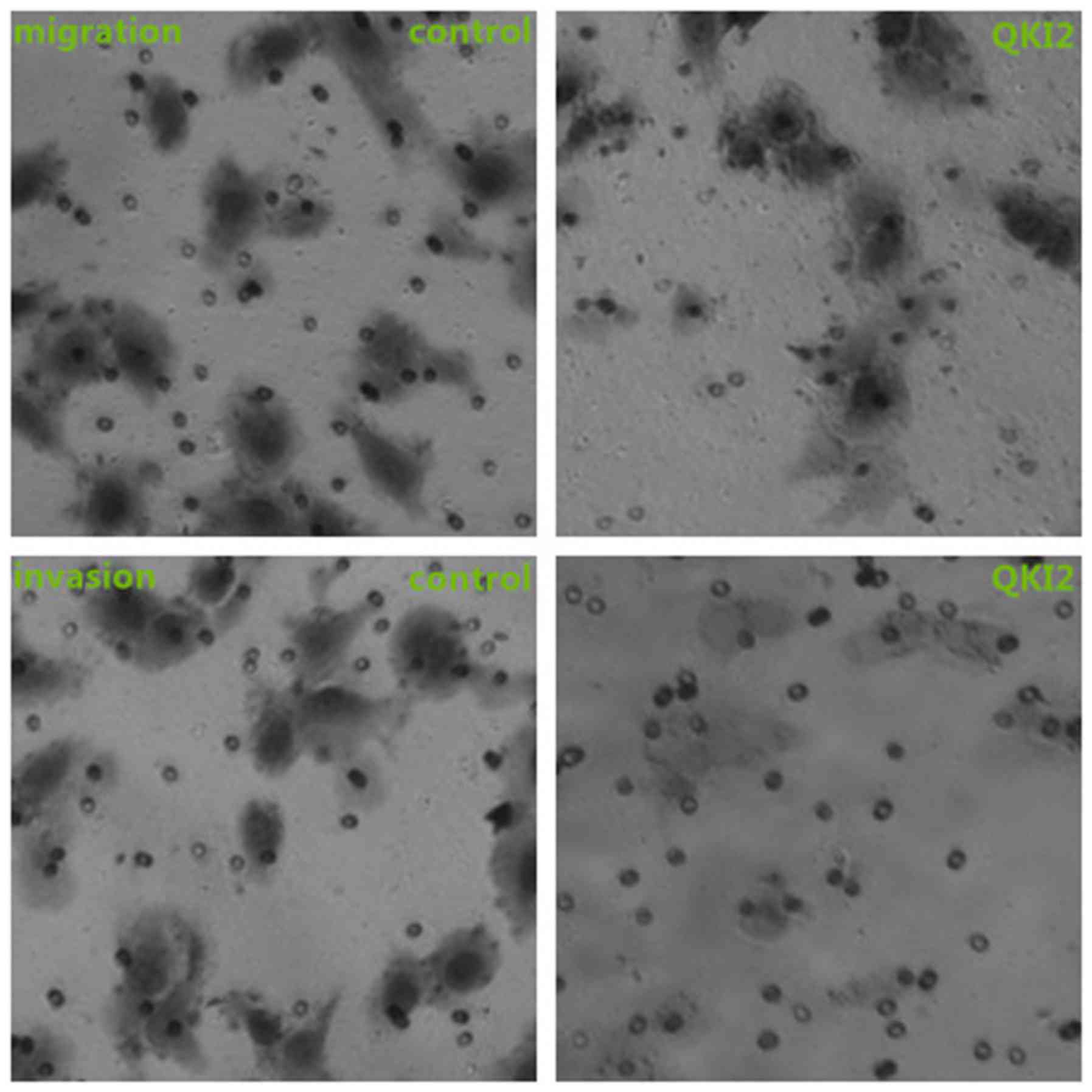
|
1
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Friebele JC, Peck J, Pan X, Abdel-Rasoul M
and Mayerson JL: Osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis and review of the
literature. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 44:547–553.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kondo T, Furuta T, Mitsunaga K, Ebersole
TA, Shichiri M, Wu J, Artzt K, Yamamura K and Abe K: Genomic
organization and expression analysis of the mouse qkI locus. Mamm
Genome. 10:662–669. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galarneau A and Richard S: Target RNA
motif and target mRNAs of the Quaking STAR protein. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 12:691–698. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Lu Z, Ku L, Chen Y, Wang H and
Feng Y: Tyrosine phosphorylation of QKI mediates developmental
signals to regulate mRNA metabolism. EMBO J. 22:1801–1810. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu F, Jin L, Yang G, Ji L, Wang F and Lu
Z: Post-transcriptional repression of FOXO1 by QKI results in low
levels of FOXO1 expression in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
31:1459–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ichimura K, Mungall AJ, Fiegler H, Pearson
DM, Dunham I, Carter NP and Collins VP: Small regions of
overlapping deletions on 6q26 in human astrocytic tumours
identified using chromosome 6 tile path array-CGH. Oncogene.
25:1261–1271. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li ZZ, Kondo T, Murata T, Ebersole TA,
Nishi T, Tada K, Ushio Y, Yamamura K and Abe K: Expression of Hqk
encoding a KH RNA binding protein is altered in human glioma. Jpn J
Cancer Res. 93:167–177. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mulholland PJ, Fiegler H, Mazzanti C,
Gorman P, Sasieni P, Adams J, Jones TA, Babbage JW, Vatcheva R,
Ichimura K, et al: Genomic profiling identifies discrete deletions
associated with translocations in glioblastoma multiforme. Cell
Cycle. 5:783–791. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yin D, Ogawa S, Kawamata N, Tunici P,
Finocchiaro G, Eoli M, Ruckert C, Huynh T, Liu G, Kato M, et al:
High-resolution genomic copy number profiling of glioblastoma
multiforme by single nucleotide polymorphism DNA microarray. Mol
Cancer Res. 7:665–677. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu X and Feng Y: QKI-5 suppresses cyclin
D1 expression and proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells via MAPK signalling pathway. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
44:562–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bian Y, Wang L, Lu H, Yang G, Zhang Z, Fu
H, Lu X, Wei M, Sun J, Zhao Q, et al: Downregulation of tumor
suppressor QKI in gastric cancer and its implication in cancer
prognosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 422:187–193. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang G, Fu H, Zhang J, Lu X, Yu F, Jin L,
Bai L, Huang B, Shen L, Feng Y, et al: RNA-binding protein quaking,
a critical regulator of colon epithelial differentiation and a
suppressor of colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 138:231–240.e1-5.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen AJ, Paik JH, Zhang H, Shukla SA,
Mortensen R, Hu J, Ying H, Hu B, Hurt J, Farny N, et al: STAR
RNA-binding protein Quaking suppresses cancer via stabilization of
specific miRNA. Genes Dev. 26:1459–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mendell JT: miRiad roles for the miR-17-92
cluster in development and disease. Cell. 133:217–222. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jafarzadeh-Samani Z, Sohrabi S,
Shirmohammadi K, Effatpanah H, Yadegarazari R and Saidijam M:
Evaluation of miR-22 and miR-20a as diagnostic biomarkers for
gastric cancer. Chin Clin Oncol. 6:162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Mao F, Shen T, Luo Q, Ding Z,
Qian L and Huang J: Plasma miR-145, miR-20a, miR-21 and miR-223 as
novel biomarkers for screening early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:669–676. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Babu KR and Muckenthaler MU: miR-20a
regulates expression of the iron exporter ferroportin in lung
cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:347–359. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng J, Thakur A, Zhang S, Dong Y, Wang X,
Yuan R, Zhang K and Guo X: Expressions of miR-181a and miR-20a in
RPMI8226 cell line and their potential as biomarkers for multiple
myeloma. Tumour Biol. 36:8545–8552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sokolova V, Fiorino A, Zoni E, Crippa E,
Reid JF, Gariboldi M and Pierotti MA: The effects of miR-20a on
p21: Two mechanisms blocking growth arrest in TGF-β-responsive
colon carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 230:3105–3114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pesta M, Klecka J, Kulda V, Topolcan O,
Hora M, Eret V, Ludvikova M, Babjuk M, Novak K, Stolz J and Holubec
L: Importance of miR-20a expression in prostate cancer tissue.
Anticancer Res. 30:3579–3583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang Y, Liu C, Yang J, Liu G, Feng F,
Tang J, Hu L, Li L, Jiang F, Chen C, et al: MiR-20a triggers
metastasis of gallbladder carcinoma. J Hepatol. 59:518–527. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Barøy T,
Østensen IH, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, Serra M, Bürger H,
Cleton-Jansen AM and Myklebost O: Modulation of the osteosarcoma
expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 7:e480862012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arabi L, Gsponer JR, Smida J, Nathrath M,
Perrina V, Jundt G, Ruiz C, Quagliata L and Baumhoer D:
Upregulation of the miR-17-92 cluster and its two paraloga in
osteosarcoma - reasons and consequences. Genes Cancer. 5:56–63.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu PK, Chen WM, Chen CF, Lee OK, Haung CK
and Chen TH: Primary osteogenic sarcoma with pulmonary metastasis:
Clinical results and prognostic factors in 91 patients. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 39:514–522. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Costa FF: Non-coding RNAs, epigenetics and
complexity. Gene. 410:9–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun J, Liu HP, Deng JE and Zhou M:
Systematic analysis of genomic organization and heterogeneities of
miRNA cluster in vertebrates. Mol Biol Rep. 39:5143–5149. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang QH, Zhou M, Sun J, Ning SW, Li Y,
Chen L, Zheng Y and Li X, Lv SL and Li X: Systematic analysis of
human microRNA divergence based on evolutionary emergence. FEBS
Lett. 585:240–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou M, Wang Q, Sun J, Li X, Xu L, Yang H,
Shi H, Ning S, Chen L, Li Y, et al: In silico detection and
characteristics of novel microRNA genes in the Equus
caballus genome using an integrated ab initio and comparative
genomic approach. Genomics. 94:125–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer.
94:776–780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Passetti F, Ferreira CG and Costa FF: The
impact of microRNAs and alternative splicing in pharmacogenomics.
Pharmacogenomics J. 9:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Z, Wang B, Shi Y, Xu C, Xiao HL, Ma
LN, Xu SL, Yang L, Wang QL, Dang WQ, et al: Oncogenic miR-20a and
miR-106a enhance the invasiveness of human glioma stem cells by
directly targeting TIMP-2. Oncogene. 34:1407–1419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang RL, Yang JP, Peng LX, Zheng LS, Xie
P, Wang MY, Cao Y, Zhang ZL, Zhou FJ, Qian CN and Bao YX:
RNA-binding protein QKI-5 inhibits the proliferation of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma via post-transcriptional stabilization of
RASA1 mRNA. Cell Cycle. 15:3094–3104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
de Miguel FJ, Pajares MJ, Martínez-Terroba
E, Ajona D, Morales X, Sharma RD, Pardo FJ, Rouzaut A, Rubio A,
Montuenga LM and Pio R: A large-scale analysis of alternative
splicing reveals a key role of QKI in lung cancer. Mol Oncol.
10:1437–1449. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|