|
1
|
Li L, Wu J, Pu D, Zhao Y, Wan C, Sun L,
Shen C, Sun W, Yuan Z, Shen Q, et al: Factors associated with the
age of natural menopause and menopausal symptoms in Chinese women.
Maturitas. 73:354–360. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murali R, Soslow RA and Weigelt B:
Classification of endometrial carcinoma: More than two types.
Lancet Oncol. 15:e268–e278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fung-Kee-Fung M, Dodge J, Elit L, Lukka H,
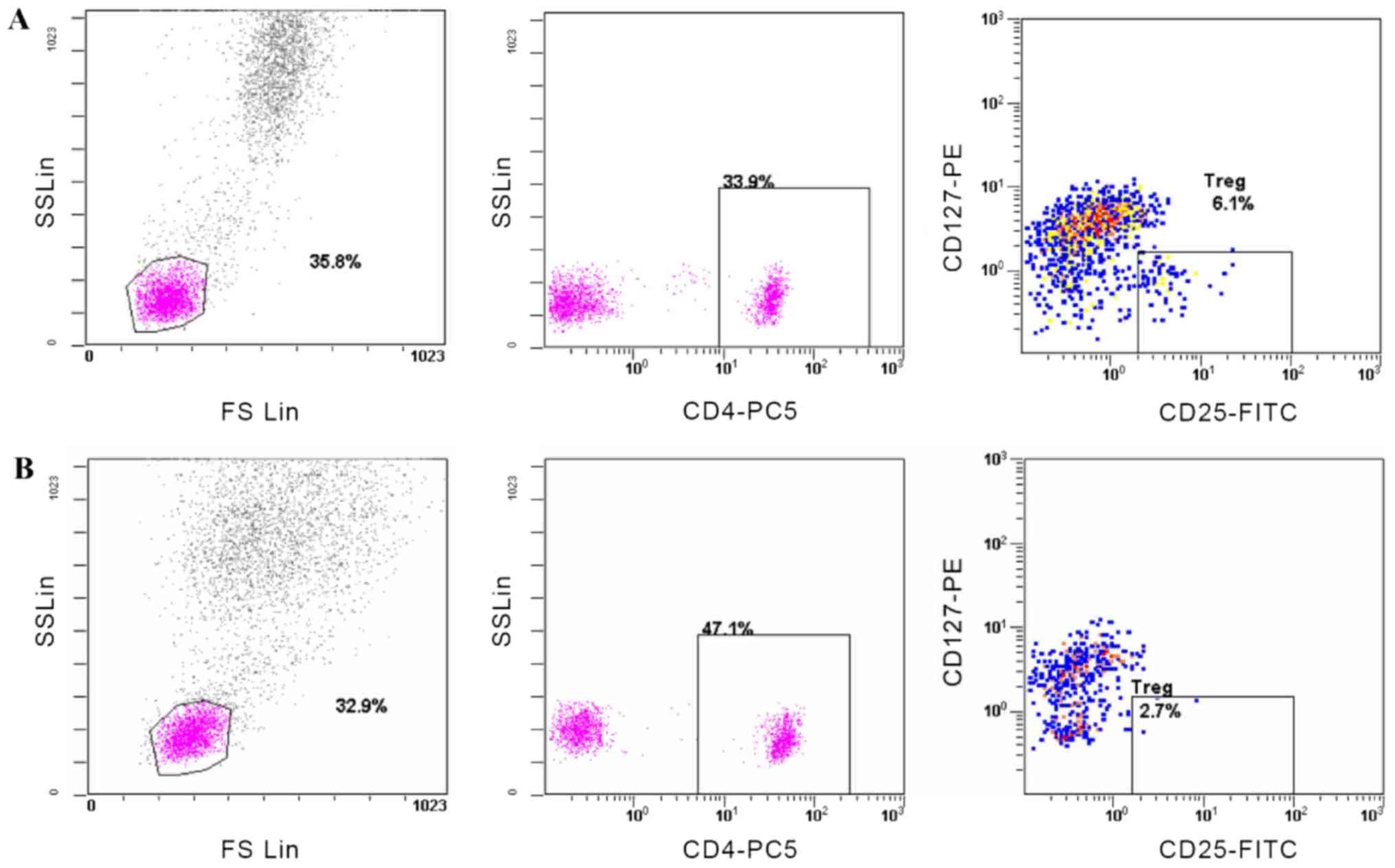
Chambers A and Oliver T; Cancer Care Ontario Program in
Evidence-based Care Gynecology Cancer Disease Site, : Follow-up
after primary therapy for endometrial cancer: A systematic review.
Gynecol Oncol. 101:520–529. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lajer H, Elnegaard S, Christensen RD,
Ortoft G, Schledermann DE and Mogensen O: Survival after stage IA
endometrial cancer; can follow-up be altered? A prospective
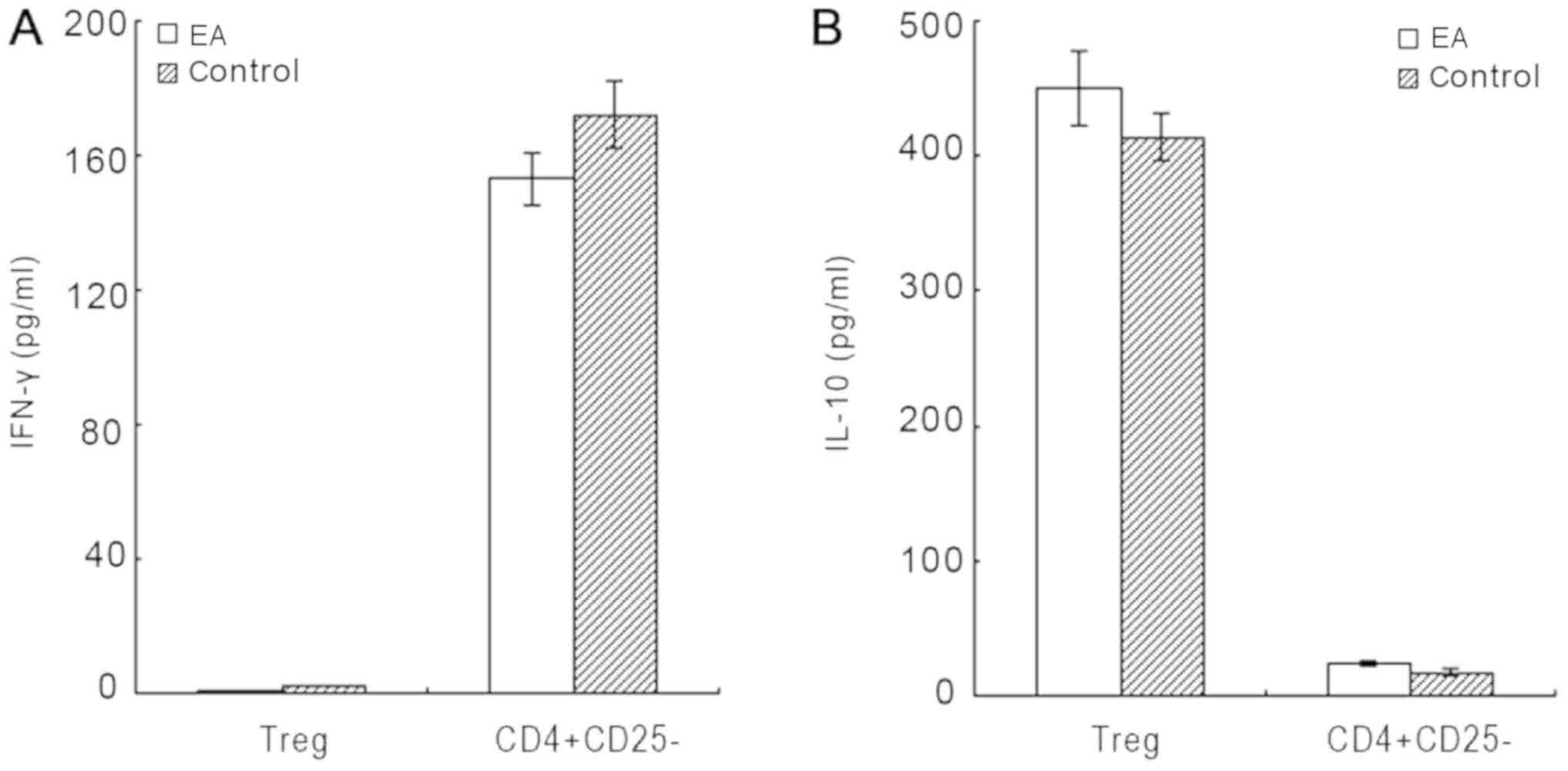
nationwide Danish survey. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 91:976–982.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vanderstraeten A, Tuyaerts S and Amant F:
The immune system in the normal endometrium and implications for
endometrial cancer development. J Reprod Immunol. 109:7–16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM and
Hafler DA: FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system.
Nat Rev Immunol. 10:490–500. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wing K and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T cells
exert checks and balances on selftolerance and autoimmunity. Nat
Immunol. 11:7–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shevach EM: Mechanisms of foxp3+ T
regulatory cell-mediated suppression. Immunity. 30:636–645. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beyer M and Schultze JL: Regulatory T
cells in cancer. Blood. 108:804–811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miller AM, Lundberg K, Ozenci V, Banham
AH, Hellstrom M, Egevad L and Pisa P: CD4+CD25high T cells are
enriched in the tumor and peripheral blood of prostate cancer
patients. J Immunol. 177:7398–7405. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perez SA, Karamouzis MV, Skarlos DV,
Ardavanis A, Sotiriadou NN, Iliopoulou EG, Salagianni ML, Orphanos
G, Baxevanis CN, Rigatos G and Papamichail M: CD4+CD25+ Regulatory
T-cell frequency in HER-2/neu (HER)-positive and HER-negative
advanced-stage breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
13:2714–2721. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hanagiri T, Shigematsu Y, Shinohara S,
Takenaka M, Oka S, Chikaishi Y, Nagata Y, Iwata T, Uramoto H, So T
and Tanaka F: Clinical significance of the frequency of regulatory
T cells in regional lymph node lymphocytes as a prognostic factor
for non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 81:475–479. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sellitto A, Galizia G, De Fanis U, Lieto
E, Zamboli A, Orditura M, De Vita F, Giunta R, Lucivero G and
Romano C: Behavior of circulating CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory t
cells in colon cancer patients undergoing surgery. J Clin Immunol.
31:1095–1104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wertel I, Surówka J, Polak G, Barczyński
B, Bednarek W, Jakubowicz-Gil J, Bojarska-Junak A and Kotarski J:
Macrophage-derived chemokine CCL22 and regulatory T cells in
ovarian cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 36:4811–4817. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Turk MJ, Guevara-Patiño JA, Rizzuto GA,
Engelhorn ME Sakaguchi S and Houghton AN: Concomitant tumor
immunity to a poorly immunogenic melanoma is prevented by
regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 200:771–782. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang WC, Li CH, Huang SC, Chang DY, Chou
LY and Sheu BC: Clinical significance of regulatory T cells and
CD8+ effector populations in patients with human endometrial
carcinoma. Cancer. 116:5777–5788. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fattorossi A, Battaglia A, Ferrandina G,
Buzzonetti A, Legge F, Salutari V and Scambia G: Lymphocyte
composition of tumor draining lymph nodes from cervical and
endometrial cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol. 92:106–115. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamagami W, Susumu N, Tanaka H, Hirasawa
A, Banno K, Suzuki N, Tsuda H, Tsukazaki K and Aoki D:
Immunofluorescence-detected infiltration of CD4+FOXP3+ regulatory t
cells is relevant to the prognosis of patients with endometrial
cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:1628–1634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sawan S, Burt DJ, Stern PL, Holland C and
Elkord E: Circulating regulatory T cells in endometrial cancer: A
role for age and menopausal status. Immunol Invest. 40:62–75. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Creasman W: Revised FIGO staging for
carcinoma of the endometrium. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 105:1092009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kong A, Johnson N, Kitchener HC and Lawrie
TA: Adjuvant radiotherapy for stage I endometrial cancer: An
updated cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 104:1625–1634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee
MR, Zhu S, Gottlieb PA, Kapranov P, Gingeras TR, Fazekas de St
Groth B, et al: CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3
and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J Exp Med.
203:1701–1711. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sawan S, Burt DJ, Stern PL, Holland C and
Elkord E: Circulating regulatory T cells in endometrial cancer: A
role for age and menopausal status. Immunol Invest. 40:62–75. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C,
Abu-Rustum N and Darai E: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
387:1094–1108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsaknaridis L, Spencer L, Culbertson N,
Hicks K, LaTocha D, Chou YK, Whitham RH, Bakke A, Jones RE, Offner
H, et al: Functional assay for human CD4+CD25+ Treg cells reveals
an age-dependent loss of suppressive activity. J Neurosci Res.
74:296–308. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Santner-Nanan B, Seddiki N, Zhu E, Quent
V, Kelleher A, Fazekas de St Groth B and Nanan R: Accelerated
age-dependent transition of human regulatory T cells to effector
memory phenotype. Int Immunol. 20:375–383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dejaco C, Duftner C and Schirmer M: Are
regulatory T-cells linked with aging? Exper Gerontol. 41:339–345.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yao X, Ahmadzadeh M, Lu YC, Liewehr DJ,
Dudley ME, Liu F, Schrump DS, Steinberg SM, Rosenberg SA and
Robbins PF: Levels of peripheral CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells
are negatively associated with clinical response to adoptive
immunotherapy of human cancer. Blood. 119:5688–5696. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Arruvito L, Sanz M, Banham AH and Fainboim
L: Expansion of CD4+CD25+ and FOXP3+ regulatory T cells during the
follicular phase of the menstrual cycle: Implications for human
reproduction. J Immunol. 178:2572–2578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
El-Hamarneh T, Hey-Cunningham AJ, Berbic
M, Al-Jefout M, Fraser IS and Black K: Cellular immune environment
in endometrial polyps. Fertil Steril. 100:1364–1372. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murphy KM, Ouyang W, Szabo SJ, Jacobson
NG, Guler ML, Gorham JD, Gubler U and Murphy TL: T helper
differentiation proceeds through Stat1-dependent, Stat4-dependent
and Stat4-independent phases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
238:13–26. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Caretto D, Katzman SD, Villarino AV, Gallo
E and Abbas AK: Cutting edge: The Th1 response inhibits the
generation of peripheral regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 184:30–34.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Asseman C, Mauze S, Leach MW, Coffman RL
and Powrie F: An essential role for interleukin 10 in the function
of regulatory T cells that inhibit intestinal inflammation. J Exp
Med. 190:995–1004. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Belkaid Y, Piccirillo CA, Mendez S,
Shevach EM and Sacks DL: CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control
Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature. 420:502–507.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Loser K, Apelt J, Voskort M, Mohaupt M,
Balkow S, Schwarz T, Grabbe S and Beissert S: IL-10 controls
ultraviolet-induced carcinogenesis in mice. J Immunol. 179:365–371.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Larmonier N, Marron M, Zeng Y, Cantrell J,
Romanoski A, Sepassi M, Thompson S, Chen X, Andreansky S and
Katsanis E: Tumor-derived CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell
suppression of dendritic cell function involves TGF-beta and IL-10.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 56:48–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vieweg J, Su Z, Dahm P and Kusmartsev S:
Reversal of tumor-mediated immunosuppression. Clin Cancer Res.
13:727s–732s. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nishikawa H and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 27:1–7. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|