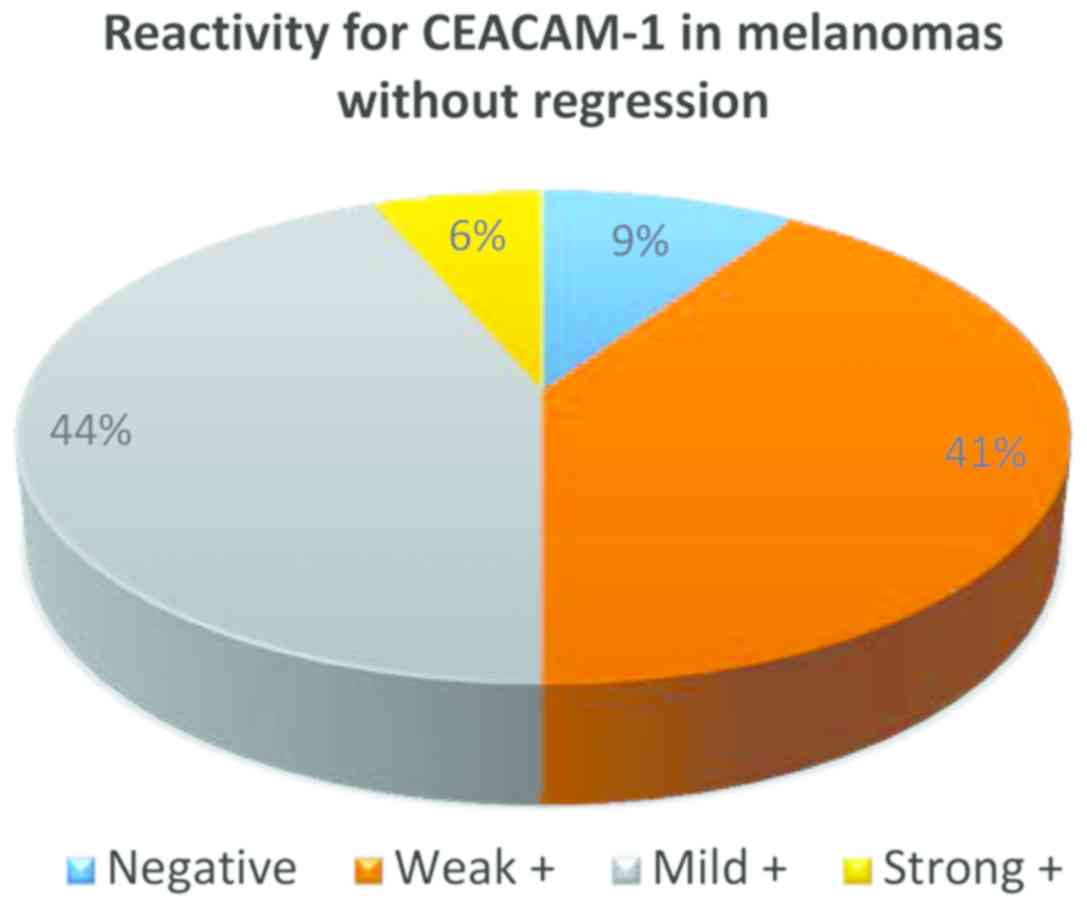
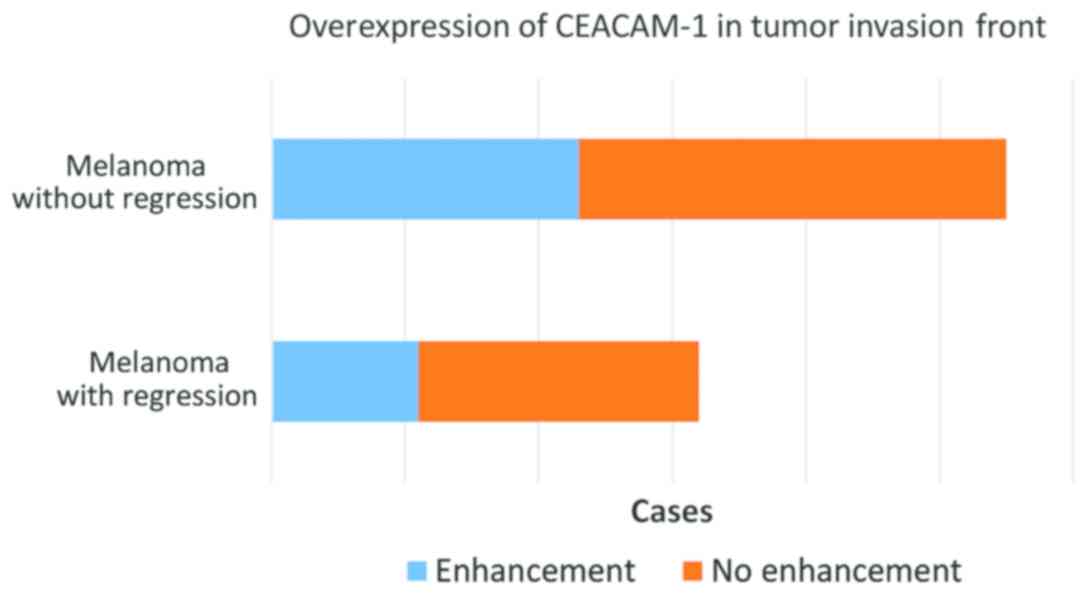
|
1
|
Fiori V, Magnani M and Cianfriglia M: The
expression and modulation of CEACAM1 and tumor cell transformation.
Ann Ist Super Sanita. 48:161–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beauchemin N, Draber P, Dveksler G, Gold
P, Gray-Owen S, Grunert F, Hammarström S, Holmes KV, Karlsson A,
Kuroki M, et al: Redefined nomenclature for members of the
carcinoembryonic antigen family. Exp Cell Res. 252:243–249. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dankner M, Gray-Owen SD, Huang YH,
Blumberg RS and Beauchemin N: CEACAM1 as a multi-purpose target for
cancer immunotherapy. OncoImmunology. 6:e13283362017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neagu M: The immune system - a hidden
treasure for biomarker discovery in cutaneous melanoma. Adv Clin
Chem. 58:89–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sapoznik S, Ortenberg R, Schachter J and
Markel G: CEACAM1 in malignant melanoma: A diagnostic and
therapeutic target. Curr Top Med Chem. 12:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sivan S, Suzan F, Rona O, Tamar H, Vivian
B, Tamar P, Jacob S, Gal M and Michal L: Serum CEACAM1 correlates
with disease progression and survival in malignant melanoma
patients. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012:2905362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thies A, Berlin A, Brunner G, Schulze HJ,
Moll I, Pfüller U, Wagener C, Schachner M, Altevogt P and
Schumacher U: Glycoconjugate profiling of primary melanoma and its
sentinel node and distant metastases: Implications for diagnosis
and pathophysiology of metastases. Cancer Lett. 248:68–80. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khatib N, Pe'er J, Ortenberg R, Schachter
J, Frenkel S, Markel G and Amer R: Carcinoembryonic antigen cell
adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM1) in posterior uveal melanoma:
Correlation with clinical and histological survival markers. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:9368–9372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nittka S, Günther J, Ebisch C,
Erbersdobler A and Neumaier M: The human tumor suppressor CEACAM1
modulates apoptosis and is implicated in early colorectal
tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 23:9306–9313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turcu G, Nedelcu RI, Ion DA, Brînzea A,
Cioplea MD, Jilaveanu LB and Zurac SA: CEACAM1: Expression and role
in melanocyte transformation. Dis Markers. 2016:94063192016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Markel G, Seidman R, Stern N, Cohen-Sinai
T, Izhaki O, Katz G, Besser M, Treves AJ, Blumberg RS, Loewenthal
R, et al: Inhibition of human tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
effector functions by the homophilic carcinoembryonic cell adhesion
molecule 1 interactions. J Immunol. 177:6062–6071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ortenberg R, Sapoznik S, Zippel D,
Shapira-Frommer R, Itzhaki O, Kubi A, Zikich D, Besser MJ,
Schachter J and Markel G: Serum CEACAM1 elevation correlates with
melanoma progression and failure to respond to adoptive cell
transfer immunotherapy. J Immunol Res. 2015:9021372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kluger HM, Hoyt K, Bacchiocchi A, Mayer T,
Kirsch J, Kluger Y, Sznol M, Ariyan S, Molinaro A and Halaban R:
Plasma markers for identifying patients with metastatic melanoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:2417–2425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ortenberg R, Sapir Y, Raz L, Hershkovitz
L, Ben Arav A, Sapoznik S, Barshack I, Avivi C, Berkun Y, Besser
MJ, et al: Novel immunotherapy for malignant melanoma with a
monoclonal antibody that blocks CEACAM1 homophilic interactions.
Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1300–1310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ebrahimnejad A, Streichert T, Nollau P,
Horst AK, Wagener C, Bamberger AM and Brümmer J: CEACAM1 enhances
invasion and migration of melanocytic and melanoma cells. Am J
Pathol. 165:1781–1787. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gambichler T, Grothe S, Rotterdam S,
Altmeyer P and Kreuter A: Protein expression of carcinoembryonic
antigen cell adhesion molecules in benign and malignant melanocytic
skin lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 131:782–787. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gimotty PA and Guerry D: Prognostication
in thin cutaneous melanomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 134:1758–1763.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aung PP, Nagarajan P and Prieto VG:
Regression in primary cutaneous melanoma: Etiopathogenesis and
clinical significance. Lab Invest. 97:657–668. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zurac S, Neagu M, Constantin C, Cioplea M,
Nedelcu R, Bastian A, Popp C, Nichita L, Andrei R, Tebeica T, et
al: Variations in the expression of TIMP1, TIMP2 and TIMP3 in
cutaneous melanoma with regression and their possible function as
prognostic predictors. Oncol Lett. 11:3354–3360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zurac S, Negroiu G, Petrescu S, Andrei R,
Tebeica T, Popp C, Musţată R, Neagu M, Constantin C, Solovan C, et
al: Spectrum of morphologic alterations of regression in cutaneous
melanoma - potential for improving disease prognosis. Rom J Intern
Med. 50:145–153. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nedelcu RI, Zurac SA, Brînzea A, Cioplea
MD, Turcu G, Popescu R, Popescu CM and Ion DA: Morphological
features of melanocytic tumors with depigmented halo: Review of the
literature and personal results. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 56 (Suppl
2):659–663. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saleh FH, Crotty KA, Hersey P and Menzies
SW: Primary melanoma tumour regression associated with an immune
response to the tumour-associated antigen melan-A/MART-1. Int J
Cancer. 94:551–557. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lupu M, Caruntu A, Caruntu C, Papagheorghe
LM, Ilie MA, Voiculescu V, Boda D, Constantin C, Tanase C, Sifaki
M, et al: Neuroendocrine factors: The missing link in non-melanoma
skin cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 38:1327–1340. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shashanka R and Smitha BR: Head and neck
melanoma. ISRN Surg. 2012:9483022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rubinstein JC, Han G, Jackson L, Bulloch
K, Ariyan S, Narayan D, Rothberg BG and Han D: Regression in thin
melanoma is associated with nodal recurrence after a negative
sentinel node biopsy. Cancer Med. 5:2832–2840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Diaconeasa A, Boda D, Solovan C, Enescu
DM, Vîlcea AM and Zurac S: Histopathologic features of Spitzoid
lesions in different age groups. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 54:51–62.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Blendea A, Georgescu CV, Ţolea I,
Brănişteanu DE and Costache A: An unusual cutaneous malignant
melanoma arised de novo: A case report. Rom J Morphol Embryol.
56:1217–1221. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ortenberg R, Galore-Haskel G, Greenberg I,
Zamlin B, Sapoznik S, Greenberg E, Barshack I, Avivi C, Feiler Y,
Zan-Bar I, et al: CEACAM1 promotes melanoma cell growth through
Sox-2. Neoplasia. 16:451–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ludewig P, Flachsbarth K, Wegscheid C,
Tiegs G, Richard G, Wagener C, Bartsch U and Horst AK: CEACAM1
confers resistance toward oxygen-induced vessel damage in a mouse
model of retinopathy of prematurity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
55:7950–7960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Horst AK, Ito WD, Dabelstein J, Schumacher
U, Sander H, Turbide C, Brümmer J, Meinertz T, Beauchemin N and
Wagener C: Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule
1 modulates vascular remodeling in vitro and in vivo. J Clin
Invest. 116:1596–1605. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bulman A, Neagu M and Constantin C:
Immunomics in skin cancer - improvement in diagnosis, prognosis and
therapy monitoring. Curr Proteomics. 10:202–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boda D: Cellomics as integrative omics for
cancer. Curr Proteomics. 10:237–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Thies A, Moll I, Berger J, Wagener C,
Brümmer J, Schulze HJ, Brunner G and Schumacher U: CEACAM1
expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma predicts the development
of metastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 20:2530–2536. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Caruntu C, Boda D, Constantin C, Caruntu A
and Neagu M: Catecholamines increase in vitro proliferation of
murine B16F10 melanoma cells. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 10:545–558.
2014.
|
|
35
|
Markel G, Seidman R, Cohen Y, Besser MJ,
Sinai TC, Treves AJ, Orenstein A, Berger R and Schachter J: Dynamic
expression of protective CEACAM1 on melanoma cells during specific
immune attack. Immunology. 126:186–200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Markel G, Ortenberg R, Seidman R, Sapoznik
S, Koren-Morag N, Besser MJ, Bar J, Shapira R, Kubi A, Nardini G,
et al: Systemic dysregulation of CEACAM1 in melanoma patients.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 59:215–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Neagu M, Constantin C and Tanase C:
Immune-related biomarkers for diagnosis/prognosis and therapy
monitoring of cutaneous melanoma. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 10:897–919.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Neagu M, Caruntu C, Constantin C, Boda D,
Zurac S, Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis AM: Chemically induced skin
carcinogenesis: Updates in experimental models (Review). Oncol Rep.
35:2516–2528. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|