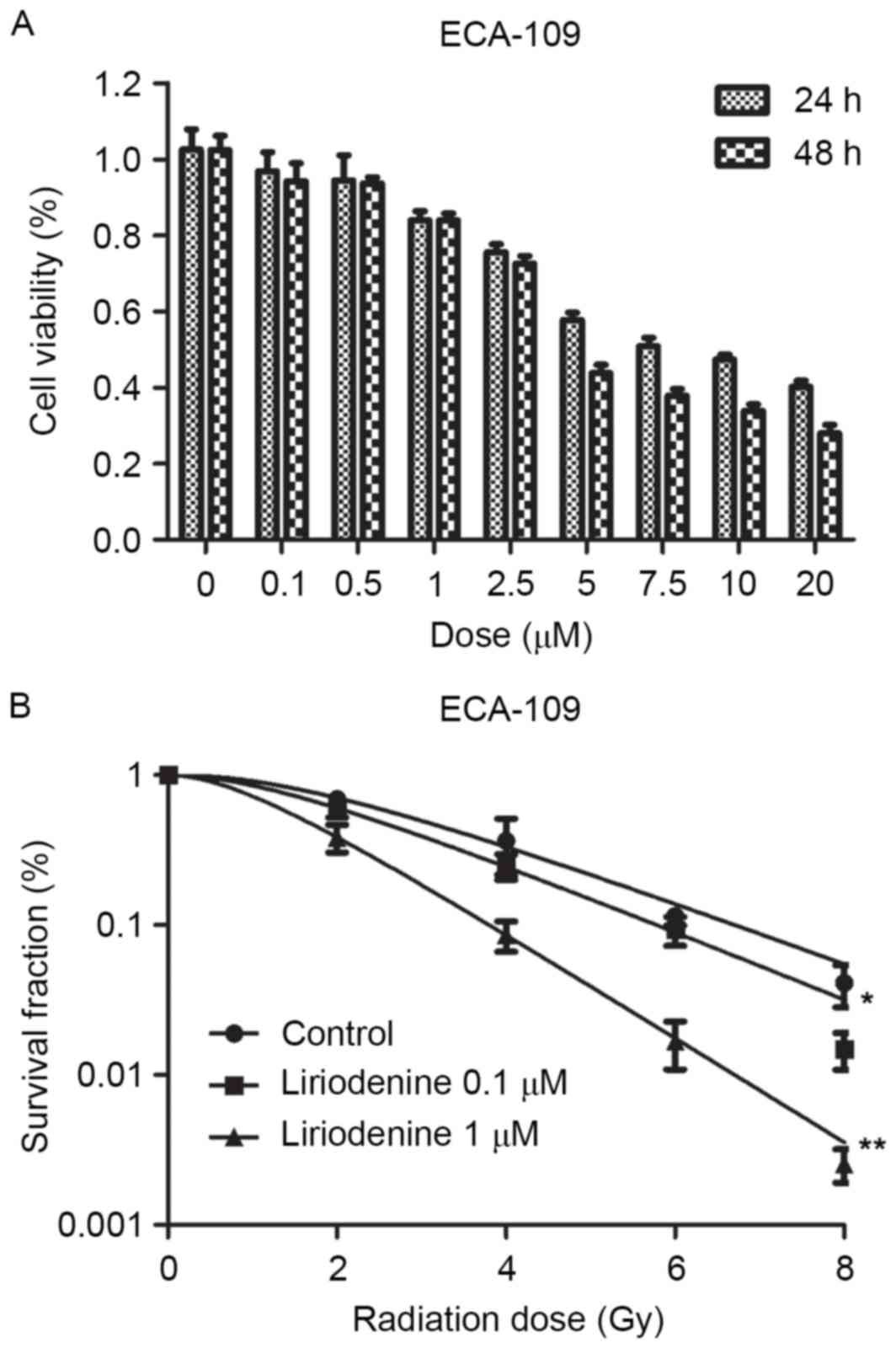
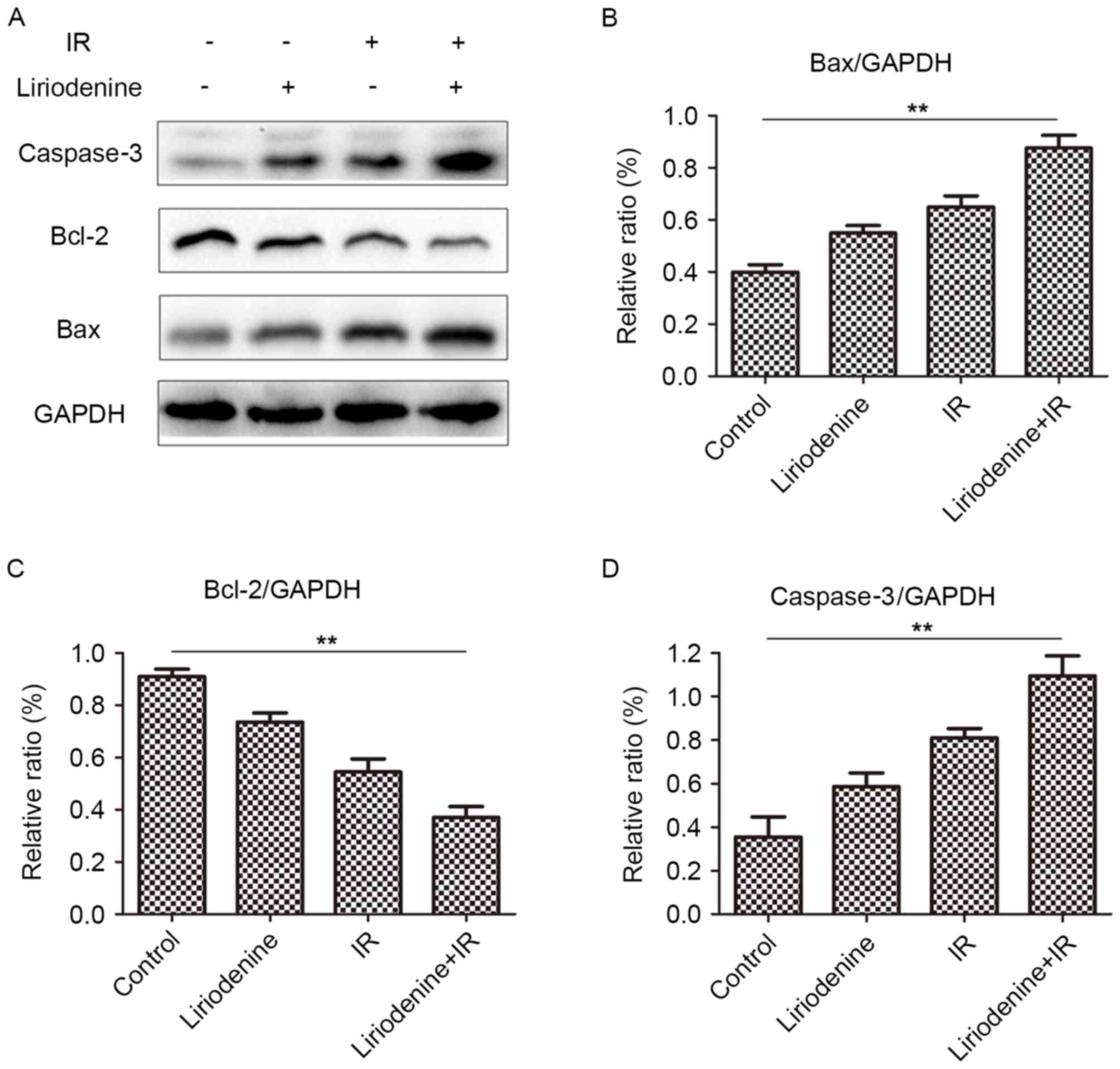
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pennathur A, Farkas A, Krasinskas AM,
Ferson PF, Gooding WE, Gibson MK, Schuchert MJ, Landreneau RJ and
Luketich JD: Esophagectomy for T1 esophageal cancer: Outcomes in
100 patients and implications for endoscopic therapy. Ann Thorac
Surg. 87:1054–1055. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Warthen D, Gooden EL and Jacobson M: Tumor
inhibitors: Liriodenine, a cytotoxic alkaloid from Annona glabra. J
Pharm Sci. 58:637–638. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bentley KW: Beta-phenylethylamines and the
isoquinoline alkaloids. Nat Prod Rep. 23:444–463. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsieh TJ, Liu TZ, Chern CL, Tsao DA, Lu
FJ, Syu YH, Hsieh PY, Hu HS, Chang TT and Chen CH: Liriodenine
inhibits the proliferation of human hepatoma cell lines by blocking
cell cycle progression and nitric oxide mediated activation of p53
expression. Food Chem Toxicol. 43:1117–1126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang GJ, Wu MH, Wu YC and Su MJ:
Electrophysiological mechanisms for antiarrhythmic efficacy and
positive inotropy of liriodenine, a natural aporphine alkaloid from
Fissistigma glaucescens. Br J Pharmacol. 118:1571–1583. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Clark AM, Watson ES, Ashfaq MK and Hufford
CD: In vivo efficacy of antifungal oxoaporphine alkaloids in
experimental disseminated candidiasis. Pharm Res. 4:495–498. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hufford CD, Funderburk MJ, Morgan JM and
Robertson LW: Two antimicrobial alkaloids from heartwood of
Liriodendron tulipifera L. J Pharm Sci. 64:789–792. 1975.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li L, Xu Y and Wang B: Liriodenine induces
the apoptosis of human laryngocarcinoma cells via the upregulation
of p53 expression. Oncol Lett. 9:1121–1127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chang HC, Chang FR, Wu YC and Lai YH:
Anti-cancer effect of liriodenine on human lung cancer cells.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 20:365–371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsieh TJ, Liu TZ, Chern CL, Tsao DA, Lu
FJ, Syu YH, Hsieh PY, Hu HS, Chang TT and Chen CH: Liriodenine
inhibits the proliferation of human hepatoma cell lines by blocking
cell cycle progression and nitric oxide-mediated activation of p53
expression. Food Chem Toxicol. 43:1117–1126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Almeida R, Fernández-Justel JM,
Santa-María C, Cadoret JC, Cano-Aroca L, Lombraña R, Herranz G,
Agresti A and Gómez M: Chromatin conformation regulates the
coordination between DNA replication and transcription. Nat Commun.
9:15902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li YL, Qin QP, Liu YC, Chen ZF and Liang
H: A platinum (II) complex of liriodenine from traditional Chinese
medicine (TCM): Cell cycle arrest, cell apoptosis induction and
telomerase inhibition activity via G-quadruplex DNA stabilization.
J Inorg Biochem. 137:12–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chiu CC, Chou HL, Wu PF, Chen HL, Wang HM
and Chen CY: Bio-functional constituents from the stems of
liriodendron tulipifera. Molecules. 17:4357–4372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Efimova EV, Liang H, Pitroda SP, Labay E,
Darga TE, Levina V, Lokshin A, Roizman B, Weichselbaum RR and
Khodarev NN: Radioresistance of Stat1 overexpressingtumour cellsis
associated with suppressed apoptotic responseto cytotoxic agents
and increased IL6-IL8 signalling. Int J Radiat Biol. 85:421–431.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ezekwudo D, Shashidharamurthy R, Devineni
D, Bozeman E, Palaniappan R and Selvaraj P: Inhibition ofexpression
of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and induction of cell death in
radioresistant human prostate adenocarcinoma cell line (PC-3)
bymethyl jasmonate. Cancer Lett. 270:277–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Csuka O, Remenár E, Koronczay K,
Doleschall Z and Németh G: Predictive value of p53, Bcl2 and bax in
the radiotherapy of head and neck cancer. Pathol Oncol Res.
3:204–210. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Z, Ding Y, Ye N, Wild C, Chen H and
Zhou J: Direct activation of bax protein for cancer therapy. Med
Res Rev. 36:313–341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Modjtahedi N, Giordanetto F, Madeo F and
Kroemer G: Apoptosis-inducing factor: Vital and lethal. Trends Cell
Biol. 16:264–272. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kötter B, Frey B, Winderl M, Rubner Y,
Scheithauer H, Sieber R, Fietkau R and Gaipl US: The in vitro
immunogenic potential of caspase-3 proficient breast cancer cells
with basal low immunogenicity is increased by hypofractionated
irradiation. Radiat Oncol. 10:1972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|