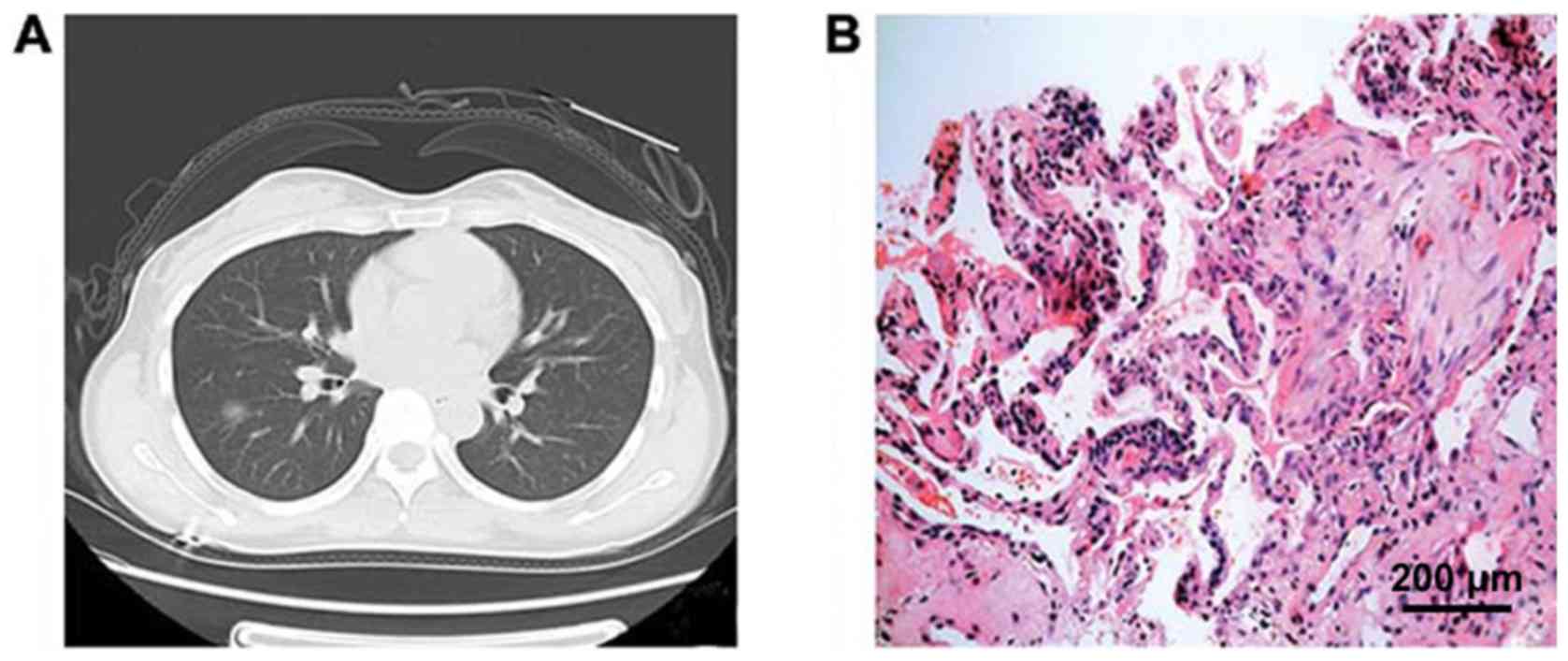
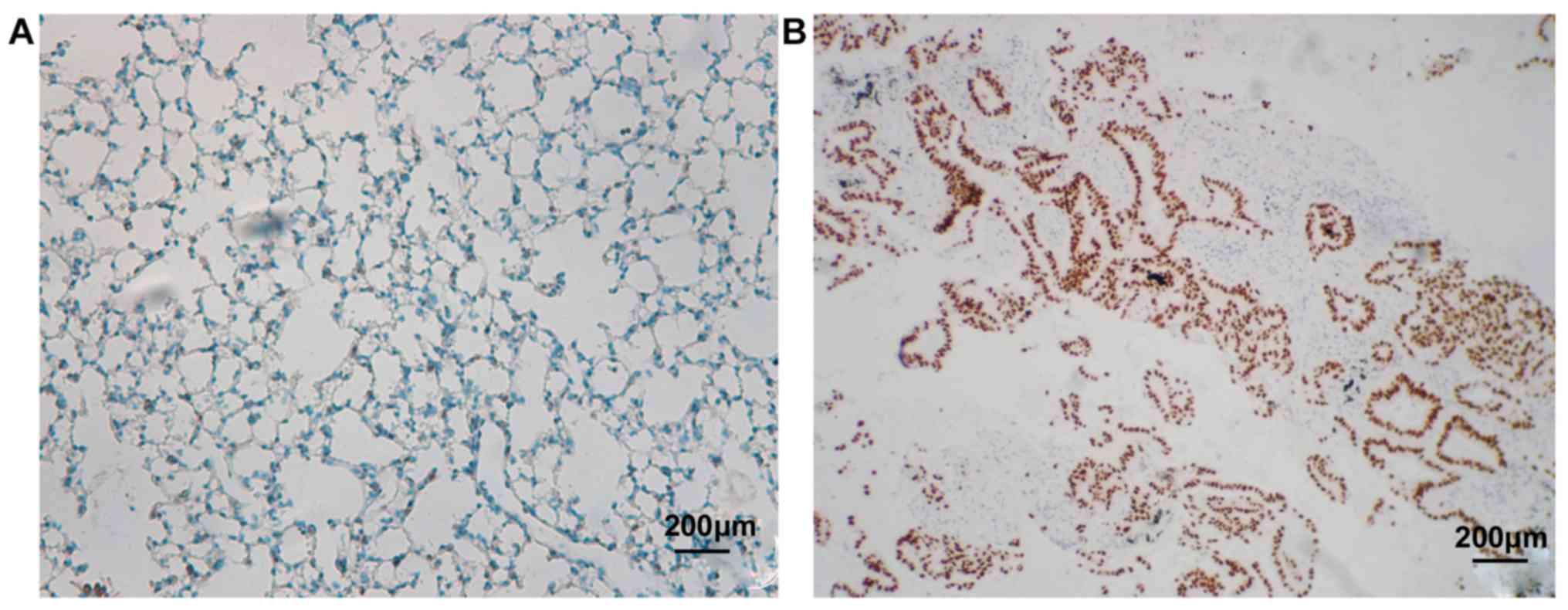
|
1
|
Grunnet M and Sorensen JB:
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 76:138–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC,
Clapp JD, Fagerstrom RM, Gareen IF, Gatsonis C, Marcus PM and Sicks
JD: National Lung Screening Trial Research Team: Reduced
lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening.
N Engl J Med. 365:395–409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wood DE: National Comprehensive Cancer
Network (NCCN) clinical practice guidelines for lung cancer
screening. Thorac Surg Clin. 25:185–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuki K, Asamura H, Kusumoto M, Kondo H
and Tsuchiya R: ‘Early’ peripheral lung cancer: Prognostic
significance of ground glass opacity on thin-section computed
tomographic scan. Ann Thorac Surg. 74:1635–1639. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li F, Sone S, Abe H, Macmahon H and Doi K:
Malignant versus benign nodules at CT screening for lung cancer:
Comparison of thin-section CT findings. Radiology. 233:793–798.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aoki T, Tomoda Y, Watanabe H, Nakata H,
Kasai T, Hashimoto H, Kodate M, Osaki T and Yasumoto K: Peripheral
lung adenocarcinoma: Correlation of thin-section CT findings with
histologic prognostic factors and survival. Radiology. 220:803–809.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hattori A, Suzuki K, Matsunaga T, Fukui M,
Tsushima Y, Takamochi K and Oh S: Tumour standardized uptake value
on positron emission tomography is a novel predictor of
adenocarcinoma in situ for c-stage IA lung cancer patients with a
part-solid nodule on thin-section computed tomography scan.
Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 18:329–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Detterbeck FC, Marom EM, Arenberg DA,
Franklin WA, Nicholson AG, Travis WD, Girard N, Mazzone PJ,
Donington JS, Tanoue LT, et al: The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging
Project: Background data and proposals for the application of TNM
staging rules to lung cancer presenting as multiple nodules with
ground glass or lepidic features or a pneumonic type of involvement
in the forthcoming eighth edition of the TNM classification. J
Thorac Oncol. 11:666–680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee HY, Choi YL, Lee KS, Han J, Zo JI,
Shim YM and Moon JW: Pure ground-glass opacity neoplastic lung
nodules: Histopathology, imaging, and management. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 202:W224–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goo JM, Park CM and Lee HJ: Ground-glass
nodules on chest CT as imaging biomarkers in the management of lung
adenocarcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196:533–543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harris CC: p53 tumor suppressor gene: At
the crossroads of molecular carcinogenesis, molecular epidemiology,
and cancer risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect. 104 Suppl
3:435–439. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kakeji Y, Korenaga D, Tsujitani S, Baba H,
Anai H, Maehara Y and Sugimachi K: Gastric cancer with p53
overexpression has high potential for metastasising to lymph nodes.
Br J Cancer. 67:589–593. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tao Y, Lu L, Dewan M, Chen AY, Corso J,
Xuan J, Salganicoff M and Krishnan A: Multi-level ground glass
nodule detection and segmentation in CT lung images. Med Image
Comput Comput Assist Interv. 12:715–723. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou Q, Fan Y, Wang Y, Qiao Y, Wang G,
Huang Y, Wang X, Wu N, Zhang G, Zheng X, et al: China national
guideline of classification, diagnosis and treatment for lung
nodules (2016 version). Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 19:793–798.
2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu C, Zhao C, Yang Y, He Y, Hou L, Li X,
Gao G, Shi J, Ren S, Chu H, et al: High discrepancy of driver
mutations in patients with NSCLC and synchronous multiple lung
ground-glass nodules. J Thorac Oncol. 10:778–783. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Qiang JW, Ye JD, Ye XD and Zhang
J: High resolution CT in differentiating minimally invasive
component in early lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 84:236–241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Muller PA and Vousden KH: Mutant p53 in
cancer: New functions and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Cell.
25:304–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lane DP, Cheok CF and Lain S: p53-based
cancer therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0012222010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jolly KW, Malkin D, Douglass EC, Brown TF,
Sinclair AE and Look AT: Splice-site mutation of the p53 gene in a
family with hereditary breast-ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 9:97–102.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Olivier M, Hollstein M and Hainaut P: TP53
mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical
use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0010082010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|