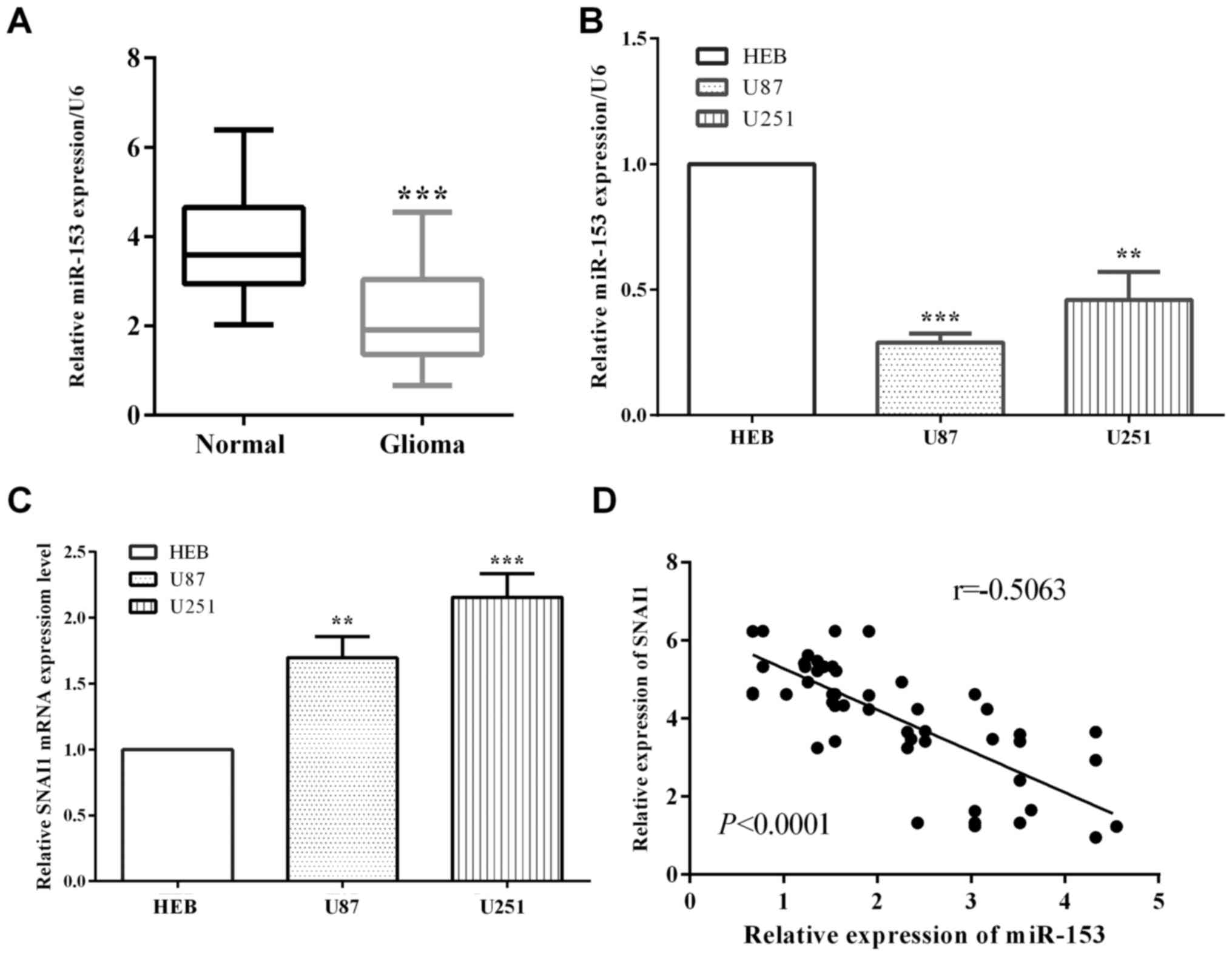
|
1
|
Westphal M and Lamszus K: The neurobiology
of gliomas: From cell biology to the development of therapeutic
approaches. Nat Rev Neurosci. 12:495–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kwiatkowski SC, Guerrero PA, Hirota S,
Chen Z, Morales JE, Aghi M and McCarty JH: Neuropilin-1 modulates
TGFβ signaling to drive glioblastoma growth and recurrence after
anti-angiogenic therapy. PLoS One. 12:e01850652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Louis DN: Molecular pathology of malignant
gliomas. Annu Rev Pathol. 1:97–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sayegh ET, Kaur G, Bloch O and Parsa AT:
Systematic review of protein biomarkers of invasive behavior in
glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 49:1212–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Munthe S, Halle B, Boldt HB, Christiansen
H, Schmidt S, Kaimal V, Xu J, Zabludoff S, Mollenhauer J, Poulsen
FR, et al: Shift of microRNA profile upon glioma cell migration
using patient-derived spheroids and serum-free conditions. J
Neurooncol. 132:45–54. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siomi H and Siomi MC: Posttranscriptional
regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals. Mol Cell. 38:323–332.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fabbri M: MicroRNAs and cancer: Towards a
personalized medicine. Curr Mol Med. 13:751–756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gonzalez-Duarte RJ, Cazares-Ordonez V and
Avila-Chavez E: The microRNA biogenesis machinery: Regulation by
steroid hormones and alterations in cancer. Rev Invest Clin.
66:460–464. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Sun J, Bai Z, Li H, He S, Chen R
and Che X: MicroRNA-153 acts as a prognostic marker in gastric
cancer and its role in cell migration and invasion. Onco Targets
Ther. 8:357–364. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang W, Peng B, Wang D, Ma X, Jiang D,
Zhao J and Yu L: Human tumor microRNA signatures derived from
large-scale oligonucleotide microarray datasets. Int J Cancer.
129:1624–1634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zuo J, Wang D, Shen H, Liu F, Han J and
Zhang X: MicroRNA-153 inhibits tumor progression in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting SNAI1. Tumour Biol.
37:16135–16140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu X, Li L, Li Y and Liu Z: miR-153
promotes breast cancer cell apoptosis by targeting HECTD3. Am J
Cancer Res. 6:1563–1571. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bai Z, Sun J, Wang X, Wang H, Pei H and
Zhang Z: MicroRNA-153 is a prognostic marker and inhibits cell
migration and invasion by targeting SNAI1 in human pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 34:595–602. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shan N, Shen L, Wang J, He D and Duan C:
miR-153 inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell
lung cancer by targeting ADAM19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
456:385–391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng HF, Yan S and Wu SF: MicroRNA-153-3p
suppress cell proliferation and invasion by targeting SNAI1 in
melanoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:140–145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Pickard K, Jenei V, Bullock MD,
Bruce A, Mitter R, Kelly G, Paraskeva C, Strefford J, Primrose J,
et al: miR-153 supports colorectal cancer progression via
pleiotropic effects that enhance invasion and chemotherapeutic
resistance. Cancer Res. 73:6435–6447. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nieto MA: The snail superfamily of
zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:155–166. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M and
Cano A: Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of
the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell
Biol. 24:306–319. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Natsugoe S, Uchikado Y, Okumura H,
Matsumoto M, Setoyama T, Tamotsu K, Kita Y, Sakamoto A, Owaki T,
Ishigami S, et al: Snail plays a key role in E-cadherin-preserved
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 17:517–523.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong Q, Cai N, Tao T, Zhang R, Yan W, Li
R, Zhang J, Luo H, Shi Y, Luan W, et al: An axis involving SNAI1,
microRNA-128 and SP1 modulates glioma progression. PLoS One.
9:e986512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Allen M, Bjerke M, Edlund H, Nelander S
and Westermark B: Origin of the U87MG glioma cell line: Good news
and bad news. Sci Transl Med. 8:54re32016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Scmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui Y, Zhao J, Yi L and Jiang Y:
microRNA-153 targets mTORC2 component rictor to inhibit glioma
cells. PLoS One. 11:e01569152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Christodoulatos GS and Dalamaga M:
Micro-RNAs as clinical biomarkers and therapeutic targets in breast
cancer: Quo vadis? World J Clin Oncol. 5:71–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lauressergues D, Couzigou JM, Clemente HS,
Martinez Y, Dunand C, Bécard G and Combier JP: Primary transcripts
of microRNAs encode regulatory peptides. Nature. 520:90–93. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Niu G, Li B, Sun L and An C: MicroRNA-153
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion by targeting
TGF-β2. PLoS One. 10:e01192252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|