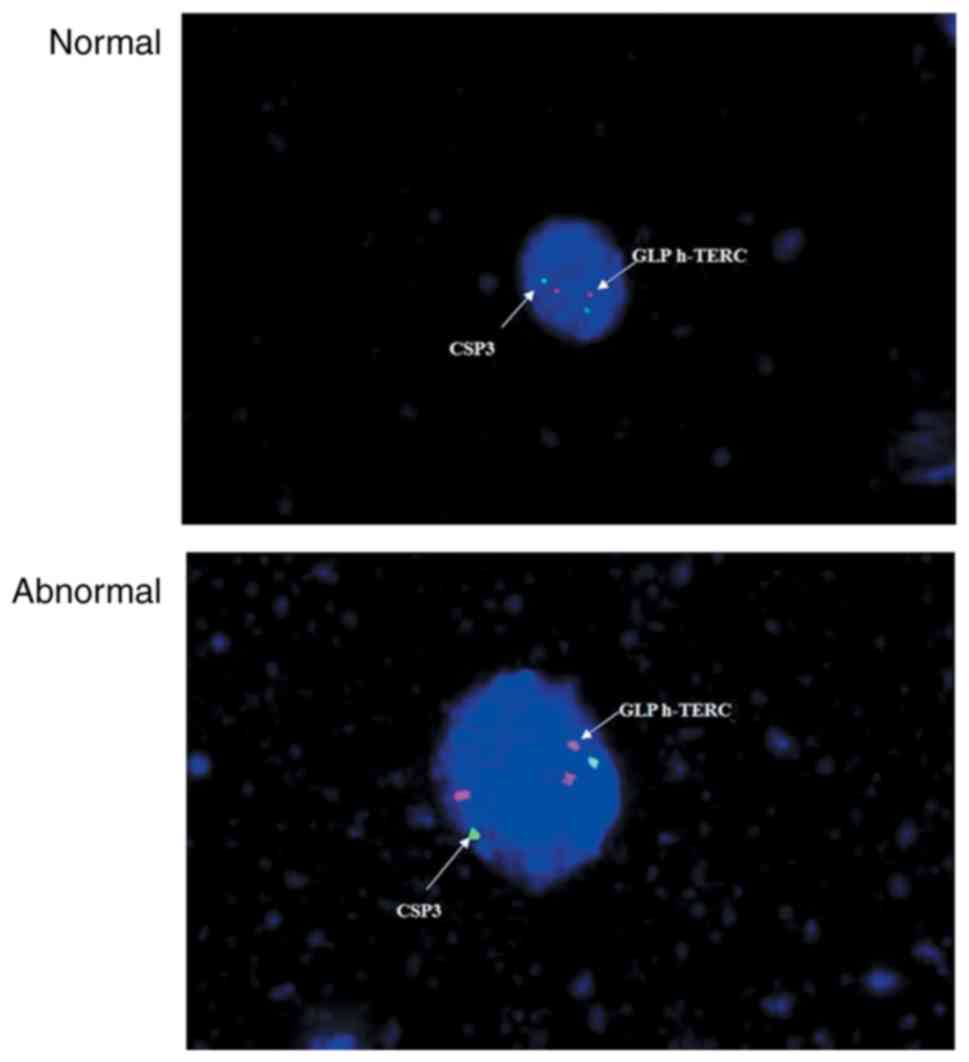
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Di J, Rutherford S and Chu C: Review of
the cervical cancer burden and population-based cervical cancer
screening in China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:7401–7407. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang XZ, Liu KR, Yuan FM, Hou JZ, Zhang JJ
and Zhang YZ: An analysis of both high incidence of esophageal and
cervical cancer in Yangcheng County, Shanxi Province. China Cancer.
4:259–261. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Wang J, Fan J, Zhao W, Yang X, Wu
L, Li D, Ding L, Wang W, Xu J, et al: Risk factors for cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer in Chinese women:
Large study in Jiexiu, Shanxi Province, China. J Cancer. 8:924–932.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Zhang L, Zhao G, Che L, Zhang H and
Fang J: The clinical research of Thinprep Cytology Test (TCT)
combined with HPV-DNA detection in screening cervical cancer. Cell
Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 63:92–95. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Guo C, Liu Z and
Nie S: Prevalence of human papillomavirus infection and genotyping
for population-based cervical screening in developed regions in
China. Oncotarget. 7:62411–62424. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang JL, Yang YZ, Dong WW, Sun J, Tao HT,
Li RX and Hu Y: Application of human papillomavirus in screening
for cervical cancer and precancerous lesions. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:2979–2982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao K, Eurasian M, Zhang J, Wei Y, Zheng
Q, Ye H and Li L: Can genomic amplification of human telomerase
gene and C-MYC in liquid-based cytological specimens be used as a
method for opportunistic cervical cancer screening? Gynecol Obstet
Invest. 80:153–163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szarewski A: HPV vaccination and cervical
cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 14:559–567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chandra R: Relevance of persistent
infection with high-risk HPV genotypes in cervical cancer
progression. MLO Med Lab Obs. 45:40, 42, 44. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li T, Tang L, Bian D, Jia Y, Huang X and
Zhang X: Detection of hTERC and c-MYC genes in cervical epithelial
exfoliated cells for cervical cancer screening. Int J Mol Med.
33:1289–1297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuglik P, Kasikova K, Smetana J, Vallova
V, Lastuvkova A, Moukova L, Cvanova M and Brozova L: Molecular
cytogenetic analyses of hTERC (3q26) and MYC (8q24) genes
amplifications in correlation with oncogenic human papillomavirus
infection in Czech patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
and cervical carcinomas. Neoplasma. 62:130–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao Y, Bryan TM and Reddel RR: Increased
copy number of the TERT and TERC telomerase subunit genes in cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 99:1092–1099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bin H, Ruifang W, Ruizhen L, Yiheng L,
Zhihong L, Juan L, Chun W, Yanqiu Z and Leiming W: Detention of HPV
L1 capsid protein and hTERC gene in screening of cervical cancer.
Iran J Basic Med Sci. 16:797–802. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ferber MJ, Thorland EC, Brink AA, Rapp AK,
Phillips LA, Mcgovern R, Gostout BS, Cheung TH, Chung TK, Fu WY and
Smith DI: Preferential integration of human papillomavirus type 18
near the c-myc locus in cervical carcinoma. Oncogene. 22:7233–7242.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abba MC, Laguens RM, Dulout FN and Golijow
CD: The c-myc activation in cervical carcinomas and HPV 16
infections. Mutat Res. 557:151–158. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kübler K, Heinenberg S, Rudlowski C,
Keyver-Paik MD, Abramian A, Merkelbach-Bruse S, Büttner R, Kuhn W
and Schildhaus HU: c-myc copy number gain is a powerful
prognosticator of disease outcome in cervical dysplasia.
Oncotarget. 6:825–835. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng X, Liang P, Zheng Y, Yi P, Liu Q,
Han J, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Guo J and Li L: Clinical significance of
hTERC gene detection in exfoliated cervical epithelial cells for
cervical lesions. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 23:785–790. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao WH, Hao M, Cheng XT, Yang X, Wang ZL,
Cheng KY, Liu FL and Bai YX: c-myc gene copy number variation in
cervical exfoliated cells detected on fluorescence in situ
hybridization for cervical cancer screening. Gynecol Obstet Invest.
81:416–423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang J, Wei LH, Li YL, Wu RF, Xie X, Feng
YJ, Zhang G, Zhao C, Zhao Y and Chen Z: Detection of TERC
amplification in cervical epithelial cells for the diagnosis of
high-grade cervical lesions and invasive cancer: A multicenter
study in China. J Mol Diagn. 12:808–817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gu Y, Ma C, Zou J, Zhu Y, Yang R, Xu Y and
Zhang Y: Prevalence characteristics of high-risk human
papillomaviruses in women living in Shanghai with cervical
precancerous lesions and cancer. Oncotarget. 7:24656–24663. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Solomon D, Davey D, Kurman R, Moriarty A,
O'Connor D, Prey M, Raab S, Sherman M, Wilbur D, Wright T Jr, et
al: The 2001 Bethesda System: Terminology for reporting results of
cervical cytology. JAMA. 287:2114–2119. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He X, Yang P, Wang H, Wang Y and Liu S:
Human papillomavirus genotyping by surface plasmon resonance-based
test. Clin Lab. 62:2079–2084. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang S, Yang H, Zhang H, Yang F, Zhou M,
Jia C, Lan Y, Ma Y, Zhou L, Tian S, et al: A surface plasmon
resonance--based system to genotype human papillomavirus. Cancer
Genet Cytogenet. 200:100–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan QJ, Hu SY, Guo HQ, Zhang WH, Zhang X,
Chen W, Cao J, Jiang Y, Zhao FH and Qiao YL: Liquid-based cytology
and human papillomavirus testing: A pooled analysis using the data
from 13 population-based cervical cancer screening studies from
China. Gynecol Oncol. 133:172–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Castle PE, Aslam S and Behrens C: Cervical
precancer and cancer risk by human papillomavirus status and
cytologic interpretation: Implications for risk-based management.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:1595–1599. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zappacosta R, Ianieri MM, Buca D, Repetti
E, Ricciardulli A and Liberati M: Clinical role of the detection of
human telomerase RNA component gene amplification by fluorescence
in situ hybridization on liquid-based cervical samples: Comparison
with human papillomavirus-DNA testing and histopathology. Acta
Cytol. 59:345–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Baena-Del Valle JA, Zheng Q, Esopi DM,
Rubenstein M, Hubbard GK, Moncaliano MC, Hruszkewycz A, Vaghasia A,
Yegnasubramanian S, Wheelan SJ, et al: MYC drives overexpression of
telomerase RNA (hTR/TERC) in prostate cancer. J Pathol. 244:11–24.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Penzo M, Ludovini V, Treré D, Siggillino
A, Vannucci J, Bellezza G, Crinò L and Montanaro L: Dyskerin and
TERC expression may condition survival in lung cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 6:21755–21760. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Li H, Yao G, Li W, Wang F, Jiang Z
and Li M: Inhibition of telomerase RNA (hTR) in cervical cancer by
adenovirus-delivered siRNA. Cancer Gene Ther. 14:748–755. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan Y, Zhang J, Cai L, Ding C, Wang X,
Chen H, Wang X, Yan J and Lu J: Leptin induces cell proliferation
and reduces cell apoptosis by activating c-myc in cervical cancer.
Oncol Rep. 29:2291–2296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liao LM, Sun XY, Liu AW, Wu JB, Cheng XL,
Lin JX, Zheng M and Huang L: Low expression of long noncoding
XLOC_010588 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes proliferation
through upregulation of c-Myc in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
133:616–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cui F, Hou J, Huang C, Sun X, Zeng Y,
Cheng H, Wang H and Li C: C-Myc regulates radiation-induced G2/M
cell cycle arrest and cell death in human cervical cancer cells. J
Obstet Gynaecol Res. 43:729–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luan T, Hua Q, Liu X, Xu P, Gu Y, Qian H,
Yan L, Xu X, Geng R and Zeng X and Zeng X: PAX1 methylation as a
potential biomarker to predict the progression of cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia: A meta-analysis of related studies. Int
J Gynecol Cancer. 27:1480–1488. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liou YL, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Cao L, Qin CZ,
Zhang TL, Chang CF, Wang HJ, Lin SY, Chu TY, et al: Comparison of
HPV genotyping and methylated ZNF582 as triage for women with
equivocal liquid-based cytology results. Clin Epigenetics.
7:502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|