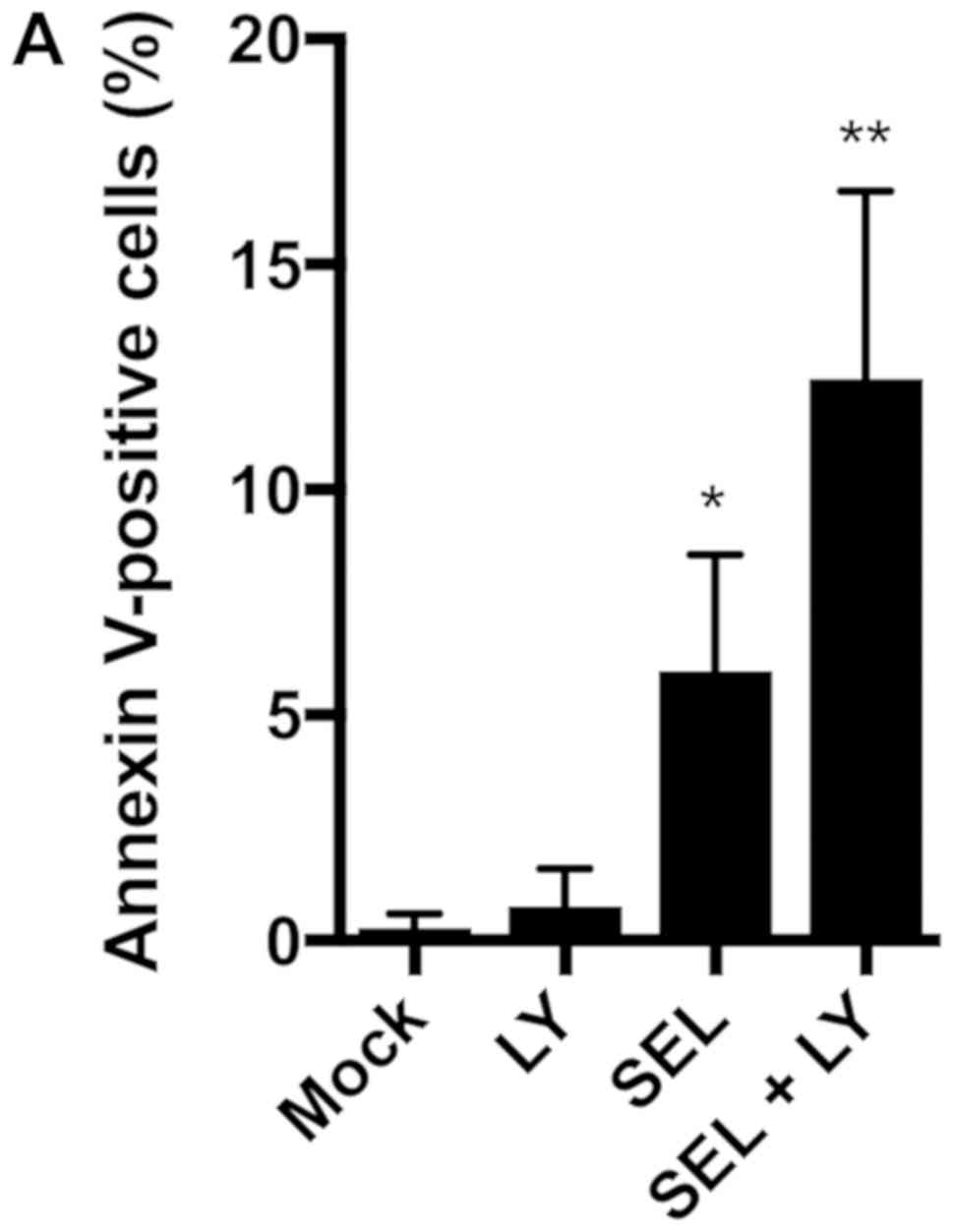
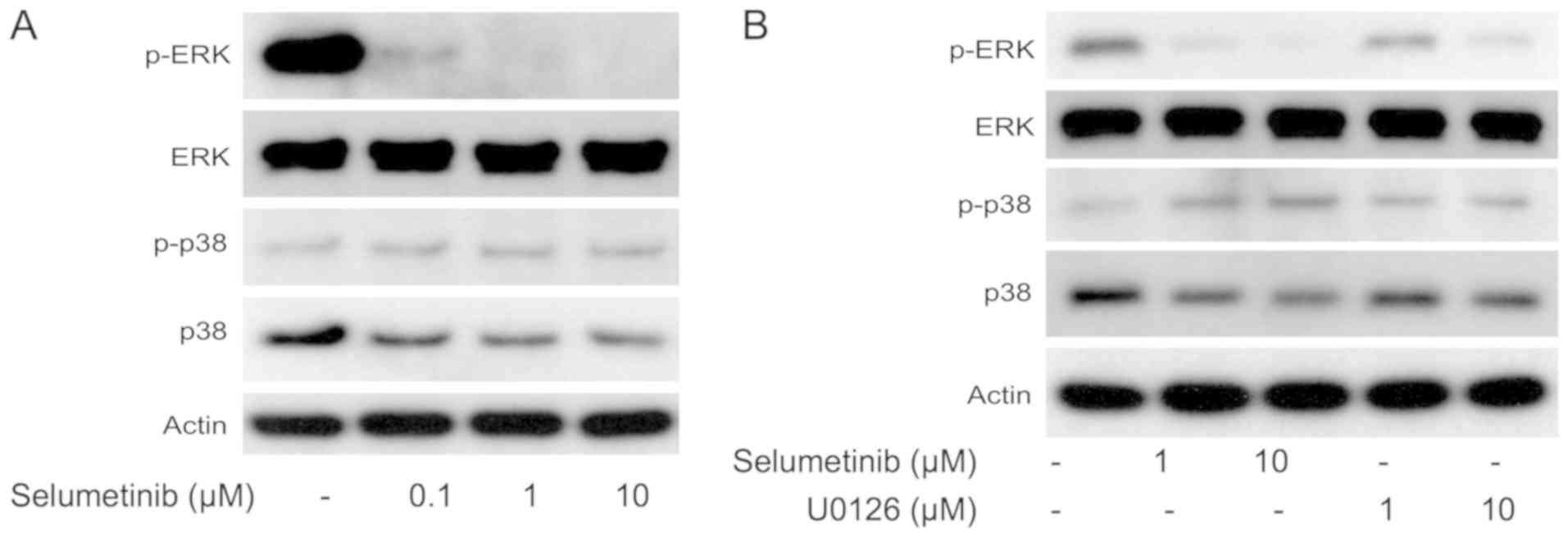
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Houston KA, Henley SJ, Li J, White MC and
Richards TB: Patterns in lung cancer incidence rates and trends by
histologic type in the United States, 2004–2009. Lung Cancer.
86:22–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saito M, Shiraishi K, Kunitoh H,
Takenoshita S, Yokota J and Kohno T: Gene aberrations for precision
medicine against lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 107:713–720.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, Kwiatkowski
DJ, Iafrate AJ, Wistuba II, Varella-Garcia M, Franklin WA, Aronson
SL, Su PF, et al: Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in
lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA. 311:1998–2006. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pylayeva-Gupta Y, Grabocka E and Bar-Sagi
D: RAS oncogenes: Weaving a tumorigenic web. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:761–774. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meng D, Yuan M, Li X, Chen L, Yang J, Zhao
X, Ma W and Xin J: Prognostic value of K-RAS mutations in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review with
meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 81:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ying M, Zhu XX, Zhao Y, Li DH and Chen LH:
KRAS mutation as a biomarker for survival in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer, a meta-analysis of 12 randomized
trials. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:4439–4445. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matikas A, Mistriotis D, Georgoulias V and
Kotsakis A: Targeting KRAS mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A
history of failures and a future of hope for a diverse entity. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 110:1–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blumenschein GR Jr, Smit EF, Planchard D,
Kim DW, Cadranel J, De Pas T, Dunphy F, Udud K, Ahn MJ, Hanna NH,
et al: A randomized phase II study of the MEK1/MEK2 inhibitor
trametinib (GSK1120212) compared with docetaxel in KRAS-mutant
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)†. Ann Oncol.
26:894–901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jänne PA, van den Heuvel MM, Barlesi F,
Cobo M, Mazieres J, Crinò L, Orlov S, Blackhall F, Wolf J, Garrido
P, et al: Selumetinib plus docetaxel compared with docetaxel alone
and progression-free survival in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: The SELECT-1 randomized clinical trial.
JAMA. 317:1844–1853. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sunaga N, Shames DS, Girard L, Peyton M,
Larsen JE, Imai H, Soh J, Sato M, Yanagitani N, Kaira K, et al:
Knockdown of oncogenic KRAS in non-small cell lung cancers
suppresses tumor growth and sensitizes tumor cells to targeted
therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:336–346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sunaga N, Kaira K, Imai H, Shimizu K,
Nakano T, Shames DS, Girard L, Soh J, Sato M, Iwasaki Y, et al:
Oncogenic KRAS-induced epiregulin overexpression contributes to
aggressive phenotype and is a promising therapeutic target in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 32:4034–4042. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sunaga N, Imai H, Shimizu K, Shames DS,
Kakegawa S, Girard L, Sato M, Kaira K, Ishizuka T, Gazdar AF, et
al: Oncogenic KRAS-induced interleukin-8 overexpression promotes
cell growth and migration and contributes to aggressive phenotypes
of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:1733–1744. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heigener DF, Gandara DR and Reck M:
Targeting of MEK in lung cancer therapeutics. Lancet Respir Med.
3:319–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Loesch M and Chen G: The p38 MAPK stress
pathway as a tumor suppressor or more? Front Biosci. 13:3581–3593.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiacchiera F, Grossi V, Cappellari M,
Peserico A, Simonatto M, Germani A, Russo S, Moyer MP, Resta N,
Murzilli S and Simone C: Blocking p38/ERK crosstalk affects
colorectal cancer growth by inducing apoptosis in vitro and in
preclinical mouse models. Cancer Lett. 324:98–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Houdt WJ, de Bruijn MT, Emmink BL,
Raats D, Hoogwater FJ, Borel Rinkes IH and Kranenburg O: Oncogenic
K-ras activates p38 to maintain colorectal cancer cell
proliferation during MEK inhibition. Cell Oncol. 32:245–257.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wright LN, Ryscavage A, Merlino G and
Yuspa SH: Modeling the transcriptional consequences of epidermal
growth factor receptor ablation in Ras-initiated squamous cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:170–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miura Y and Sunaga N: Role of
immunotherapy for oncogene-driven non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 10(pii): E2452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tolcher AW, Khan K, Ong M, Banerji U,
Papadimitrakopoulou V, Gandara DR, Patnaik A, Baird RD, Olmos D,
Garrett CR, et al: Antitumor activity in RAS-driven tumors by
blocking AKT and MEK. Clin Cancer Res. 21:739–748. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tao Z, Le Blanc JM, Wang C, Zhan T, Zhuang
H, Wang P, Yuan Z and Lu B: Coadministration of trametinib and
palbociclib radiosensitizes KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancers
in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 22:122–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park KS, Oh B, Lee MH, Nam KY, Jin HR,
Yang H, Choi J, Kim SW and Lee DH: The HSP90 inhibitor, NVP-AUY922,
sensitizes KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with intrinsic
resistance to MEK inhibitor, trametinib. Cancer Lett. 372:75–81.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Manchado E, Weissmueller S, Morris JP IV,
Chen CC, Wullenkord R, Lujambio A, de Stanchina E, Poirier JT,
Gainor JF, Corcoran RB, et al: A combinatorial strategy for
treating KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Nature. 534:647–651. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kitai H, Ebi H, Tomida S, Floros KV,
Kotani H, Adachi Y, Oizumi S, Nishimura M, Faber AC and Yano S:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition defines feedback activation of
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling induced by MEK inhibition in
KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 6:754–769. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|