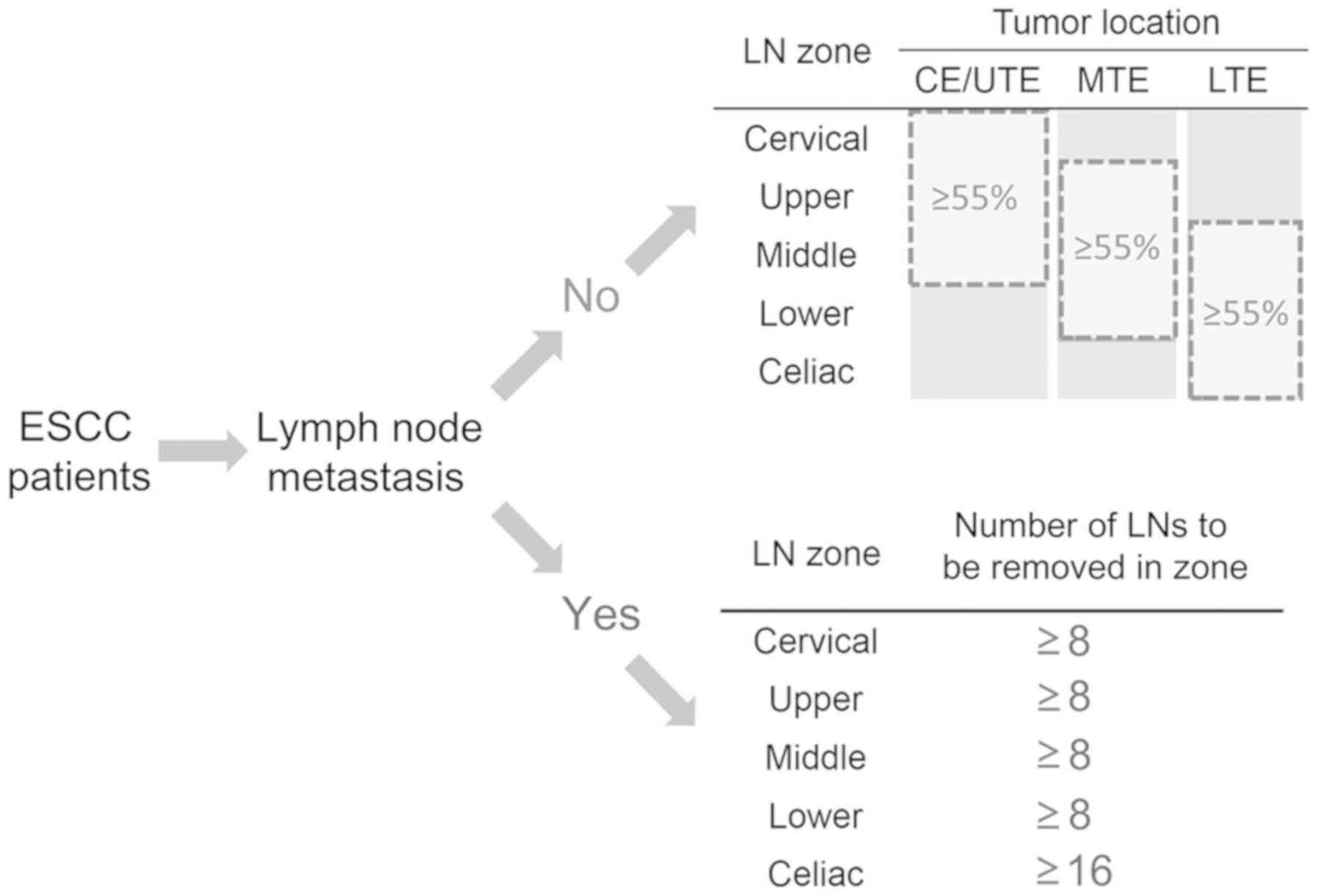
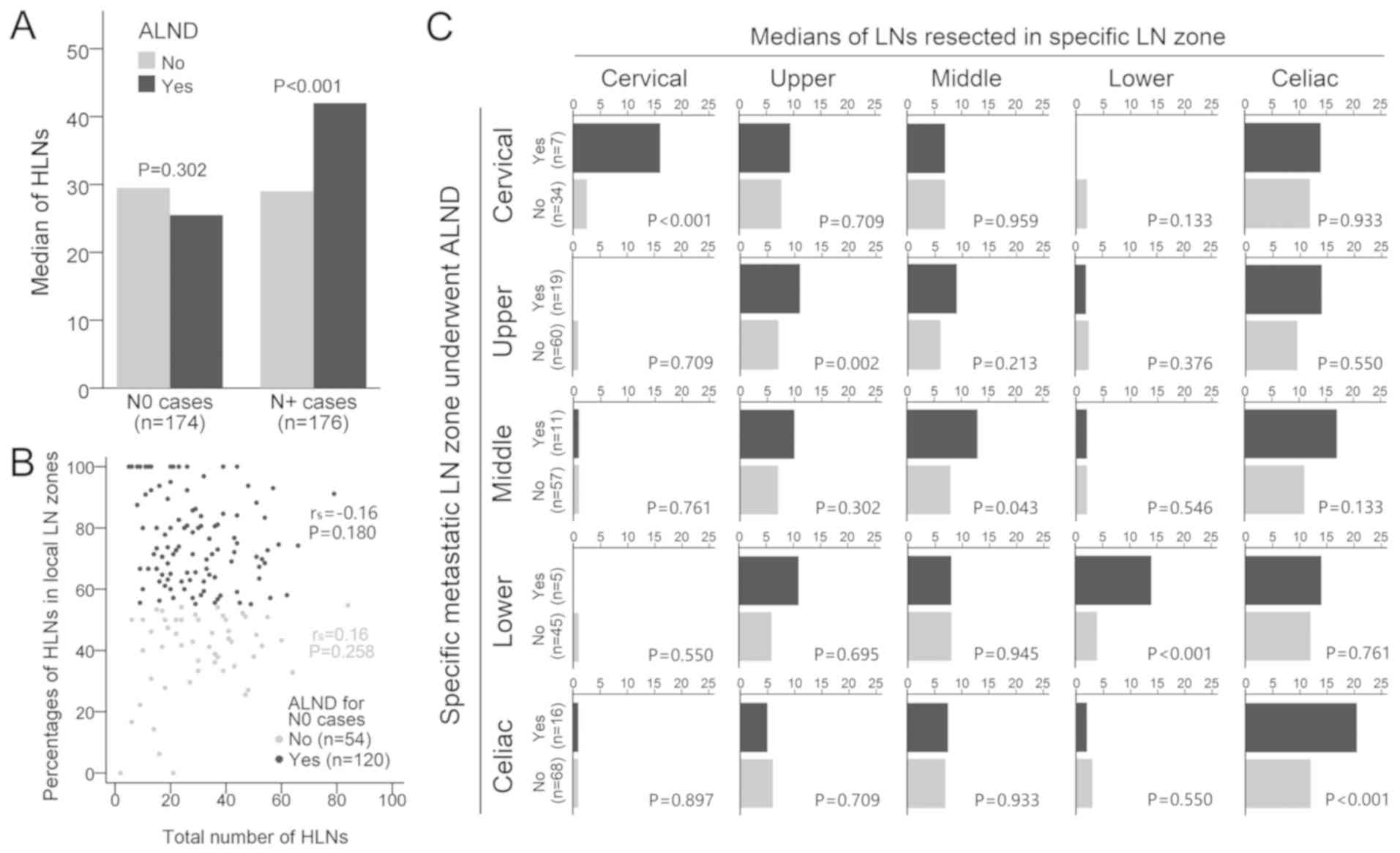
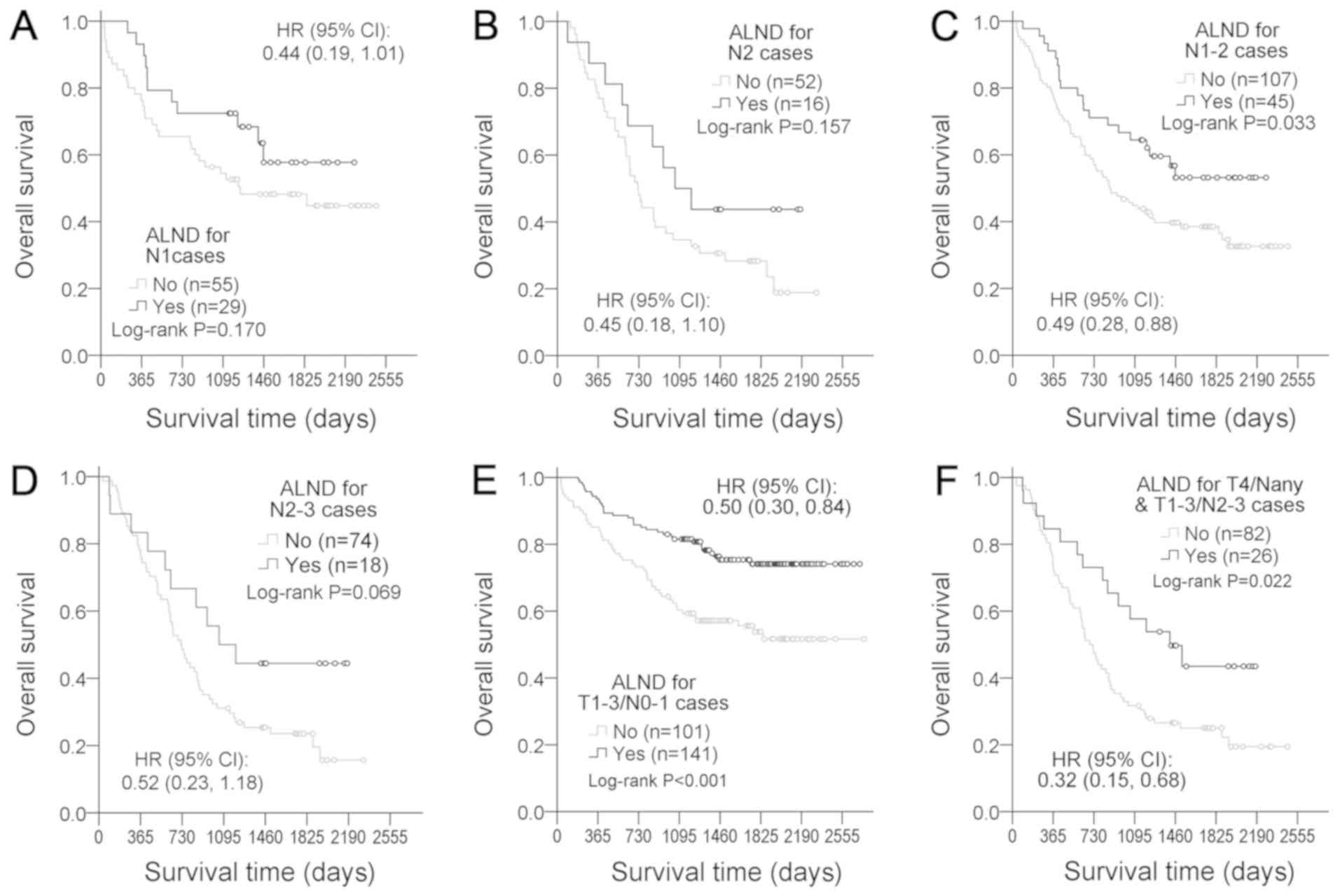
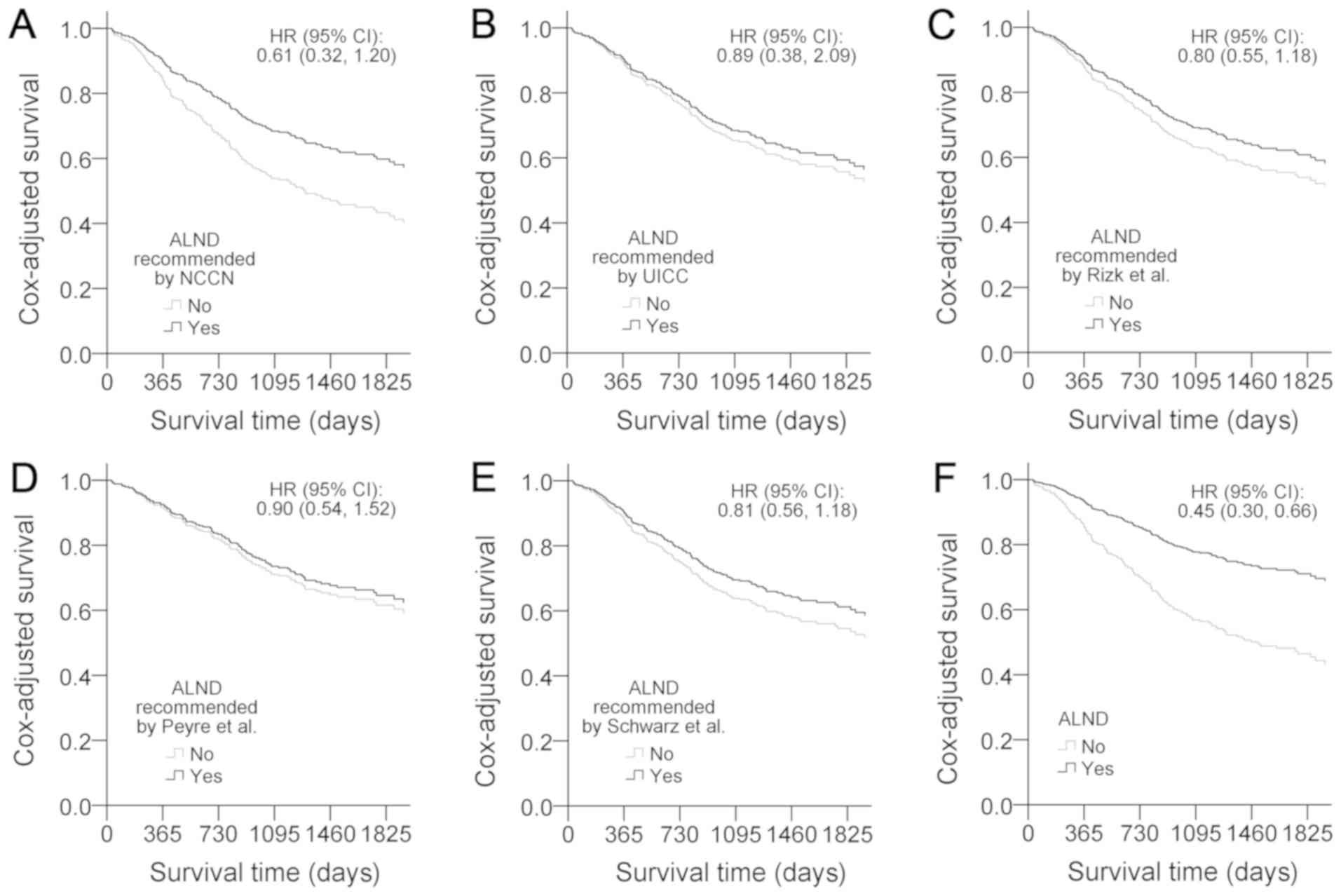
|
1
|
Vashist YK, Loos J, Dedow J, Tachezy M,
Uzunoglu G, Kutup A, Yekebas EF and Izbicki JR: Glasgow prognostic
score is a predictor of perioperative and long-term outcome in
patients with only surgically treated esophageal cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 18:1130–1138. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Sullivan B, Brierley J and International
Union against Cancer: UICC manual of clinical oncology. John Wiley
and Sons Ltd.; Chichester, West Sussex, UK; Hoboken, NJ: 2015,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Edge SB and American Joint Committee on
Cancer, . AJCC cancer staging manual. Springer; New York: 2010
|
|
4
|
Hu Y, Hu C, Zhang H, Ping Y and Chen LQ:
How does the number of resected lymph nodes influence TNM staging
and prognosis for esophageal carcinoma? Ann Surg Oncol. 17:784–790.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peyre CG, Hagen JA, DeMeester SR, Altorki
NK, Ancona E, Griffin SM, Hölscher A, Lerut T, Law S, Rice TW, et
al: The number of lymph nodes removed predicts survival in
esophageal cancer: An international study on the impact of extent
of surgical resection. Ann Surg. 248:549–556. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rizk NP, Ishwaran H, Rice TW, Chen LQ,
Schipper PH, Kesler KA, Law S, Lerut TE, Reed CE, Salo JA, et al:
Optimum lymphadenectomy for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 251:46–50.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Groth SS, Virnig BA, Whitson BA, DeFor TE,
Li ZZ, Tuttle TM and Maddaus MA: Determination of the minimum
number of lymph nodes to examine to maximize survival in patients
with esophageal carcinoma: Data from the surveillance epidemiology
and end results database. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 139:612–620.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen YJ, Schultheiss TE, Wong JY and
Kernstine KH: Impact of the number of resected and involved lymph
nodes on esophageal cancer survival. J Surg Oncol. 100:127–132.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schwarz RE and Smith DD: Clinical impact
of lymphadenectomy extent in resectable esophageal cancer. J
Gastrointest Surg. 11:1384–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rizk N: Surgery for esophageal cancer:
Goals of resection and optimizing outcomes. Thorac Surg Clin.
23:491–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Phillips AW, Lagarde SM, Navidi M, Disep B
and Griffin SM: Impact of extent of lymphadenectomy on survival,
post neoadjuvant chemotherapy and transthoracic esophagectomy. Ann
Surg. 265:750–756. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baba Y, Watanabe M, Shigaki H, Iwagami S,
Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M and Baba H: Negative lymph-node count is
associated with survival in patients with resected esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 153:234–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bogoevski D, Onken F, Koenig A, Kaifi JT,
Schurr P, Sauter G, Izbicki JR and Yekebas EF: Is it time for a new
TNM classification in esophageal carcinoma? Ann Surg. 247:633–641.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin Z, Chen W, Chen Y, Peng X, Zhu K, Lin
Y, Lin Q and Hu Z: A new classification of lymph node metastases
according to the lymph node stations for predicting prognosis in
surgical patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:76261–76273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rice TW, Blackstone EH and Rusch VW: 7th
edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: Esophagus and
esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1721–1724. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Niwa Y, Koike M, Hattori M, Iwata N,
Takami H, Hayashi M, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Kanda M, Yamada S, et
al: The prognostic relevance of subcarinal lymph node dissection in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 23:611–618.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kato H and Nakajima M: Treatments for
esophageal cancer: A review. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
61:330–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsieh FY and Lavori PW: Sample-size
calculations for the Cox proportional hazards regression model with
nonbinary covariates. Control Clin Trials. 21:552–560. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M and Rimm DL:
X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and
outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7252–7259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schoenfeld D: Partial residuals for the
proportional hazards regression model. Biometrika. 69:239–241.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nafteux P, Lerut A, Moons J, Hölscher AH,
Bollschweiler E, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Lagarde SM, van Lanschot
JJ, Messager M, Mariette C, et al: International multicenter study
on the impact of extracapsular lymph node involvement in primary
surgery adenocarcinoma of the esophagus on overall survival and
staging systems. Ann Surg. 262:809–816. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lagergren J, Mattsson F, Zylstra J, Chang
F, Gossage J, Mason R, Lagergren P and Davies A: Extent of
lymphadenectomy and prognosis after esophageal cancer surgery. JAMA
Surg. 151:32–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van der Schaaf M, Johar A, Wijnhoven B,
Lagergren P and Lagergren J: Extent of lymph node removal during
esophageal cancer surgery and survival. J Natl Cancer Inst.
107(pii): djv0432015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Talsma AK, Damhuis RA, Steyerberg EW,
Rosman C, van Lanschot JJ and Wijnhoven BP: Determinants of
improved survival after oesophagectomy for cancer. Br J Surg.
102:668–675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hulscher JB, van Sandick JW, de Boer AG,
Wijnhoven BP, Tijssen JG, Fockens P, Stalmeier PF, ten Kate FJ, van
Dekken H, Obertop H, et al: Extended transthoracic resection
compared with limited transhiatal resection for adenocarcinoma of
the esophagus. N Engl J Med. 347:1662–1669. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chu KM, Law SY, Fok M and Wong J: A
prospective randomized comparison of transhiatal and transthoracic
resection for lower-third esophageal carcinoma. Am J Surg.
174:320–324. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishihira T, Hirayama K and Mori S: A
prospective randomized trial of extended cervical and superior
mediastinal lymphadenectomy for carcinoma of the thoracic
esophagus. Am J Surg. 175:47–51. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu PK, Wang BY, Chou TY, Huang CS, Wu YC
and Hsu WH: The total number of resected lymph node is not a
prognostic factor for recurrence in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma patients undergone transthoracic esophagectomy. J Surg
Oncol. 103:416–420. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chao YK, Liu HP, Hsieh MJ, Wu YC, Liu YH,
Yeh CH, Chang HK and Tseng CK: Impact of the number of lymph nodes
sampled on outcome in ypT0N0 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
patients. J Surg Oncol. 106:436–440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Makino T, Miyazaki
Y, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori M and
Doki Y: Therapeutic value of lymph node dissection for esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Surg
Oncol. 112:60–65. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rizk N, Venkatraman E, Park B, Flores R,
Bains MS and Rusch V; American Joint Committee on Cancer staging
system, : The prognostic importance of the number of involved lymph
nodes in esophageal cancer: Implications for revisions of the
American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 132:1374–1381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Barbour AP, Rizk NP, Gonen M, Tang L,
Bains MS, Rusch VW, Coit DG and Brennan MF: Lymphadenectomy for
adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ): Impact of
adequate staging on outcome. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:306–316. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lerut T, Nafteux P, Moons J, Coosemans W,
Decker G, De Leyn P, Van Raemdonck D and Ectors N: Three-field
lymphadenectomy for carcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal
junction in 174 R0 resections: Impact on staging, disease-free
survival, and outcome: A plea for adaptation of TNM classification
in upper-half esophageal carcinoma. Ann Surg. 240:962–974. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen J, Liu S, Pan J, Zheng X, Zhu K, Zhu
J, Xiao J and Ying M: The pattern and prevalence of lymphatic
spread in thoracic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 36:480–486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tachimori Y, Ozawa S, Numasaki H,
Matsubara H, Shinoda M, Toh Y, Udagawa H, Fujishiro M, Oyama T, Uno
T, et al: Efficacy of lymph node dissection by node zones according
to tumor location for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Esophagus. 13:1–7. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brotons ML, Bolca C, Fréchette E and
Deslauriers J: Anatomy and physiology of the thoracic lymphatic
system. Thorac Surg Clin. 22:139–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Motoyama S, Maruyama K, Sato Y, Usami S,
Nakatsu T, Saito H, Minamiya Y and Ogawa J: Status of involved
lymph nodes and direction of metastatic lymphatic flow between
submucosal and t2-4 thoracic squamous cell esophageal cancers.
World J Surg. 33:512–517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Izbicki JR, Hosch SB, Pichlmeier U,
Rehders A, Busch C, Niendorf A, Passlick B, Broelsch CE and Pantel
K: Prognostic value of immunohistochemically identifiable tumor
cells in lymph nodes of patients with completely resected
esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 337:1188–1194. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Imamura Y, Hayashi N, Sato N, Kinoshita K,
Kurashige J, Saito S, Hirashima K, Karashima R, Hiyoshi Y, Nagai Y,
et al: Extensive lymphatic spread of cancer cells in patients with
thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Detection of CEA-mRNA
in the three-field lymph nodes. J Surg Oncol. 102:509–515. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang LS, Chow KC, Chi KH, Liu CC, Li WY,
Chiu JH and Huang MH: Prognosis of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma: Analysis of clinicopathological and biological factors.
Am J Gastroenterol. 94:1933–1940. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zheng YZ, Zhao W, Hu Y, Ding-Lin XX, Wen
J, Yang H, Liu QW, Luo KJ, Huang QY, Chen JY and Fu JH: Aggressive
surgical resection does not improve survival in operable esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma with N2-3 status. World J Gastroenterol.
21:8644–8652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stein HJ, Feith M, Bruecher BL, Naehrig J,
Sarbia M and Siewert JR: Early esophageal cancer: Pattern of
lymphatic spread and prognostic factors for long-term survival
after surgical resection. Ann Surg. 242:566–575. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Smyth EC, Fassan M, Cunningham D, Allum
WH, Okines AF, Lampis A, Hahne JC, Rugge M, Peckitt C, Nankivell M,
et al: Effect of pathologic tumor response and nodal status on
survival in the medical research council adjuvant gastric
infusional chemotherapy trial. J Clin Oncol. 34:2721–2727. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Su D, Zhou X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Yang X,
Zheng W, Tao K, Wu J, Yan Z, Liu L, et al: Prognostic nomogram for
thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after radical
esophagectomy. PLoS One. 10:e01244372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Haverkamp L, Seesing MF, Ruurda JP, Boone
J and V Hillegersberg R: Worldwide trends in surgical techniques in
the treatment of esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer.
Dis Esophagus. 30:1–7. 2017.
|