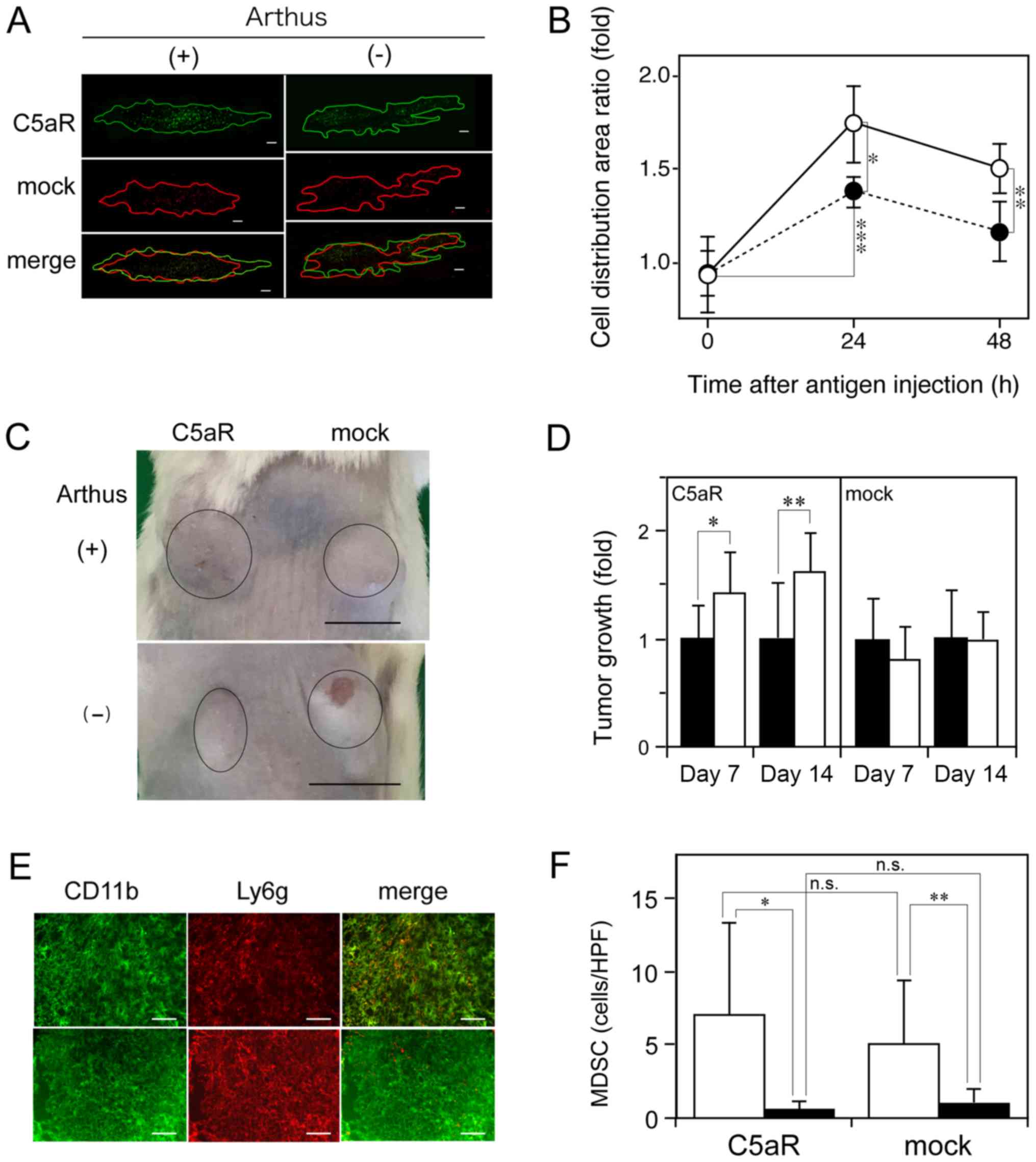
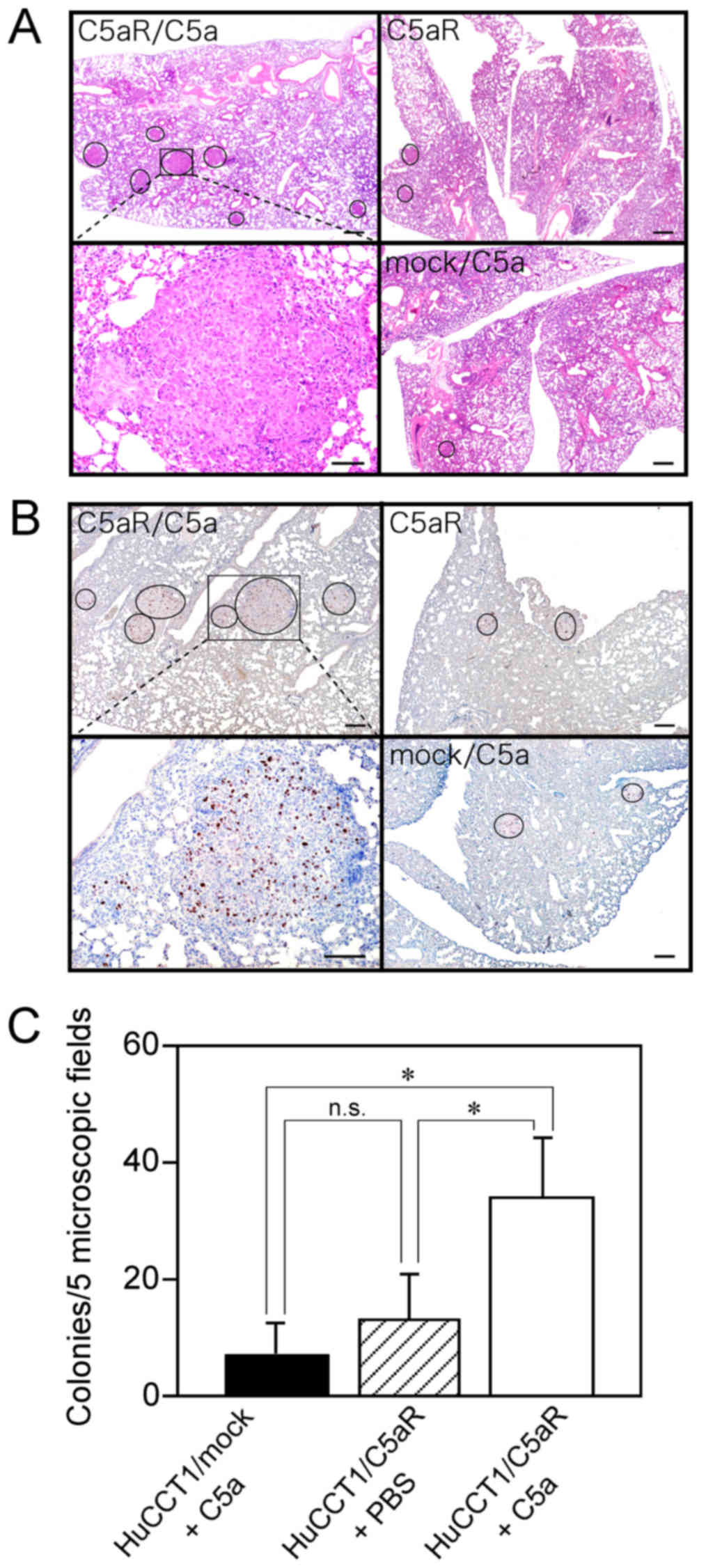
|
1
|
Hellewell PG and Rossi AG: Arthus
reaction. In: Encyclopedia of immunology. 2nd. Delves PJ and Roitt
IM: Elsevier Academic Press; Amsterdam (Netherlands): pp. 237–240.
1998
|
|
2
|
Pak JK, Yang JA, Ahn EY, Chang SH, Song
YW, Curtis JR and Lee EB: Survival rate of cancer patients with and
without rheumatic disease: A retrospective cohort analysis. BMC
Cancer. 16:3812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Criscitiello C, Bangnardi V, Esposito A,
Gelao L, Santillo B, Viale G, Rotmensz N, Goldhirsch A and
Curigliano G: Impact of autoimmune diseases on outcome of patients
with early breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:51184–51192. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Souza SL, Montalli Da Assumpção LV and
Ward LS: Impact of previous thyroid autoimmune diseases on
prognosis of patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer.
Thyroid. 13:491–495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fernandez HN and Hugli TE: Primary
structural analysis of the polypeptide portion of human C5a
anaphylatoxin. Polypeptide sequence determination and assignment of
the oligosaccharide attachment site in C5a. J Biol Chem.
253:6955–6964. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo RF and Ward PA: Role of C5a in
inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 23:821–852. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Markiewski MM and Lambris JD: The role of
complement in inflammatory diseases from behind the scenes into the
spotlight. Am J Pathol. 171:715–727. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Markiewski MM, DeAngelis RA, Benencia F,
Ricklin-Lichtsteiner SK, Koutoulaki A, Gerard C, Coukos G and
Lambris JD: Modulation of the antitumor immune response by
complement. Nat Immunol. 9:1225–1235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Corrales L, Ajona D, Rafail S, Lasarte JJ,
Riezu-Boj JI, Lambris JD, Rouzaut A, Pajares MJ, Montuenga LM and
Pio R: Anaphylatoxin C5a creates a favorable microenvironment for
lung cancer progression. J Immunol. 189:4674–4683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nozaki M, Raisler BJ, Sakurai E, Sarma JV,
Barnum SR, Lambris JD, Chen Y, Zhang K, Ambati BK, Baffi JZ and
Ambati J: Drusen complement components C3a and C5a promote
choroidal neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:2328–2333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gerard NP and Gerard C: The chemotactic
receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin. Nature. 349:614–617. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nitta H, Wada Y, Kawano Y, Murakami Y,
Irie A, Taniguchi K, Kikuchi K, Yamada G, Suzuki K, Honda J, et al:
Enhancement of human cancer cell motility and invasiveness by
anaphylatoxin C5a via aberrantly expressed C5a receptor (CD88).
Clin Cancer Res. 19:2004–2013. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niculescu F, Rus HG, Retegan M and Vlaicu
R: Persistent complement activation on tumor cells in breast
cancer. Am J Pathol. 140:1039–1043. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bjørge L, Hakulinen J, Vintermyr OK, Jarva
H, Jensen TS, Iversen OE and Meri S: Ascitic complement system in
ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 92:895–905. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nitta H, Murakami Y, Wada Y, Eto M, Baba H
and Imamura T: Cancer cells release anaphylatoxin C5a from C5 by
serine protease to enhance invasiveness. Oncol Rep. 32:1715–1719.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu J, Ding JY, Lu CL, Lin ZW, Chu YW, Zhao
GY, Guo J and Ge D: Overexpression of CD88 predicts poor prognosis
in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 81:259–265. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imamura T, Yamamoto-Ibusuki M, Sueta A,
Kubo T, Irie A, Kikuchi K, Kariu T and Iwase H: Influence of the
C5a-C5a receptor system on breast cancer progression and patient
prognosis. Breast Cancer. 23:876–885. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wada Y, Maeda Y, Kubo T, Kikuchi K, Eto M
and Imamura T: C5a receptor expression is associated with poor
prognosis in urothelial cell carcinoma patients treated with
radical cystectomy or nephroureterectomy. Oncol Lett. 12:3995–4000.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xi W, Liu L, Wang J, Xia Y, Bai Q, Xiong
Y, Qu Y, Long Q, Xu J and Guo J: Enrichment of C5a-C5aR axis
predicts poor postoperative prognosis of patients with clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:80925–80934. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kaida T, Nitta H, Kitano Y, Yamamura K,
Arima K, Izumi D, Higashi T, Kurashige J, Imai K, Hayashi H, et al:
C5a receptor (CD88) promotes motility and invasiveness of gastric
cancer by activating RhoA. Oncotarget. 7:84798–84809. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nitta H, Shimose T, Emi Y, Imamura T,
Ohnishi K, Kusumoto T, Yamamoto M, Fukuzawa K, Takahashi I, Higashi
H, et al: Expression of the anaphylatoxin C5a receptor in gastric
cancer: Implications for vascular invasion and patient outcomes.
Med Oncol. 33:1182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sakuma Y, Nagai T, Yoshio T and Hirohata
S: Differential activation mechanisms of serum C5a in lupus
nephritis and neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod
Rheumatol. 27:292–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hornum L, Hansen AJ, Tornehave D, Fjording
MS, Colmenero P, Wätjen IF, Søe Nielsen NH, Bliddal H and Bartels
EM: C5a and C5aR are elevated in joints of rheumatoid and psoriatic
arthritis patients, and C5aR blockade attenuates leukocyte
migration to synovial fluid. PLoS One. 12:e01890172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cream JJ, Bryceson AD and Ryder G:
Disappearance of immunoglobulin and complement from the Arthus
reaction and its relevance to studies of vasculitis in man. Br J
Dermatol. 84:106–109. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ramos BF, Zhan Y and Jakschik BA:
Neutrophil elicitation in the reverse passive Arthus reaction.
Complement-dependent and -independent mast cell involvement. J
Immunol. 152:1380–1384. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Maeda Y, Kawano Y, Wada Y, Yatsuda J,
Motoshima T, Murakami Y, Kikuchi K, Imamura T and Eto M: C5aR is
frequently expressed in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and plays a
crucial role in cell invasion via the ERK and PI3 kinase pathways.
Oncol Rep. 33:1844–1850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shojaei F, Wu X, Malik AK, Zhong C,
Baldwin ME, Schanz S, Fuh G, Gerber HP and Ferrara N: Tumor
refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by
CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells. Nat Biotechnol.
25:911–920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
FIGO Committee on Gynecologic Oncology:
FIGO staging for carcinoma of the vulva, cervix, and corpus uteri.
Int J Gynecol Obstet. 125:97–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Koomägi R and Volm M: Expression of Fas
(CD95/APO-1) and Fas ligand in lung cancer, its prognostic and
predictive relevance. Int J Cancer. 84:239–243. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rahman MA, Dhar DK, Yamaguchi E, Maruyama
S, Sato T, Hayashi H, Ono T, Yamanoi A, Kohno H and Nagasue N:
Coexpression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and COX-2 in
hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding liver: Possible
involvement of COX-2 in the angiogenesis of hepatitis C
virus-positive case. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1325–1332. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shvarts O, Janzen N, Lam JS, Leppert JT,
Caliliw R, Figlin RA, Belldegrum AS and Zeng G: RENCA/carbonic
anhydrase-IX: A murine model of a carbonic anhydrase-IX-expressing
renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 68:1132–1138. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vignesh P, Rawat A, Sharma M and Singh S:
Complement in autoimmune diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 465:123–130.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Landgren AM, Landgren O, Gridley G, Dores
GM, Linet MS and Morton LM: Autoimmune disease and subsequent risk
of developing alimentary tract cancers among 4.5 million US male
veterans. Cancer. 117:1163–1171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu KH, Kuo CF, Huang LH, Huang WK and See
LC: Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory systemic autoimmune
Rheumatic diseases. A nationwide population-based dynamic cohort
study in Taiwan. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e35402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu Y and Hu XB: C5a stimulates the
proliferation of breast cancer cells via Akt-dependent RGC-32 gene
activation. Oncol Rep. 32:2817–2823. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cai K, Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhao X and
Bao X: C5a promotes the proliferation of human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells through PCAF-mediated STAT3 acetylation. Oncol Rep.
32:2260–2266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zafar GI, Grimm EA, Wei W, Johnson MM and
Ellerhorst JA: Genetic deficiency of complement isoforms C4A or C4B
predicts improved survival of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J
Urol. 181:1028–1034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ajona D, Ortiz-Espinosa S, Moreno H,
Lozano T, Pajares MJ, Agorreta J, Bértolo C, Lasarte JJ, Vicent S,
Hoehlig K, et al: A combined PD-1/C5a blockade synergistically
protects against cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Discov.
7:694–703. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|