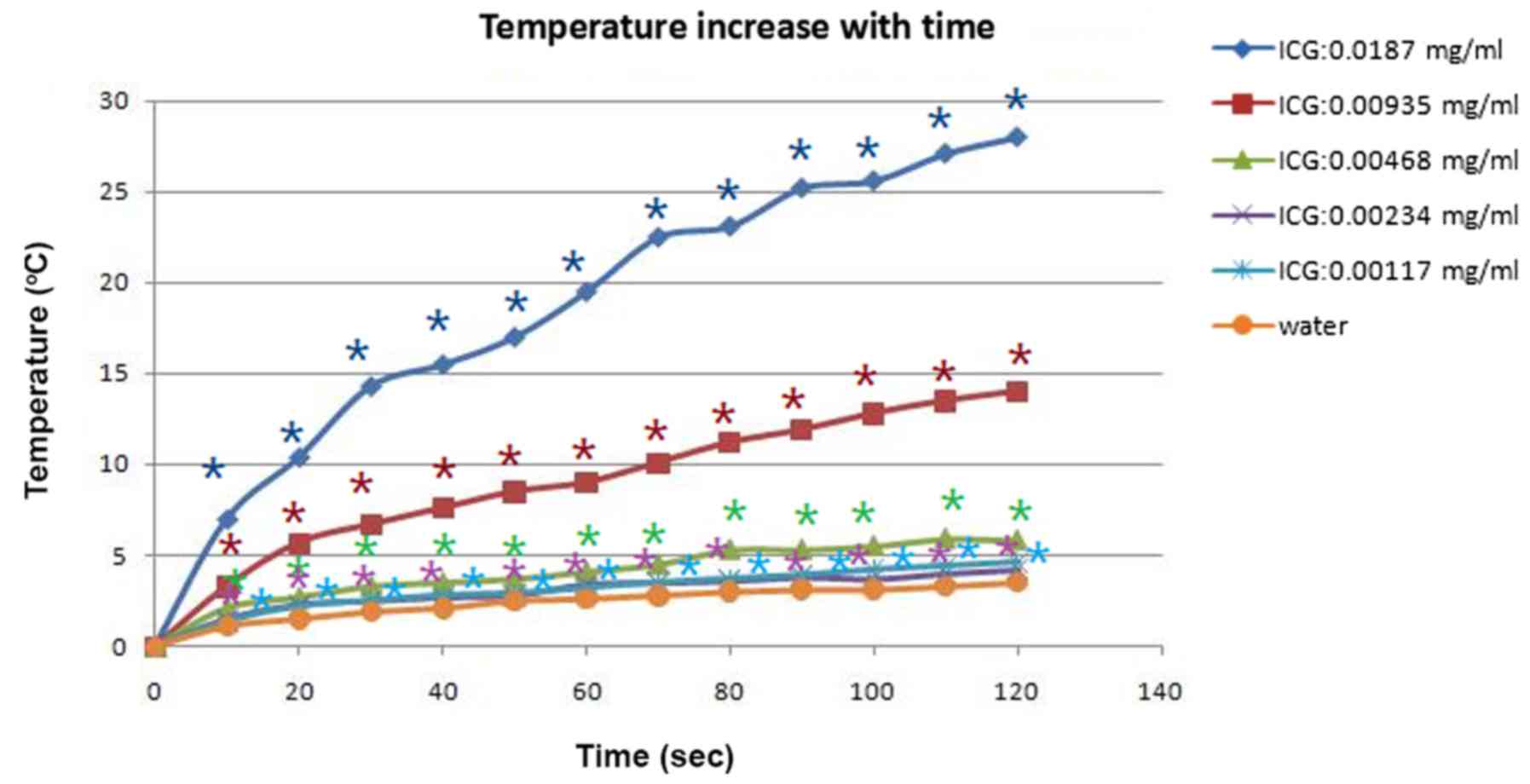
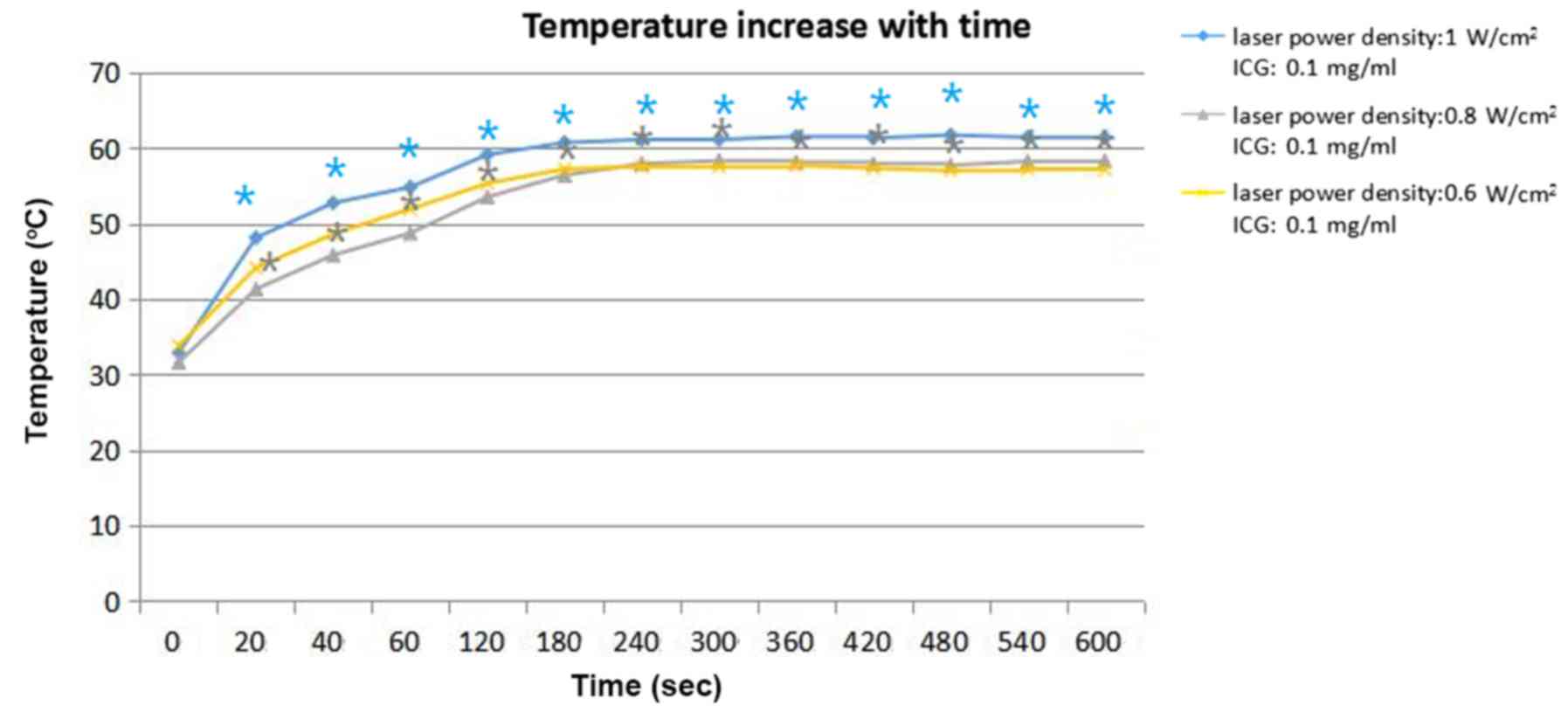
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu F: Heat-based tumor ablation: Role of
the immune response. Adv Exp Med Biol. 880:131–153. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li X, Le H, Wolf RF, Chen VA, Sarkar A,
Nordquist RE, Ferguson H, Liu H and Chen WR: Long-term effect on
EMT6 tumors in mice induced by combination of laser immunotherapy
and surgery. Integr Cancer Ther. 10:368–373. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen WR, Adams RL, Carubelli R and
Nordquist RE: Laser-photosensitizer assisted immunotherapy: A novel
modality for cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 115:25–30. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Le K, Li X, Figueroa D, Towner RA,
Garteiser P, Saunders D, Smith N, Liu H, Hode T, Nordquist RE and
Chen WR: Assessment of thermal effects of interstitial laser
phototherapy on mammary tumors using proton resonance frequency
method. J Biomed Opt. 16:1280012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li X, Ferrel GL, Guerra MC, Hode T, Lunn
JA, Adalsteinsson O, Nordquist RE, Liu H and Chen WR: Preliminary
safety and efficacy results of laser immunotherapy for the
treatment of metastatic breast cancer patients. Photochem Photobiol
Sci. 10:817–821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bailey CA, Cowan TM, Liu VG, Lemley EC and
Chen WR: Optimization of selective hyperthermia. J Biomed Opt.
9:648–654. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Slovak R, Ludwig JM, Gettinger SN, Herbst
RS and Kim HS: Immuno-thermal ablations-boosting the anticancer
immune response. J Immunother Cancer. 5:782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vankayala R, Huang YK, Kalluru P, Chiang
CS and Hwang KC: First demonstration of gold nanorods-mediated
photodynamic therapeutic destruction of tumors via near infra-red
light activation. Small. 10:1612–1622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vankayala R, Lin CC, Kalluru P, Chiang CS
and Hwang KC: Gold nanoshells-mediated bimodal photodynamic and
photothermal cancer treatment using ultra-low doses of near
infra-red light. Biomaterials. 35:5527–5538. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hou X, Tao Y, Pang Y, Li X, Jiang G and
Liu Y: Nanoparticle-based photothermal and photodynamic
immunotherapy for tumor treatment. Int J Cancer. 143:3050–3060.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Crochet JJ, Gnyawali SC, Chen Y, Lemley
EC, Wang LV and Chen WR: Temperature distribution in selective
laser-tissue interaction. J Biomed Opt. 11:340312006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Naylor MF, Le H, Nordquist RE,
Teague TK, Howard CA, Murray C and Chen WR: Clinical effects of in
situ photoimmunotherapy on late-stage melanoma patients: A
preliminary study. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:1081–1087. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou F, Li X, Naylor MF, Hode T, Nordquist
RE, Alleruzzo L, Raker J, Lam SS, Du N, Shi L, et al: InCVAX-a
novel strategy for treatment of late-stage, metastatic cancers
through photoimmunotherapy induced tumor-specific immunity. Cancer
Lett. 359:169–177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taylor JS, Zeki J, Ikegaki N, Chen LL and
Chiu B: Combined application of Indocyanine green (ICG) and laser
lead to targeted tumor cell destruction. J Pediatr Surg.
53:2475–2479. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sandberg K and Umans JG; Georgetown
Consensus Conference Work Group, : Recommendations concerning the
new U.S. National Institutes of Health initiative to balance the
sex of cells and animals in preclinical research. FASEB J.
29:1646–1652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hou G, Yao Y and Wang G: Inhibitory effect
of quercetin on ACC-M cell xenografts in nude mice in vivo. J Oral
Sci Res. 34:554–557. 2018.
|
|
18
|
Kourea H and Kotoula V: Towards tumor
immunodiagnostics. Ann Transl Med. 4:2632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang C, Diao S, Wang C, Gong H, Liu T,
Hong G, Shi X and Liu Z: Tumor metastasis inhibition by
imaging-guided photothermal therapy with single-walled carbon
nanotubes. Adv Mater. 26:5646–5652. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang HG, Mehta K, Cohen P and Guha C:
Hyperthermia on immune regulation: A temperature's story. Cancer
Lett. 271:191–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iizuka MN, Vitkin IA, Kolios MC and Sherar
MD: The effects of dynamic optical properties during interstitial
laser photocoagulation. Phys Med Biol. 45:1335–1357. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fox IJ, Brooker LG, Heseltine DW, Essex HE
and Wood EH: A tricarbocyanine dye for continuous recording of
dilution curves in whole blood independent of variations in blood
oxygen saturation. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 32:478–484.
1957.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giraudeau C, Moussaron A, Stallivieri A,
Mordon S and Frochot C: Indocyanine green: Photosensitizer or
chromophore? Still a debate. Curr Med Chem. 21:1871–1897. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Min M, Du N, Gu Y, Hode T, Naylor M,
Chen D, Nordquist RE and Chen WR: Chitin, chitosan, and glycated
chitosan regulate immune responses: The novel adjuvants for cancer
vaccine. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:3870232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Porcu EP, Salis A, Gavini E, Rassu G,
Maestri M and Giunchedi P: Indocyanine green delivery systems for
tumour detection and treatments. Biothchnol Adv. 34:768–789. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kannadorai RK and Liu Q: Optimization in
interstitial plasmonic photothermal therapy for treatment planning.
Med Phys. 40:1033012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang LV, Nordquist RE and Chen WR: Optimal
beam size for light delivery to absorption-enhanced tumors buried
in biological tissues and effect of multiple-beam delivery: A Monte
Carlo study. Appl Opt. 36:8286–8291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Xu L, Liang C, Xiang J, Peng R and
Liu Z: Immunological responses triggered by photothermal therapy
with carbon nanotubes in combination with anti-CTLA-4 therapy to
inhibit cancer metastasis. Adv Mater. 26:8154–8162. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoon TJ, Kim JY, Kim H, Hong C, Lee H, Lee
CK, Lee KH, Hong S and Park SH: Anti-tumor immunostimulatory effect
of heat-killed tumor cells. Exp Mol Med. 40:130–144. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kleinovink JW, Fransen MF, Löwik CW and
Ossendorp F: Photodynamic-immune checkpoint therapy eradicates
local and distant tumors by CD8+ T cells. Cancer Immunol
Res. 5:832–838. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X and Chen WR: Laser immunotherapy:
Novel modality to treat cancer through specific antitumor immune
response. Chin J Lasers. 37:2698–2702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dillon C, Roemer R and Payne A: Magnetic
resonance temperature imaging-based quantification of blood
flow-related energy losses. NMR Biomed. 28:840–851. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ganguly M, Miller S and Mitra K: Model
development and experimental validation for analyzing initial
transients of irradiation of tissues during thermal therapy using
short pulse lasers. Lasers Surg Med. 47:711–722. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee SS, Roche PJ, Giannopoulos PN,
Mitmaker EJ, Tamilia M, Paliouras M and Trifiro MA:
Prostate-specific membrane antigen-directed nanoparticle targeting
for extreme nearfield ablation of prostate cancer cells. Tumour
Biol. 39:10104283176959432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gnyawali SC, Chen Y, Wu F, Bartels KE,
Wicksted JP, Liu H, Sen CK and Chen WR: Temperature measurement on
tissue surface during laser irradiation. Med Biol Eng Comput.
46:159–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen Q, Xu L, Liang C, Wang C, Peng R and
Liu Z: Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles
together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer
immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 7:131932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Demaria S, Coleman CN and Formenti SC:
Radiotherapy: Changing the game in immunotherapy. Trends Cancer.
2:286–294. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|