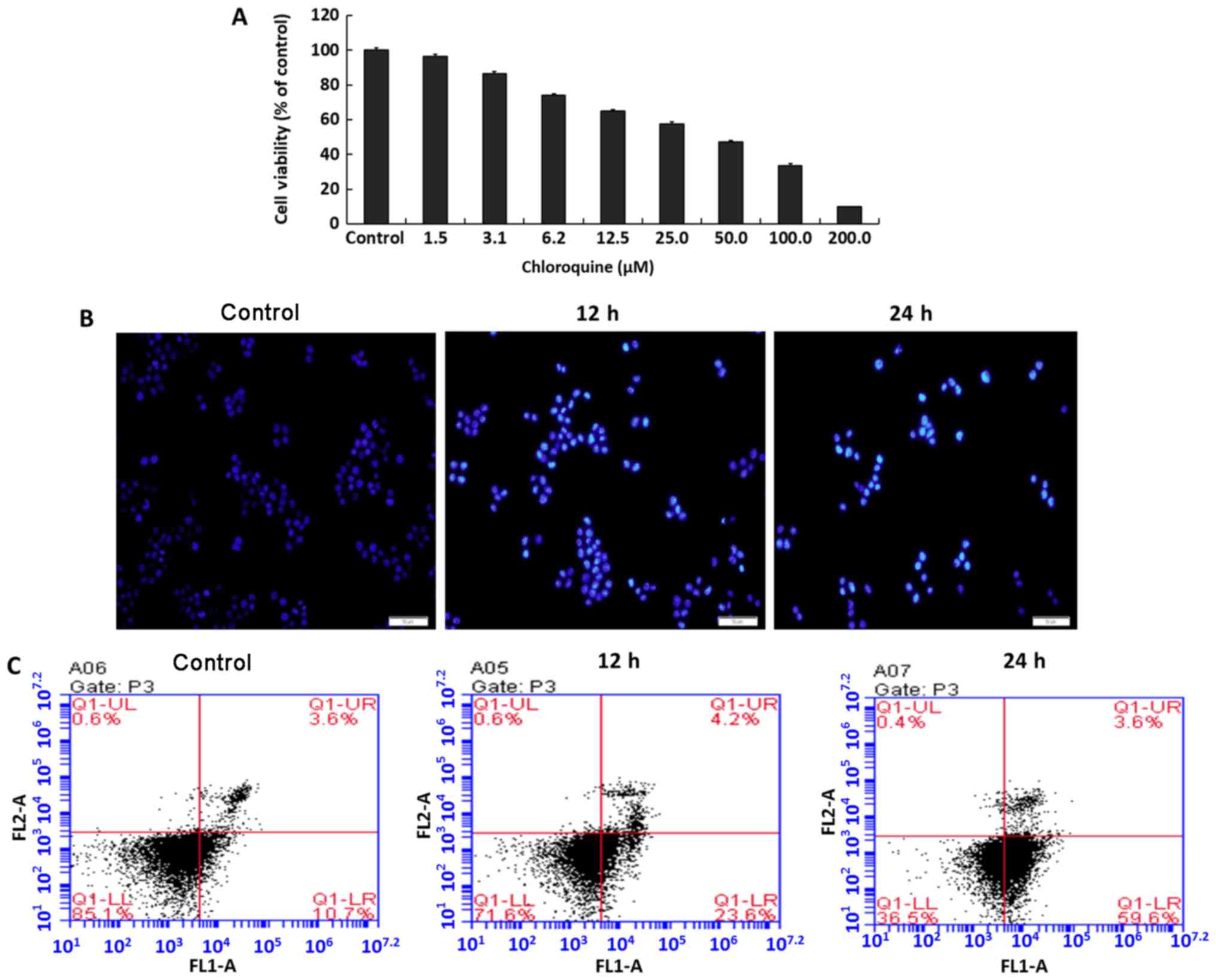
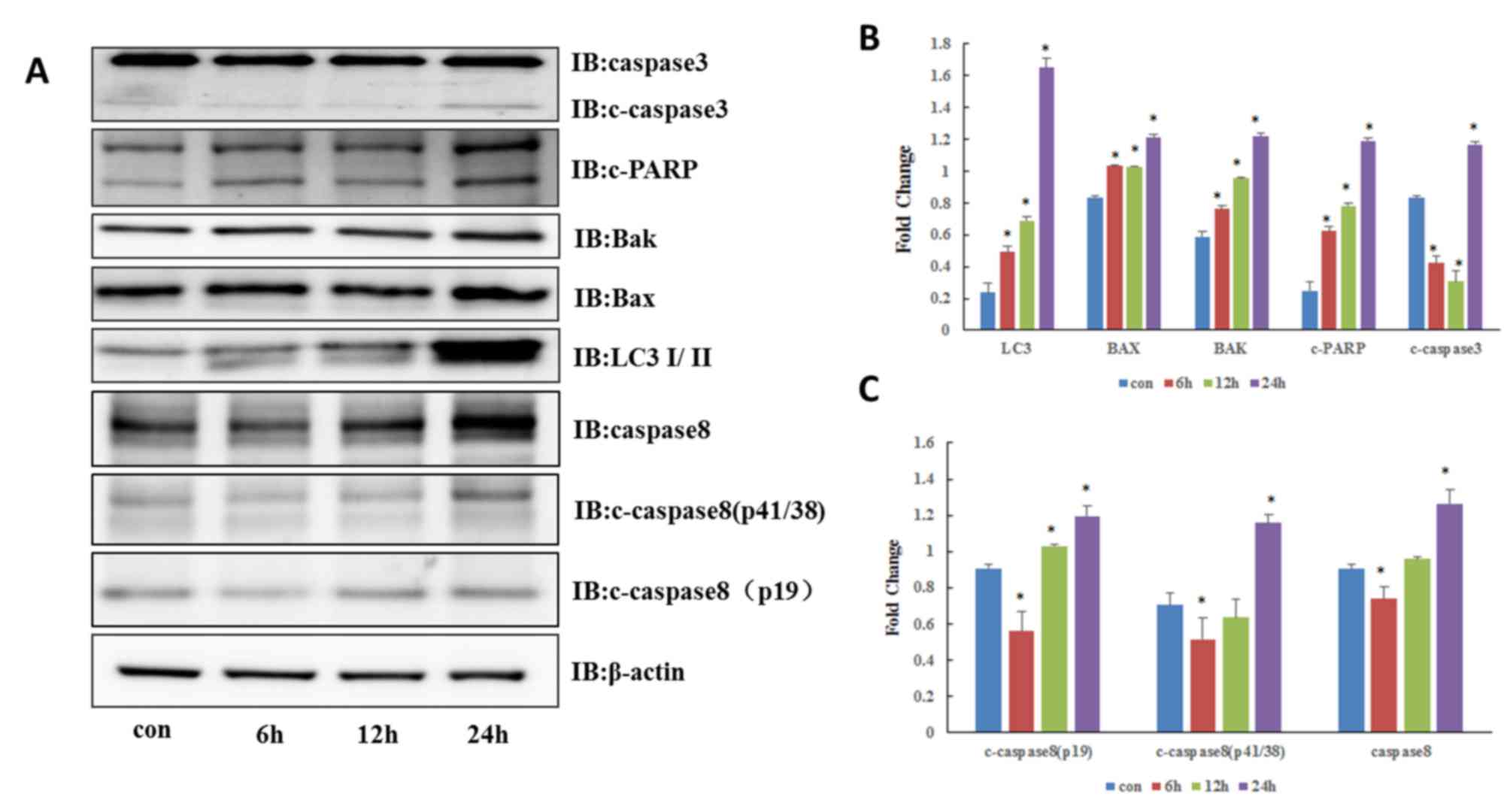
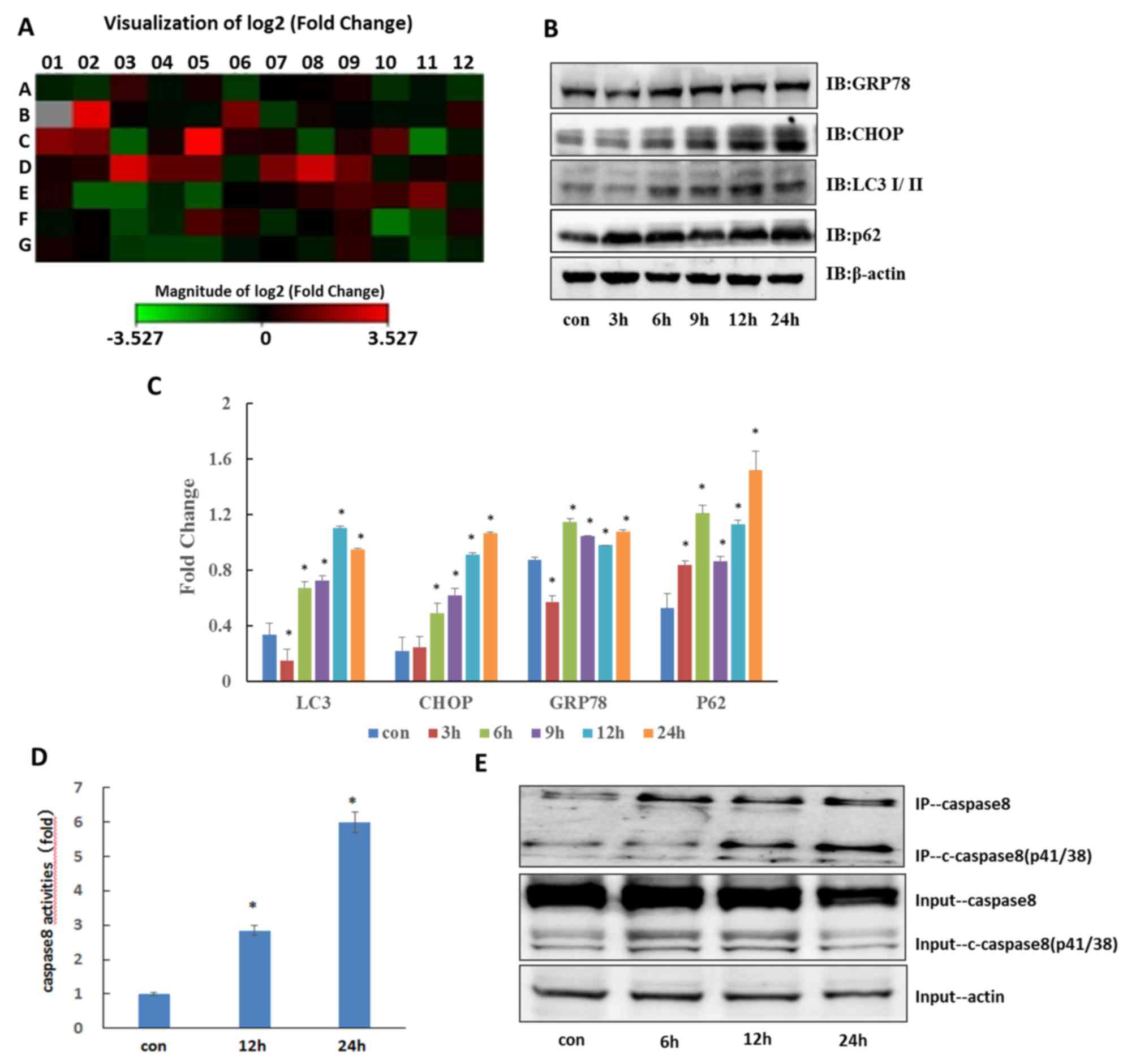
|
1
|
Likhitrattanapisal S, Tipanee J and
Janvilisri T: Meta-analysis of gene expression profiles identifies
differential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma and
cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:12755–12766. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blechacz B, Komuta M, Roskams T and Gores
GJ: Clinical diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:512–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oliveira IS, Kilcoyne A, Everett JM,
Mino-Kenudson M, Harisinghani MG and Ganesan K: Cholangiocarcinoma:
Classification, diagnosis, staging, imaging features, and
management. Abdom Radiol (NY). 42:1637–1649. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matull WR, Khan SA and Pereira SP: Re:
Impact of classification of hilar cholangiocarcinomas (Klatskin
tumors) on the incidence of intra- and extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst.
99:407–408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roskams T: Liver stem cells and their
implication in hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma. Oncogene.
25:3818–3822. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carew JS, Medina EC, Esquivel JA II,
Mahalingam D, Swords R, Kelly K, Zhang H, Huang P, Mita AC, Mita
MM, et al: Autophagy inhibition enhances vorinostat-induced
apoptosis via ubiquitinated protein accumulation. J Cell Mol Med.
14:2448–2459. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thorburn A, Thamm DH and Gustafson DL:
Autophagy and cancer therapy. Mol Pharmacol. 85:830–838. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mushtaque M and Shahjahan: Reemergence of
chloroquine (CQ) analogs as multi-targeting antimalarial agents: A
review. Eur J Med Chem. 90:280–295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ,
González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL: Melatonin and endoplasmic
reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal
Res. 59:292–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Johnson CE, Hunt DK, Wiltshire M, Herbert
TP, Sampson JR, Errington RJ, Davies DM and Tee AR: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and cell death in mTORC1-overactive cells is
induced by nelfinavir andenhanced by chloroquine. Mol Oncol.
9:675–688. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Høyer-Hansen M and Jäättelä M: Connecting
endoplasmic reticulum stress to autophagy by unfolded protein
response and calcium. Cell Death Differ. 14:1576–1582. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park EJ, Min KJ, Choi KS, Kubatka P,
Kruzliak P, Kim DE and Kwon TK: Chloroquine enhances TRAIL-mediated
apoptosis through up-regulation of DR5 by stabilization of mRNA and
protein in cancer cells. Sci Rep. 6:229212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu Y, Li D, Zeng L, Wang C, Zhang L, Wang
Y, Yu Y, Liu S and Li Z: Proteasome inhibitor lactacystin enhances
cisplatin cytotoxicity by increasing endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated apoptosis in HeLa cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:189–195.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiribau CB, Gaccioli F, Huang CC, Yuan CL
and Hatzoglou M: Molecular symbiosis of CHOP and C/EBP beta isoform
LIP contributes to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosi.
Mol Cell Biol. 30:3722–3731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marciniak SJ, Yun CY, Oyadomari S, Novoa
I, Zhang Y, Jungreis R, Nagata K, Harding HP and Ron D: CHOP
induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the
stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 18:3066–3077. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Teske BF, Fusakio ME, Zhou D, Shan J,
McClintick JN, Kilberg MS and Wek RC: CHOP induces activating
transcription factor 5 (ATF5) to trigger apoptosis in response to
perturbations in protein homeostasis. Mol Biol Cell. 24:2477–2490.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moon DO, Park SY, Choi YH, Ahn JS and Kim
GY: Guggulsterone sensitizes hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis through the induction of CHOP-dependent DR5: Involvement
of ROS-dependent ER-stress. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:1641–1650. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen CM, Wu CT, Chiang CK, Liao BW and Liu
SH: C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) deficiency aggravates
hippocampal cell apoptosis and impairs memory performance. PLoS
One. 7:e408012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iurlaro R and Muñoz-Pinedo C: Cell death
induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 283:2640–2652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Young MM, Takahashi Y, Khan O, Park S,
Hori T, Yun J, Sharma AK, Amin S, Hu CD, Zhang J, et al:
Autophagosomal membrane serves as platform for intracellular
death-inducing signaling complex (iDISC)-mediated caspase-8
activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 287:12455–12468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wijdeven RH, Pang B, Assaraf YG and
Neefjes J: Old drugs, novel ways out: Drug resistance toward
cytotoxic chemotherapeutics. Drug Resist Updat. 28:65–81. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He H, Ke R, Lin H, Ying Y, Liu D and Luo
Z: Metformin, an old drug, brings a new era to cancer therapy.
Cancer J. 21:70–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mudduluru G, Walther W, Kobelt D, Dahlmann
M, Treese C, Assaraf YG and Stein U: Repositioning of drugs for
intervention in tumor progression and metastasis: Old drugs for new
targets. Drug Resist Updat. 26:10–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sung B, Prasad S, Ravindran J, Yadav VR
and Aggarwal BB: Capsazepine, a TRPV1 antagonist, sensitizes
colorectal cancer cells to apoptosis by TRAIL through
ROS-JNK-CHOP-mediated upregulation of death receptors. Free Radic
Biol Med. 53:1977–1987. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He L, Jang JH, Choi HG, Lee SM, Nan MH,
Jeong SJ, Dong Z, Kwon YT, Lee KS, Lee KW, et al: Oligomycin A
enhances apoptotic effect of TRAIL through CHOP-mediated death
receptor 5 expression. Mol Carcinog. 52:85–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu M, Lawrence DA, Marsters S,
Acosta-Alvear D, Kimmig P, Mendez AS, Paton AW, Paton JC, Walter P
and Ashkenazi A: Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals
converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science.
345:98–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burikhanov R, Hebbar N, Noothi SK, Shukla
N, Sledziona J, Araujo N, Kudrimoti M, Wang QJ, Watt DS, Welch DR,
et al: Chloroquine-inducible par-4 secretion is essential for tumor
cell apoptosis and inhibition of metastasis. Cell Rep. 18:508–519.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nitta T, Sato Y, Ren XS, Harada K, Sasaki
M, Hirano S and Nakanuma Y: Autophagy may promote carcinoma cell
invasion and correlate with poor prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4913–4921. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qu X, Sheng J, Shen L, Su J, Xu Y, Xie Q,
Wu Y, Zhang X and Sun L: Autophagy inhibitor chloroquine increases
sensitivity to cisplatin in QBC939 cholangiocarcinoma cells by
mitochondrial ROS. PLoS One. 12:e01737122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: Chloroquine in cancer therapy: A double-edged sword of
autophagy. Cancer Res. 73:3–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vlahopoulos S, Critselis E, Voutsas IF,
Perez SA, Moschovi M, Baxevanis CN and Chrousos GP: New use for old
drugs? Prospective targets of chloroquines in cancer therapy. Curr
Drug Targets. 15:843–851. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rashid HO, Yadav RK, Kim HR and Chae HJ:
ER stress: Autophagy induction, inhibition and selection.
Autophagy. 11:1956–1977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 54:795–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Trivedi R, Maurya R and Mishra DP:
Medicarpin, a legume phytoalexin sensitizes myeloid leukemia cells
to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction of DR5 and
activation of the ROS-JNK-CHOP pathway. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN
and Bhutia SK: Autophagy and apoptosis: Where do they meet?
Apoptosis. 19:555–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gordy C and He YW: The crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis: Where does this lead? Protein Cell.
3:17–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang S, Okamoto K, Yu C and Sinicrope FA:
p62/sequestosome-1 up-regulation promotes ABT-263-induced caspase-8
aggregation/activation on the autophagosome. J Biol Chem.
288:33654–33666. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tomar D, Prajapati P, Sripada L, Singh K
and Singh R, Singh AK and Singh R: TRIM13 regulates caspase-8
ubiquitination, translocation to autophagosomes and activation
during ER stress induced cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1833:3134–3144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kantari C and Walczak H: Caspase-8 and
bid: Caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:558–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang H, Xie H, Pan Y, Zheng K, Xia Y and
Chen W: Plumbagin triggers ER stress-mediated apoptosis in prostate
cancer cells via induction of ROS. Cell Physiol Biochem.
45:267–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mathur A, Elmageed Abd ZY, Liu X,
Kostochka ML, Zhang H, Abdel-Mageed AB and Mondal D: Subverting
ER-stress towards apoptosis by nelfinavir and curcumin coexposure
augments docetaxel efficacy in castration resistant prostate cancer
cells. PLoS One. 9:e1031092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khan I, Paul S, Jakhar R, Bhardwaj M, Han
J and Kang SC: Novel quercetin derivative TEF induces ER stress and
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer HCT-116
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:789–799. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoshida GJ: Therapeutic strategies of drug
repositioning targeting autophagy to induce cancer cell death: From
pathophysiology to treatment. J Hematol Oncol. 10:672017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|