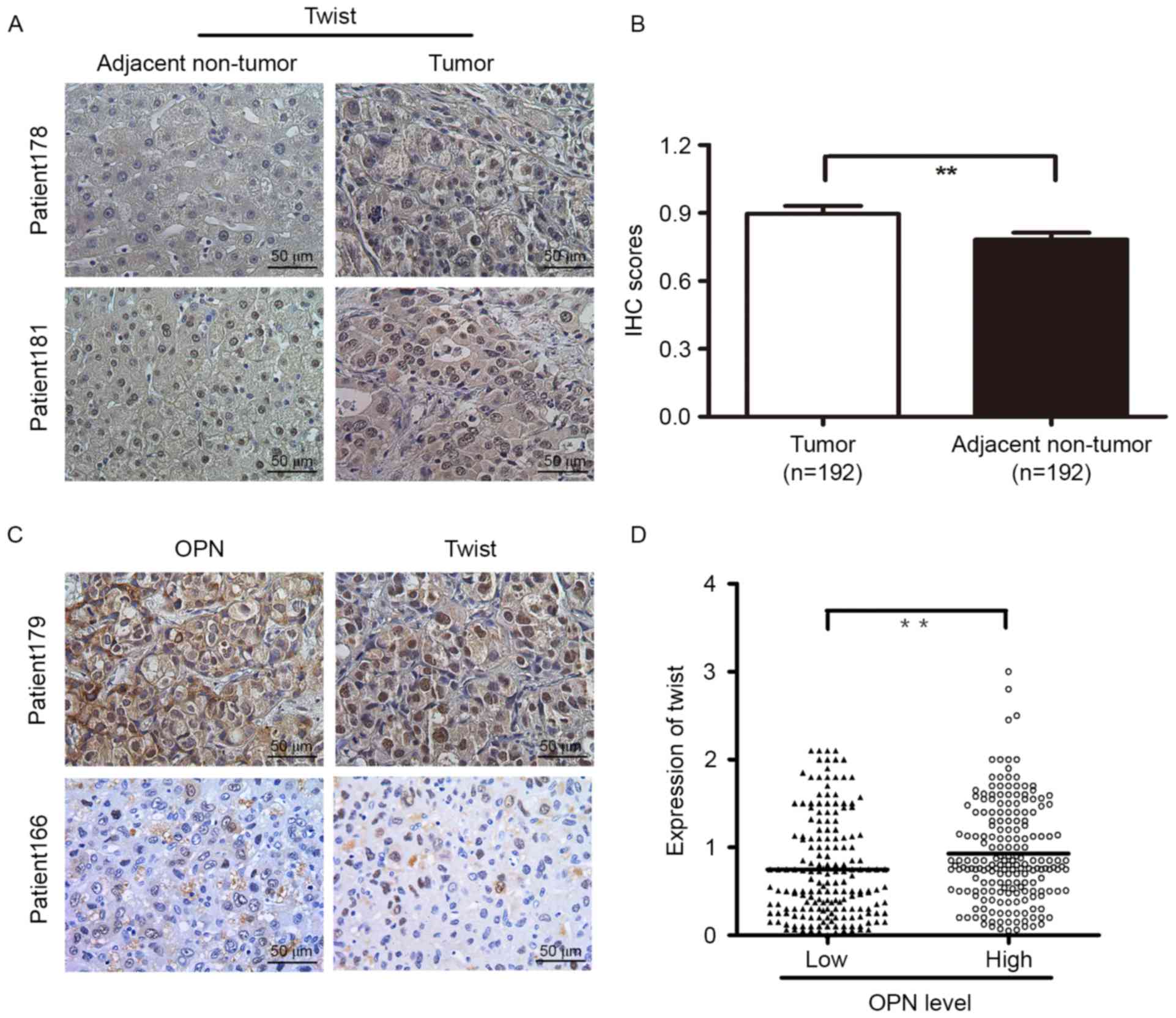
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang Y, Nagano H, Ota H, Morimoto O,
Nakamura M, Wada H, Noda T, Damdinsuren B, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A,
Miyamoto A, et al: Patterns and clinicopathologic features of
extrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
resection. Surgery. 141:196–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Qin LX, Sun HC, Ye
QH, Wang L, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Li Y, et al: A decade's studies on
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
130:187–196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wai PY and Kuo PC: Osteopontin: Regulation
in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:103–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tuck AB, Chambers AF and Allan AL:
Osteopontin overexpression in breast cancer: Knowledge gained and
possible implications for clinical management. J Cell Biochem.
102:859–868. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McAllister SS, Gifford AM, Greiner AL,
Kelleher SP, Saelzler MP, Ince TA, Reinhardt F, Harris LN, Hylander
BL, Repasky EA, et al: Systemic endocrine instigation of indolent
tumor growth requires osteopontin. Cell. 133:994–1005. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dong QZ, Zhang XF, Zhao Y, Jia HL, Zhou
HJ, Dai C, Sun HJ, Qin Y, Zhang WD, Ren N, et al: Osteopontin
promoter polymorphisms at locus-443 significantly affect the
metastasis and prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 57:1024–1034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhattacharya SD, Mi Z, Kim VM, Guo H,
Talbot LJ and Kuo PC: Osteopontin regulates epithelial mesenchymal
transition-associated growth of hepatocellular cancer in a mouse
xenograft model. Ann Surg. 255:319–325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang SH, Wu XC, Zhang MD, Weng MZ, Zhou D
and Quan ZW: Upregulation of H19 indicates a poor prognosis in
gallbladder carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Am J Cancer Res. 6:15–26. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang Q, Han J, Fan J, Duan L, Guo M, Lv
Z, Hu G, Chen L, Wu F, Tao X, et al: IL-17 induces EMT via Stat3 in
lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 6:440–451. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S,
Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and
Weinberg RA: Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an
essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 117:927–939. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang MH and Wu KJ: TWIST activation by
hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): Implications in metastasis and
development. Cell Cycle. 7:2090–2096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng GZ, Zhang W and Wang LH: Regulation
of cancer cell survival, migration, and invasion by Twist: AKT2
comes to interplay. Cancer Res. 68:957–960. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng GZ, Chan J, Wang Q, Zhang W, Sun CD
and Wang LH: Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast
cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and
resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 67:1979–1987. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kwok WK, Ling MT, Lee TW, Lau TC, Zhou C,
Zhang X, Chua CW, Chan KW, Chan FL, Glackin C, et al: Up-regulation
of TWIST in prostate cancer and its implication as a therapeutic
target. Cancer Res. 65:5153–5162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoek K, Rimm DL, Williams KR, Zhao H,
Ariyan S, Lin A, Kluger HM, Berger AJ, Cheng E, Trombetta ES, et
al: Expression profiling reveals novel pathways in the
transformation of melanocytes to melanomas. Cancer Res.
64:5270–5282. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Entz-Werle N, Stoetzel C, Berard-Marec P,
Kalifa C, Brugiere L, Pacquement H, Schmitt C, Tabone MD, Gentet
JC, Quillet R, et al: Frequent genomic abnormalities at TWIST in
human pediatric osteosarcomas. Int J Cancer. 117:349–355. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van Doorn R, Dijkman R, Vermeer MH,
Out-Luiting JJ, van der Raaij-Helmer EM, Willemze R and Tensen CP:
Aberrant expression of the tyrosine kinase receptor EphA4 and the
transcription factor twist in Sezary syndrome identified by gene
expression analysis. Cancer Res. 64:5578–5586. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, Fricke E,
Luber B, Busch R, Höfler H and Becker KF: Differential expression
of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators Snail, SIP1,
and twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol. 161:1881–1891. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang J, Hou Y, Zhou M, Wen S, Zhou J, Xu
L, Tang X, Du YE, Hu P and Liu M: Twist induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell motility in breast
cancer via ITGB1-FAK/ILK signaling axis and its associated
downstream network. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 71:62–71. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP, Ling MT, Kwok
WK, Wang XH, Wong YC, Guan XY, Man K, Chau KL and Fan ST: Twist
overexpression correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis
through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:5369–5376. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY,
Xiao YS, Xu Y, Li YW and Tang ZY: Intratumoral balance of
regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol.
25:2586–2593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang MH, Chen CL, Chau GY, Chiou SH, Su
CW, Chou TY, Peng WL and Wu JC: Comprehensive analysis of the
independent effect of twist and snail in promoting metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 50:1464–1474. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Barrat A, Askari
F, Conjeevaram HS, Su GL and Lok AS: Prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Comparison of 7 staging systems in an American cohort.
Hepatology. 41:707–716. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Llovet JM, Fuster J and Bruix J;
Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer Group, : The Barcelona approach:
Diagnosis, staging, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Liver Transpl. 10 2 Suppl 1:S115–S120. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun HC, Zhang W, Qin LX, Zhang BH, Ye QH,
Wang L, Ren N, Zhuang PY, Zhu XD, Fan J and Tang ZY: Positive serum
hepatitis B e antigen is associated with higher risk of early
recurrence and poorer survival in patients after curative resection
of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
47:684–690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qian YB, Zhang JB, Wu WZ, Fang HB, Jia WD,
Zhuang PY, Zhang BH, Pan Q, Xu Y, Wang L, et al: P48 is a
predictive marker for outcome of postoperative interferon-alpha
treatment in patients with hepatitis B virus infection-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 107:1562–1569. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1312–1327.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Singh PP, Shi Q, Foster NR, Grothey A,
Nair SG, Chan E, Shields AF, Goldberg RM, Gill S, Kahlenberg MS, et
al: Relationship between metformin use and recurrence and survival
in patients with resected Stage III colon cancer receiving adjuvant
chemotherapy: Results from north central cancer treatment group
N0147 (Alliance). Oncologist. 21:1509–1521. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu XD, Zhang JB, Zhuang PY, Zhu HG, Zhang
W, Xiong YQ, Wu WZ, Wang L, Tang ZY and Sun HC: High expression of
macrophage colony-stimulating factor in peritumoral liver tissue is
associated with poor survival after curative resection of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 26:2707–2716. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Tian B, Yang J, Zhao L, Wu X, Ye SL,
Liu YK and Tang ZY: Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials
established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on
metastatic characteristics. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 130:460–468.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tian J, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Lin ZY,
Chen J and Xue Q: New human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell
line with highly metastatic potential (MHCC97) and its expressions
of the factors associated with metastasis. Br J Cancer. 81:814–821.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong Q, Zhu X, Dai C, Zhang X, Gao X, Wei
J, Sheng Y, Zheng Y, Yu J, Xie L, et al: Osteopontin promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma
through regulating vimentin. Oncotarget. 7:12997–13012. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun BS, Dong QZ, Ye QH, Sun HJ, Jia HL,
Zhu XQ, Liu DY, Chen J, Xue Q, Zhou HJ, et al: Lentiviral-mediated
miRNA against osteopontin suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1834–1842. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fu J, Chen Y, Cao J, Luo T, Qian YW, Yang
W, Ren YB, Su B, Cao GW, Yang Y, et al: p28GANK overexpression
accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastasis
via phosphoinositol 3-kinase/AKT/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
pathways. Hepatology. 53:181–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hua Z, Gu X, Dong Y, Tan F, Liu Z, Thiele
CJ and Li Z: PI3K and MAPK pathways mediate the BDNF/TrkB-increased
metastasis in neuroblastoma. Tumour Biol. 37:16227–16236. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang C, Wang Y, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Ji B,
Wang S and Sun Y, Zhu C, Zhang D and Sun Y: Gli1 promotes
colorectal cancer metastasis in a Foxm1-dependent manner by
activating EMT and PI3K-AKT signaling. Oncotarget. 7:86134–86147.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kikuchi L, Chagas AL, Alencar RSSM, Tani
C, Diniz MA, D'Albuquerque LAC and Carrilho FJ: Adherence to BCLC
recommendations for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Impact on survival according to stage. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
72:454–460. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huo TI, Lin HC, Huang YH, Wu JC, Chiang
JH, Lee PC and Lee SD: The model for end-stage liver disease-based
Japan Integrated Scoring system may have a better predictive
ability for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing
locoregional therapy. Cancer. 107:141–148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li CW, Xia W, Lim SO, Hsu JL, Huo L, Wu Y,
Li LY, Lai CC, Chang SS, Hsu YH, et al: AKT1 Inhibits
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition in breast cancer through
phosphorylation-dependent Twist1 degradation. Cancer Res.
76:1451–1462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yasuda J,
Takamura M, Fujita N, Tsuruo T, Todo S and Hirohashi S: Critical
involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in
anchorage-independent growth and hematogeneous intrahepatic
metastasis of liver cancer. Cancer Res. 62:2971–2975. 2016.
|
|
46
|
Huang H, Zhang XF, Zhou HJ, Xue YH, Dong
QZ, Ye QH and Qin LX: Expression and prognostic significance of
osteopontin and caspase-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
after curative resection. Cancer Sci. 101:1314–1319. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ye QH, Qin LX, Forgues M, He P, Kim JW,
Peng AC, Simon R, Li Y, Robles AI, Chen Y, et al: Predicting
hepatitis B virus-positive metastatic hepatocellular carcinomas
using gene expression profiling and supervised machine learning.
Nat Med. 9:416–423. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang H, Ye QH, Ren N, Zhao L, Wang YF, Wu
X, Sun HC, Wang L, Zhang BH, Liu YK, et al: The prognostic
significance of preoperative plasma levels of osteopontin in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
132:709–717. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|