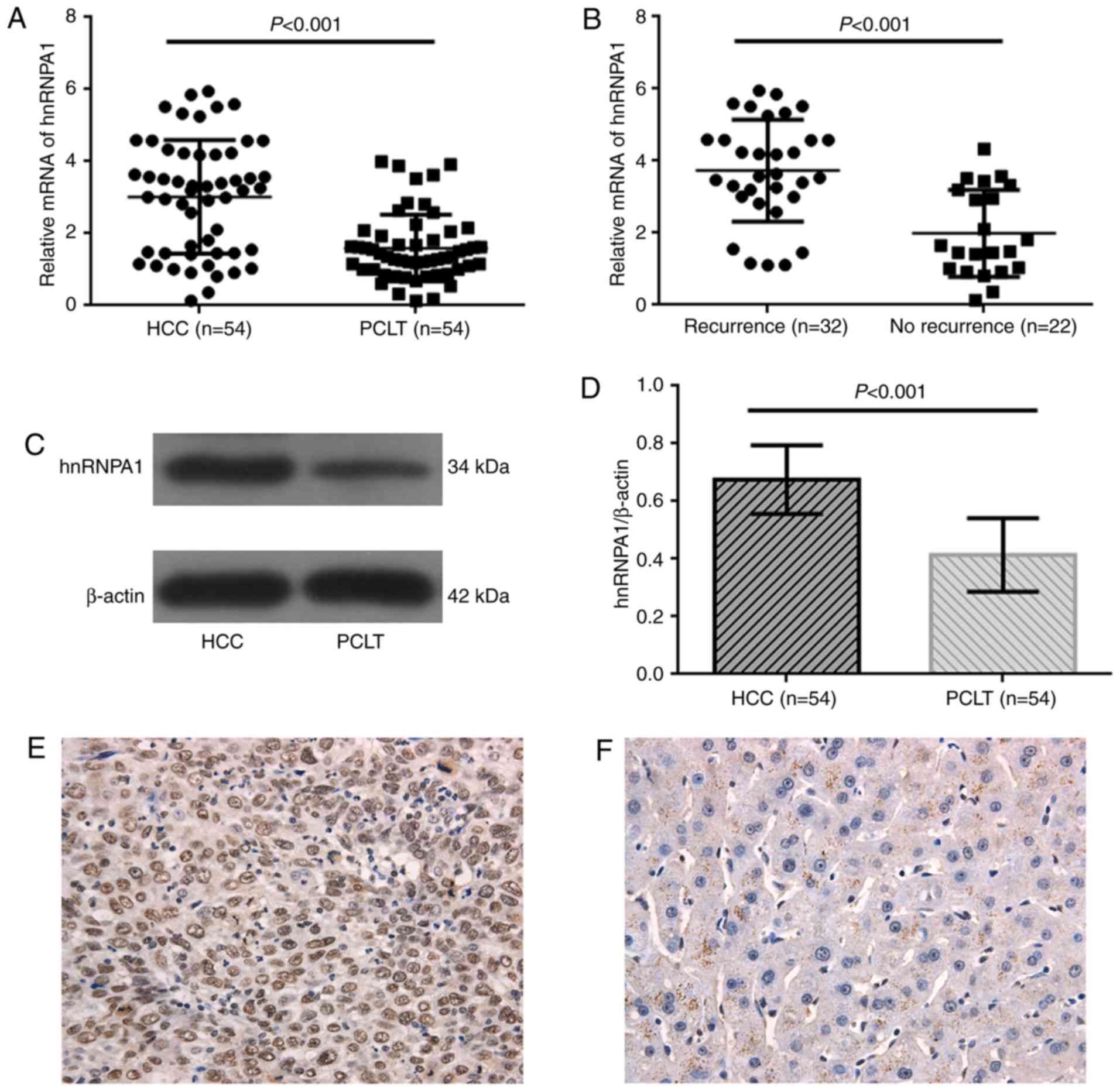
|
1
|
Yan X and Qiu Y: Impact of current staging
systems on treatment strategy for HBV-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 379:220–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H
and Zou X: Report of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010.
Ann Transl Med. 2:612014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olsen SK, Brown RS and Siegel AB:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of current treatment with a focus
on targeted molecular therapies. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 3:55–66.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang CH, Wey KC, Mo LR, Chang KK, Lin RC
and Kuo JJ: Current trends and recent advances in diagnosis,
therapy, and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:3595–3604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jonas S, Al-Abadi H, Benckert C, Thelen A,
Hippler-Benscheid M, Saribeyoglu K, Radtke B, Pratschke J and
Neuhaus P: Prognostic significance of the DNA-index in liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Ann
Surg. 250:1008–1013. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim E, Goren A and Ast G: Insights into
the connection between cancer and alternative splicing. Trends
Genet. 24:7–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Papaemmanuil E, Cazzola M, Boultwood J,
Malcovati L, Vyas P, Bowen D, Pellagatti A, Wainscoat JS,
Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Gambacorti-Passerini C, et al: Somatic SF3B1
mutation in myelodysplasia with ring sideroblasts. N Engl J Med.
365:1384–1395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han SP, Tang YH and Smith R: Functional
diversity of the hnRNPs: Past, present and perspectives. Biochem J.
430:379–392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
LaBranche H, Dupuis S, Ben-David Y, Bani
MR, Wellinger RJ and Chabot B: Telomere elongation by hnRNP A1 and
a derivative that interacts with telomeric repeats and telomerase.
Nat Genet. 19:199–202. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cammas A, Lacroix-Triki M, Pierredon S, Le
Bras M, Iacovoni JS, Teulade-Fichou MP, Favre G, Roché H, Filleron
T, Millevoi S and Vagner S: hnRNP A1-mediated translational
regulation of the G quadruplex-containing RON receptor tyrosine
kinase mRNA linked to tumor progression. Oncotarget. 7:16793–16805.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
David CJ, Chen M, Assanah M, Canoll P and
Manley JL: HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate
kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature. 463:364–368. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma YL, Peng JY, Zhang P, Huang L, Liu WJ,
Shen TY, Chen HQ, Zhou YK, Zhang M, Chu ZX and Qin HL:
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 is identified as a
potential biomarker for colorectal cancer based on differential
proteomics technology. J Proteome Res. 8:4525–4535. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Golan-Gerstl R, Cohen M, Shilo A, Suh SS,
Bakàcs A, Coppola L and Karni R: Splicing factor hnRNP A2/B1
regulates tumor suppressor gene splicing and is an oncogenic driver
in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 71:4464–4472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou ZJ, Dai Z, Zhou SL, Fu XT, Zhao YM,
Shi YH, Zhou J and Fan J: Overexpression of HnRNP A1 promotes tumor
invasion through regulating CD44v6 and indicates poor prognosis for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 132:1080–1089. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tazzyman S, Barry ST, Ashton S, Wood P,
Blakey D, Lewis CE and Murdoch C: Inhibition of neutrophil
infiltration into A549 lung tumors in vitro and in vivo
using a CXCR2-specific antagonist is associated with reduced tumor
growth. Int J Cancer. 129:847–858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki K, Kachala SS, Kadota K, Shen R, Mo
Q, Beer DG, Rusch VW, Travis WD and Adusumilli PS: Prognostic
immune markers in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
17:5247–5256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei K, Wang M, Zhang W, Mu H and Song TQ:
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of outcomes for patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing TAE combined with
Sorafenib. Med Oncol. 31:9692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao Y, Ke R, Wang S, Zhu X, Chen J, Huang
C, Jiang Y and Lv L: DNA topoisomerase IIalpha and Ki67 are
prognostic factors in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 13:4109–4116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kee KM, Wang JH, Lee CM, Chen CL,
Changchien CS, Hu TH, Cheng YF, Hsu HC, Wang CC, Chen TY, et al:
Validation of clinical AJCC/UICC TNM staging system for
hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of 5,613 cases from a medical
center in southern Taiwan. Int J Cancer. 120:2650–2655. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu X, Liu H, Liu J, Haley KN, Treadway JA,
Larson JP, Ge N, Peale F and Bruchez MP: Immunofluorescent labeling
of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor
quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 21:41–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N, Iwaku A,
Oishi M, Fushiya N, Koike K, Nishino H and Tajiri H: Comparison of
the prognostic value of inflammation-based prognostic scores in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 107:988–993.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong L, Bai K, Cao Y, Huang Q, Lv L and
Jiang Y: Prognostic value of pre-operative platelet to lymphocyte
ratio in patients with resected primary hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Lab. 62:2191–2196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jean-Philippe J, Paz S and Caputi M: hnRNP
A1: The Swiss army knife of gene expression. Int J Mol Sci.
14:18999–19024. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang S, Wei JS, Li SQ, Badgett TC, Song
YK, Agarwal S, Coarfa C, Tolman C, Hurd L, Liao H, et al: MYCN
controls an alternative RNA splicing program in high-risk
metastatic neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 371:214–224. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luan W, Wang Y, Chen X, Shi Y, Wang J,
Zhang J, Qian J, Li R, Tao T, Wei W, et al: PKM2 promotes glucose
metabolism and cell growth in gliomas through a mechanism involving
a let-7a/c-Myc/hnRNPA1 feedback loop. Oncotarget. 6:13006–13018.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ford LP, Wright WE and Shay JW: A model
for heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in telomere and
telomerase regulation. Oncogene. 21:580–583. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chettouh H, Fartoux L, Aoudjehane L,
Wendum D, Clapéron A, Chrétien Y, Rey C, Scatton O, Soubrane O,
Conti F, et al: Mitogenic insulin receptor-A is overexpressed in
human hepatocellular carcinoma due to EGFR-mediated dysregulation
of RNA splicing factors. Cancer Res. 73:3974–3986. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Zhou Y, Lou Y and Zhong H:
Knockdown of HNRNPA1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell
proliferation through cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. Gene.
576:791–797. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhen L, Shijie N and Shuijun Z: Tumor PHD2
expression is correlated with clinical features and prognosis of
patients with HCC receiving liver resection. Medicine. 93:e1792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vitale A, Morales RR, Zanus G, Farinati F,
Burra P, Angeli P, Frigo AC, Del Poggio P, Rapaccini G, Di Nolfo
MA, et al: Barcelona clinic liver cancer staging and transplant
survival benefit for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A
multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 12:654–662. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pichler M, Hutterer GC, Stoeckigt C,
Chromecki TF, Stojakovic T, Golbeck S, Eberhard K, Gerger A,
Mannweiler S, Pummer K and Zigeuner R: Validation of the
pre-treatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in
a large European cohort of renal cell carcinoma patients. Br J
Cancer. 108:901–907. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Visser KE, Eichten A and Coussens LM:
Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:24–37. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aliustaoglu M, Bilici A, Ustaalioglu BB,
Konya V, Gucun M, Seker M and Gumus M: The effect of peripheral
blood values on prognosis of patients with locally advanced gastric
cancer before treatment. Med Oncol. 27:1060–1065. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gomez D, Farid S, Malik HZ, Young AL,
Toogood GJ, Lodge JP and Prasad KR: Preoperative
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor after
curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg.
32:1757–1762. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song W, Wang K, Zhong FP, Fan YW, Peng L
and Zou SB: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:81830–81838. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qi X, Li J, Deng H, Li H, Su C and Guo X:
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for the prognostic assessment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
observational studies. Oncotarget. 7:45283–45301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|