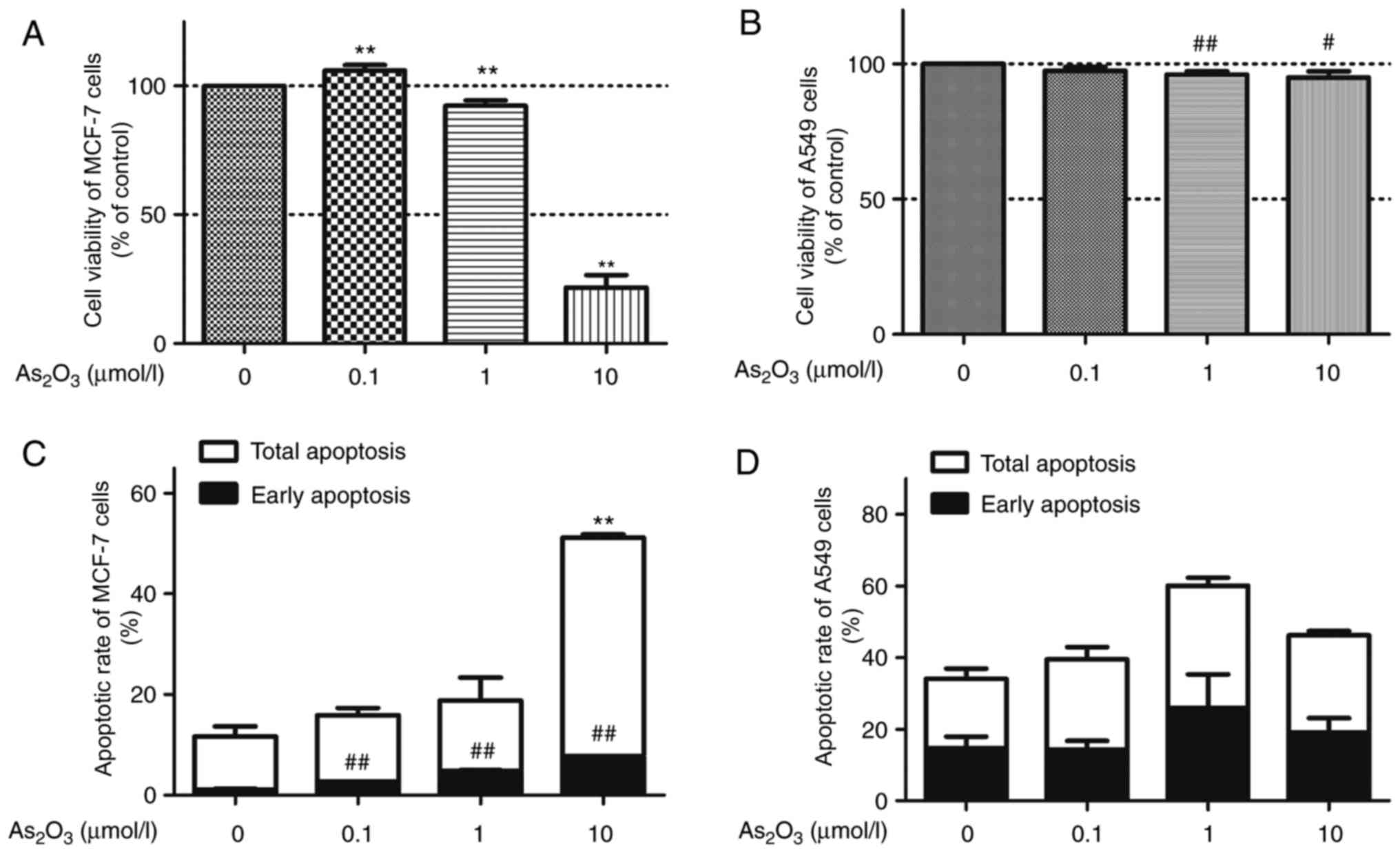
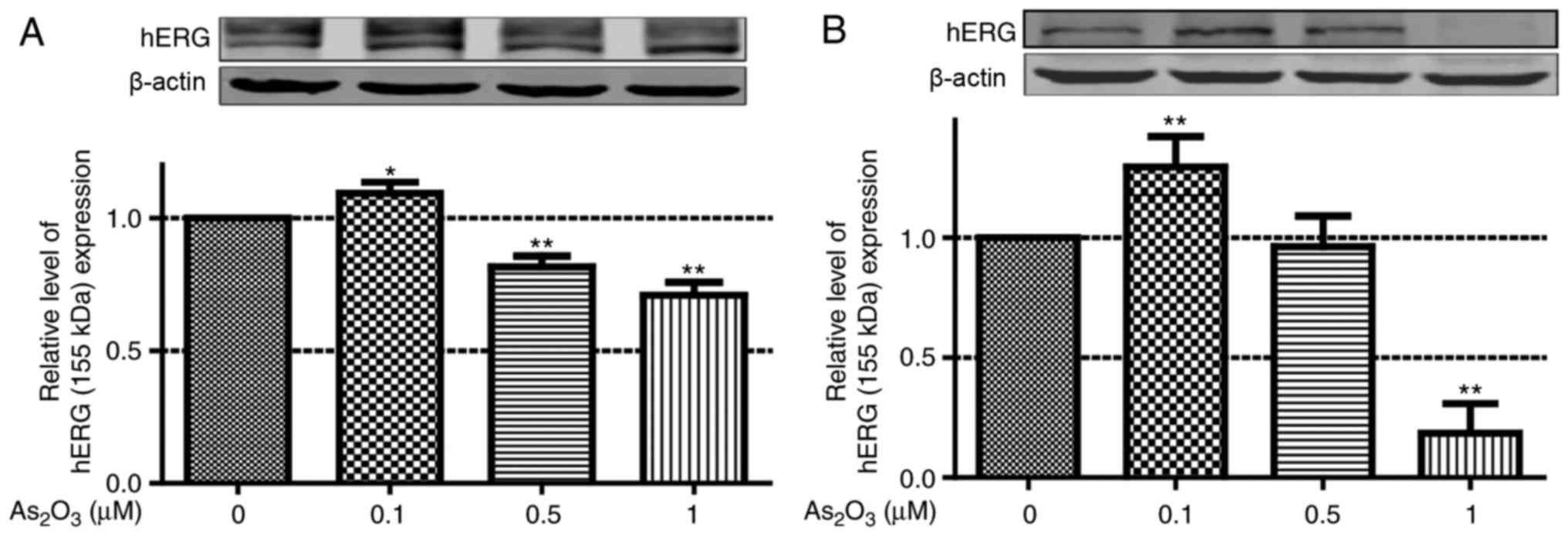
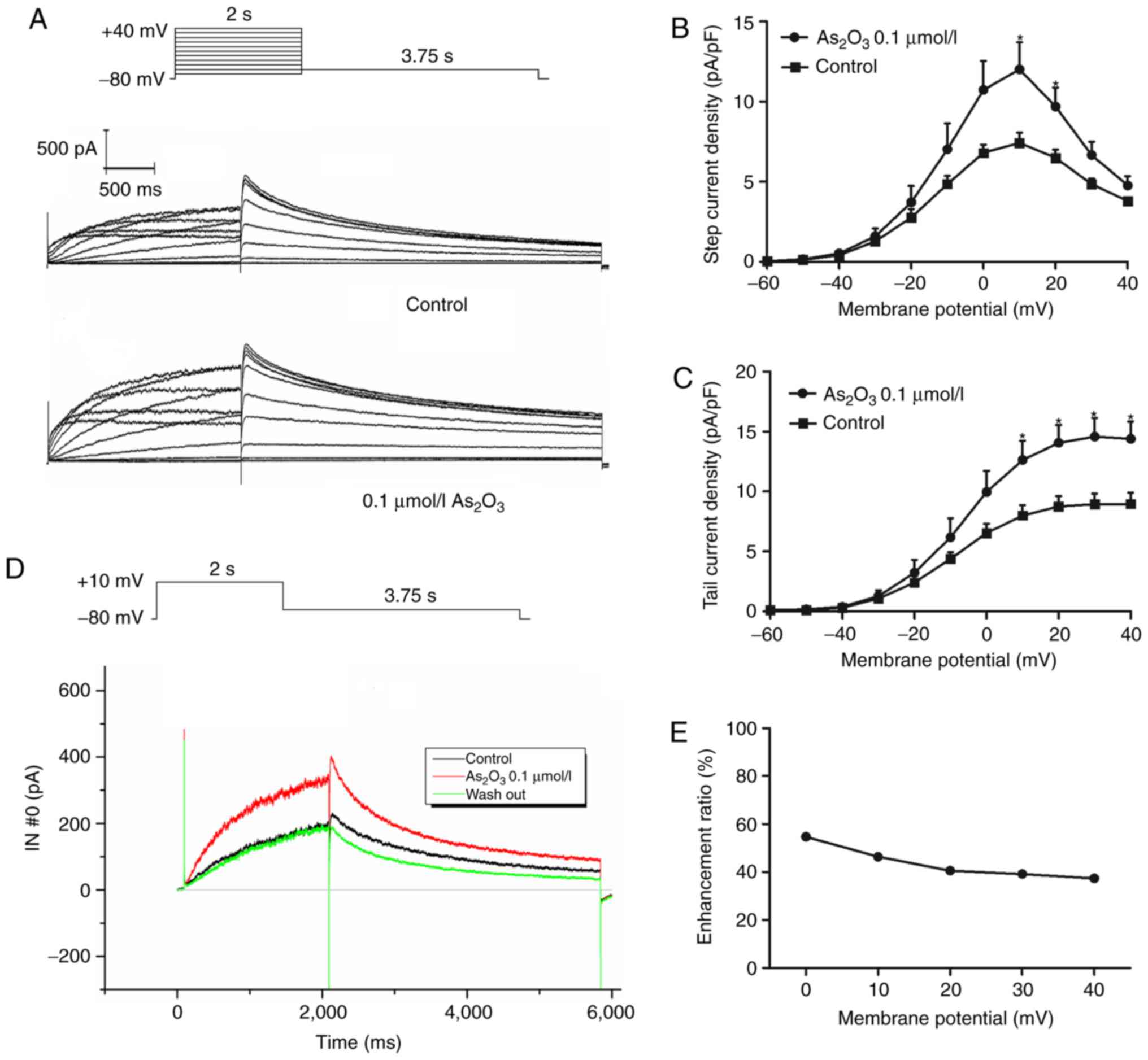
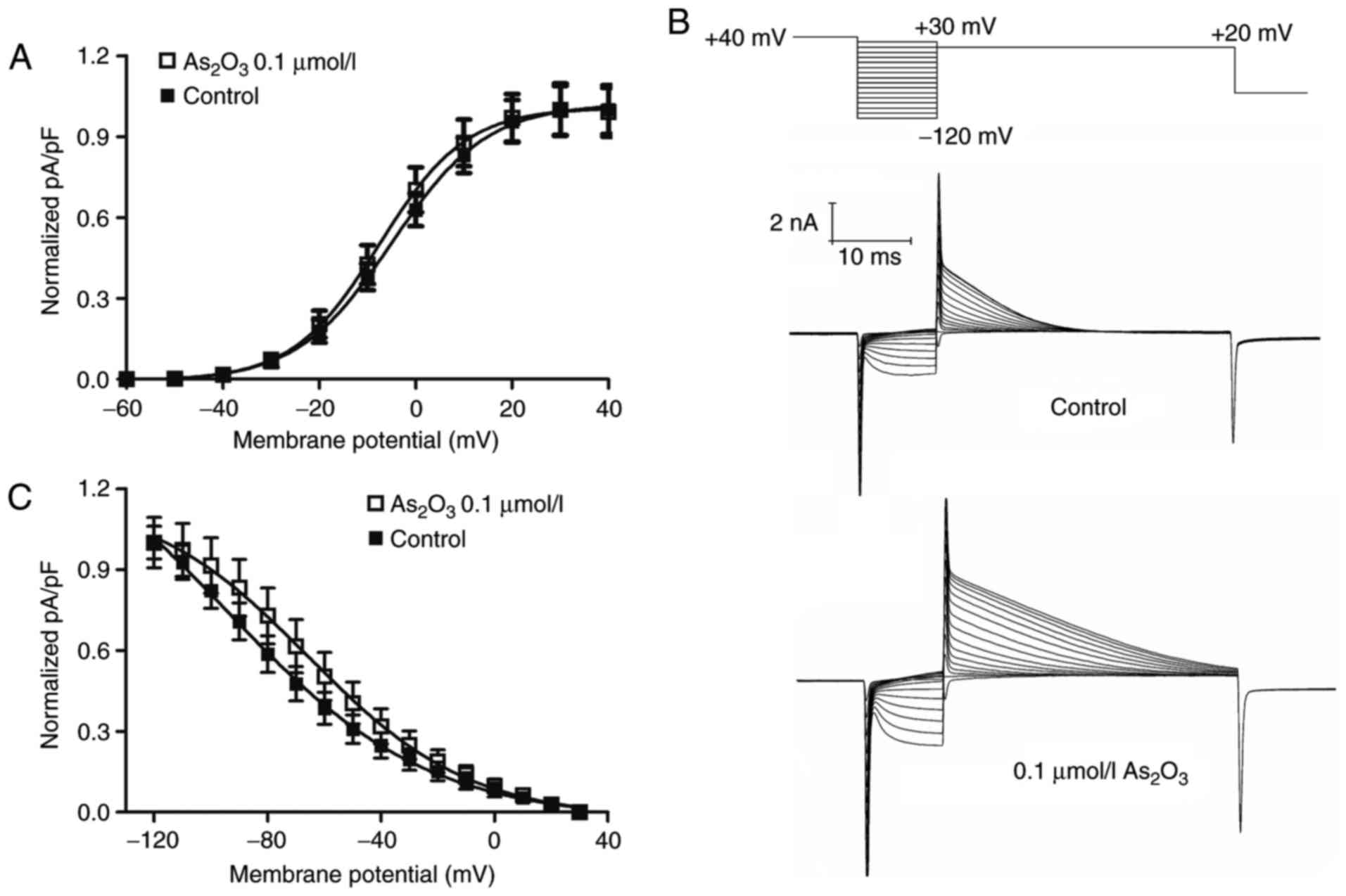
|
1
|
Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent
GM, Green ED and Keating MT: A molecular basis for cardiac
arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell.
80:795–803. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haverkamp W, Breithardt G, Camm AJ, Janse
MJ, Rosen MR, Antzelevitch C, Escande D, Franz M, Malik M, Moss A
and Shah R: The potential for QT prolongation and proarrhythmia by
non-antiarrhythmic drugs: Clinical and regulatory implications.
Report on a policy conference of the European Society of
Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 21:1216–1231. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farkas AS and Nattel S: Minimizing
repolarization-related proarrhythmic risk in drug development and
clinical practice. Drugs. 70:573–603. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kannankeril P, Roden DM and Darbar D:
Drug-induced long QT syndrome. Pharmacol Rev. 62:760–781. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bi LL, Ma Q and Wang SQ: Treatment of 32
cases with recurring acute promyelocytic leukemia with tablets of
composite natural indigo. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 43:702–703.
2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen GQ, Shi XG, Tang W, Xiong SM, Zhu J,
Cai X, Han ZG, Ni JH, Shi GY, Jia PM, et al: Use of arsenic
trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia
(APL): I. As2O3 exerts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells.
Blood. 89:3345–3353. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang TC, Cao EH, Li JF, Ma W and Qin JF:
Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of human gastric cancer
MGC-803 cell growth by arsenic trioxide. Eur J Cancer.
35:1258–1263. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye J, Li A, Liu Q, Wang X and Zhou J:
Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase enhances
apoptosis induced by arsenic trioxide in human breast cancer MCF-7
cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 32:1042–1048. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Chen X, Wu J, Liu H, Ji Z, Shi H,
Gao C, Han D, Wang L, Liu Y, et al: Low-dose arsenic trioxide
enhances 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced PpIX accumulation and
efficacy of photodynamic therapy in human glioma. J Photochem
Photobiol B. 127:61–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Raja WK, Satti J, Liu G and Castracane J:
Dose response of MTLn3 cells to serial dilutions of arsenic
trioxide and ionizing radiation. Dose Response. 11:29–40. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ganapathy S, Li P, Fagman J, Yu T,
Lafontant J, Zhang G and Chen C: Low doses of arsenic, via
perturbing p53, promotes tumorigenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
306:98–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Becchetti A, Crescioli S, Zanieri F,
Petroni G, Mercatelli R, Coppola S, Gasparoli L, D'Amico M,
Pillozzi S, Crociani O, et al: The conformational state of hERG1
channels determines integrin association, downstream signaling, and
cancer progression. Sci Signal. 10:pii: eaaf3236. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Crociani O, Lastraioli E, Boni L, Pillozzi
S, Romoli MR, D'Amico M, Stefanini M, Crescioli S, Masi A, Taddei
A, et al: hERG1 channels regulate VEGF-A secretion in human gastric
cancer: Clinicopathological correlations and therapeutical
implications. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1502–1512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fortunato A: The role of hERG1 ion
channels in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the capacity of
riluzole to reduce cisplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 40:367–378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ficker E, Kuryshev YA, Dennis AT,
Obejero-Paz C, Wang L, Hawryluk P, Wible BA and Brown AM:
Mechanisms of arsenic-induced prolongation of cardiac
repolarization. Mol Pharmacol. 66:33–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wan X, Dennis AT, Obejero-Paz C, Overholt
JL, Heredia-Moya J, Kirk KL and Ficker E: Oxidative inactivation of
the lipid phosphatase phosphatase and tensin homolog on chromosome
ten (PTEN) as a novel mechanism of acquired long QT syndrome. J
Biol Chem. 286:2843–2852. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen SZ, Jiang M and Zhen YS: Correlation
of HERG K+ channel protein expression to chemosensitivity of tumor
cells to doxorubicin and its modulation by erythromycin. Ai Zheng.
24:924–929. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Dong Z, Jin L, Zhang K, Zhao X,
Fu J, Gong Y, Sun M, Yang B and Li B: Arsenic trioxide-induced hERG
K(+) channel deficiency can be rescued by matrine and oxymatrine
through up-regulating transcription factor Sp1 expression. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:59–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nicholson GM, Blanche T, Mansfield K and
Tran Y: Differential blockade of neuronal voltage-gated Na(+) and
K(+) channels by antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 452:35–48.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pace C, Dagda R and Angermann J:
Antioxidants protect against arsenic induced mitochondrial
Cardio-toxicity. Toxics. 5:pii: E38. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sarkar A and Paul B: The global menace of
arsenic and its conventional remediation-A critical review.
Chemosphere. 158:37–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oremland RS and Stolz JF: Arsenic,
microbes and contaminated aquifers. Trends Microbiol. 13:45–49.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Orloff K, Mistry K and Metcalf S:
Biomonitoring for environmental exposures to arsenic. J Toxicol
Environ Health B Crit Rev. 12:509–524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reeve BB, Burke LB, Chiang YP, Clauser SB,
Colpe LJ, Elias JW, Fleishman J, Hohmann AA, Johnson-Taylor WL,
Lawrence W, et al: Enhancing measurement in health outcomes
research supported by Agencies within the US Department of Health
and Human Services. Qual Life Res. 16 Suppl 1:S175–S186. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu WX, Liu Y, Liu SZ, Zhang Y, Qiao GF and
Yan J: Arsenic trioxide exerts a double effect on osteoblast growth
in vitro. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 38:412–419. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin X, Chen Q, Huang C and Xu X: CYLD
promotes TNF-α-induced cell necrosis mediated by RIP-1 in human
lung cancer cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:15427862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Zhang Y, Cao L, Han H, Wang J,
Yang B, Nattel S and Wang Z: HERG K+ channel, a regulator of tumor
cell apoptosis and proliferation. Cancer Res. 62:4843–4848.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li P, Ninomiya H, Kurata Y, Kato M, Miake
J, Yamamoto Y, Igawa O, Nakai A, Higaki K, Toyoda F, et al:
Reciprocal control of hERG stability by Hsp70 and Hsc70 with
implication for restoration of LQT2 mutant stability. Circ Res.
108:458–468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dong ZX, Zhao X, Gu DF, Shi YQ, Zhang J,
Hu XX, Hu MQ, Yang BF and Li BX: Comparative effects of liensinine
and neferine on the human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium
channel and pharmacological activity analysis. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 29:431–442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Z, Prinsen JK, Bersell KR, Shen W,
Yermalitskaya L, Sidorova T, Luis PB, Hall L, Zhang W, Du L, et al:
Azithromycin causes a novel proarrhythmic syndrome. Circ Arrhythm
Electrophysiol. 10:pii: e003560. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Staudacher I, Jehle J, Staudacher K, Pledl
HW, Lemke D, Schweizer PA, Becker R, Katus HA and Thomas D: HERG K+
channel-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human
glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e881642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi YQ, Yan M, Liu LR, Zhang X, Wang X,
Geng HZ, Zhao X and Li BX: High glucose represses hERG K+ channel
expression through trafficking inhibition. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:284–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|