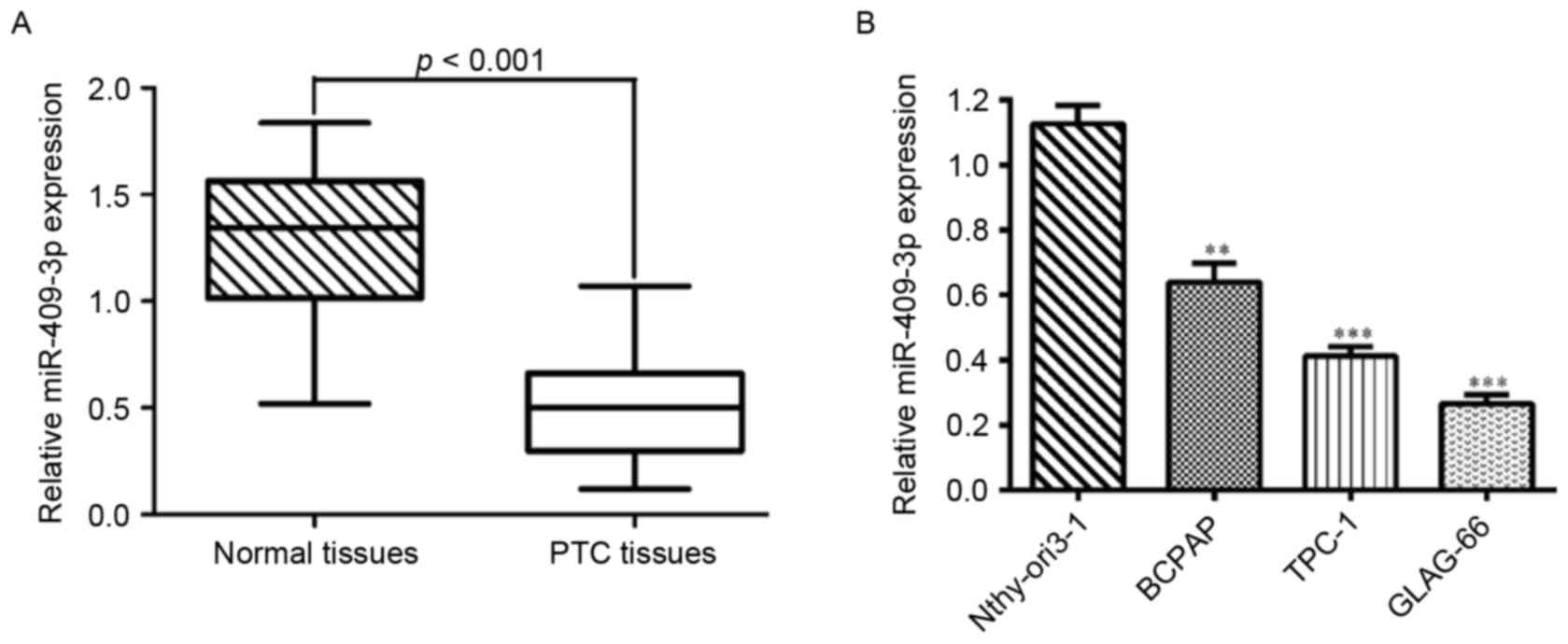
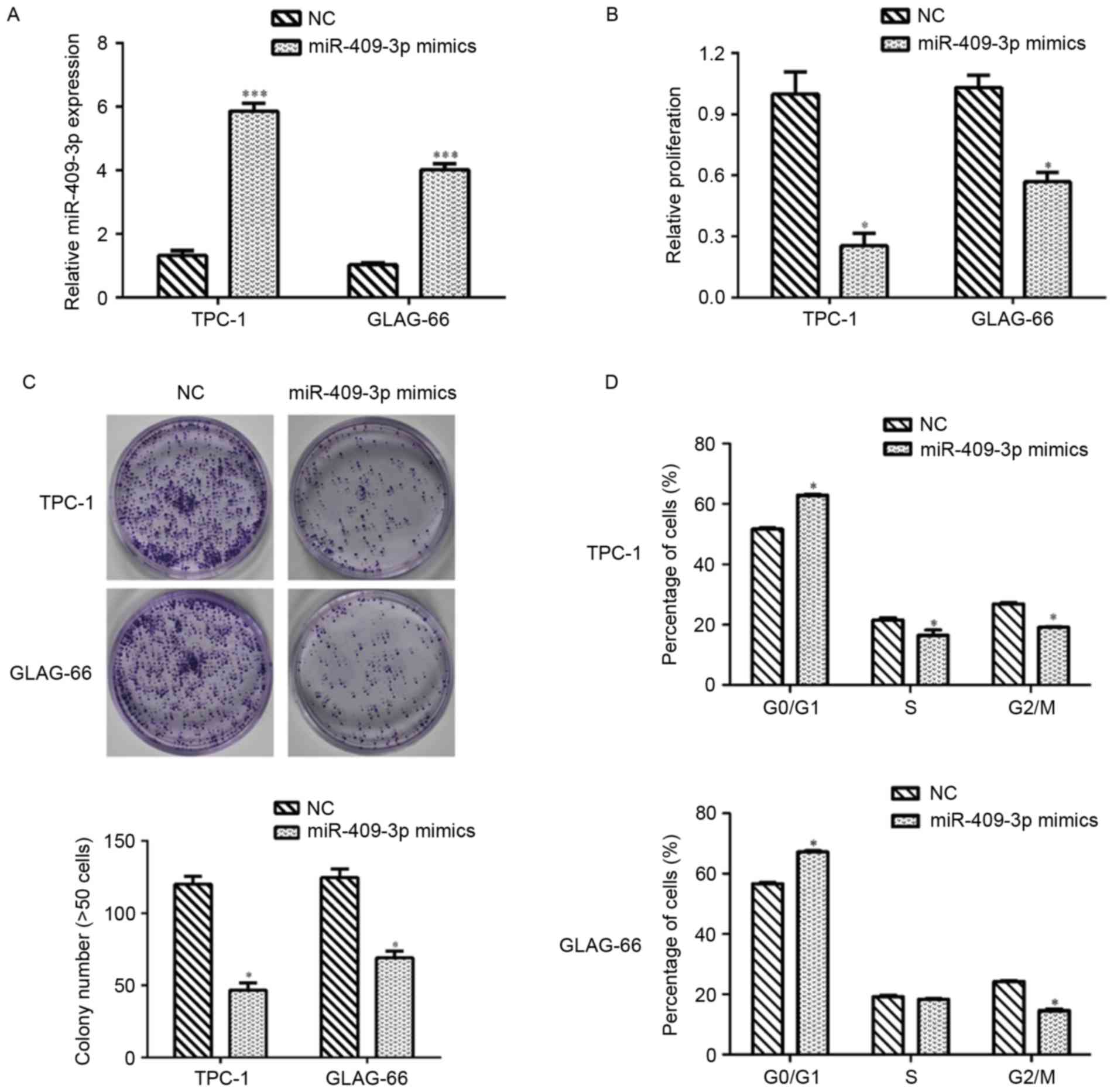
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carneiro RM, Carneiro BA, Agulnik M, Kopp
PA and Giles FJ: Targeted therapies in advanced differentiated
thyroid cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:690–698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lloyd RV, Buehler D and Khanafshar E:
Papillary thyroid carcinoma variants. Head Neck Pathol. 5:51–56.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi X, Liu R, Basolo F, Giannini R, Shen
X, Teng D, Guan H, Shan Z, Teng W, Musholt TJ, et al: Differential
clinicopathological risk and prognosis of major papillary thyroid
cancer variants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 101:264–274. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Macfarlane LA and Murphy PR: MicroRNA:
Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics. 11:537–561.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Srivastava A, Goldberger H, Dimtchev A,
Ramalinga M, Chijioke J, Marian C, Oermann EK, Uhm S, Kim JS, Chen
LN, et al: MicroRNA profiling in prostate cancer-the diagnostic
potential of urinary miR-205 and miR-214. PLoS One. 8:e769942013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Minna E, Romeo P, De Cecco L, Dugo M,
Cassinelli G, Pilotti S, Degl'Innocenti D, Lanzi C, Casalini P,
Pierotti MA, et al: miR-199a-3p displays tumor suppressor functions
in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:2513–2528. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin X, Guan H, Li H, Liu L, Liu J, Wei G,
Huang Z, Liao Z and Li Y: miR-101 inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting Rac1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Biomed Rep.
2:122–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma Y, Qin H and Cui Y: miR-34a targets
GAS1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in
papillary thyroid carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/Bad pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 441:958–963. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai R, Weng C, Dong H, Li S, Chen G and Xu
Z: MicroRNA-409-3p suppresses colorectal cancer invasion and
metastasis partly by targeting GAB1 expression. Int J Cancer.
137:2310–2322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang G, Liu Z, Xu H and Yang Q:
miR-409-3p suppresses breast cancer cell growth and invasion by
targeting Akt1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:189–195. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu G, Xie L and Miller D: Expression of
MicroRNAs in thyroid carcinoma. Methods Mol Biol. 1617:261–280.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wan L, Zhu L, Xu J, Lu B, Yang Y, Liu F
and Wang Z: MicroRNA-409-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in
human lung adenocarcinoma by targeting c-Met. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:1273–1290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu X, Chen H, Lin Y, Hu Z, Mao Y, Wu J, Xu
X, Zhu Y, Li S, Zheng X and Xie L: MicroRNA-409-3p inhibits
migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via targeting c-Met.
Mol Cells. 36:62–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li C, Nie H, Wang M, Su L, Li J, Yu B, Wei
M, Ju J, Yu Y, Yan M, et al: MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell
proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PHF10 in gastric cancer.
Cancer Lett. 320:189–197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: Living with or
without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev.
18:2699–2711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ando K, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F and
Griffin JD: Regulation of G1/S transition by cyclins D2 and D3 in
hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:9571–9575. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leone V, D'Angelo D, Rubio I, de Freitas
PM, Federico A, Colamaio M, Pallante P, Medeiros-Neto G and Fusco
A: MiR-1 is a tumor suppressor in thyroid carcinogenesis targeting
CCND2, CXCR4, and SDF-1alpha. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
96:E1388–E1398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou J, Tian Y, Li J, Lu B, Sun M, Zou Y,
Kong R, Luo Y, Shi Y, Wang K and Ji G: miR-206 is down-regulated in
breast cancer and inhibits cell proliferation through the
up-regulation of cyclinD2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 433:207–212.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong Q, Meng P, Wang T, Qin W, Qin W, Wang
F, Yuan J, Chen Z, Yang A and Wang H: MicroRNA let-7a inhibits
proliferation of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
by targeting E2F2 and CCND2. PLoS One. 5:e101472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|