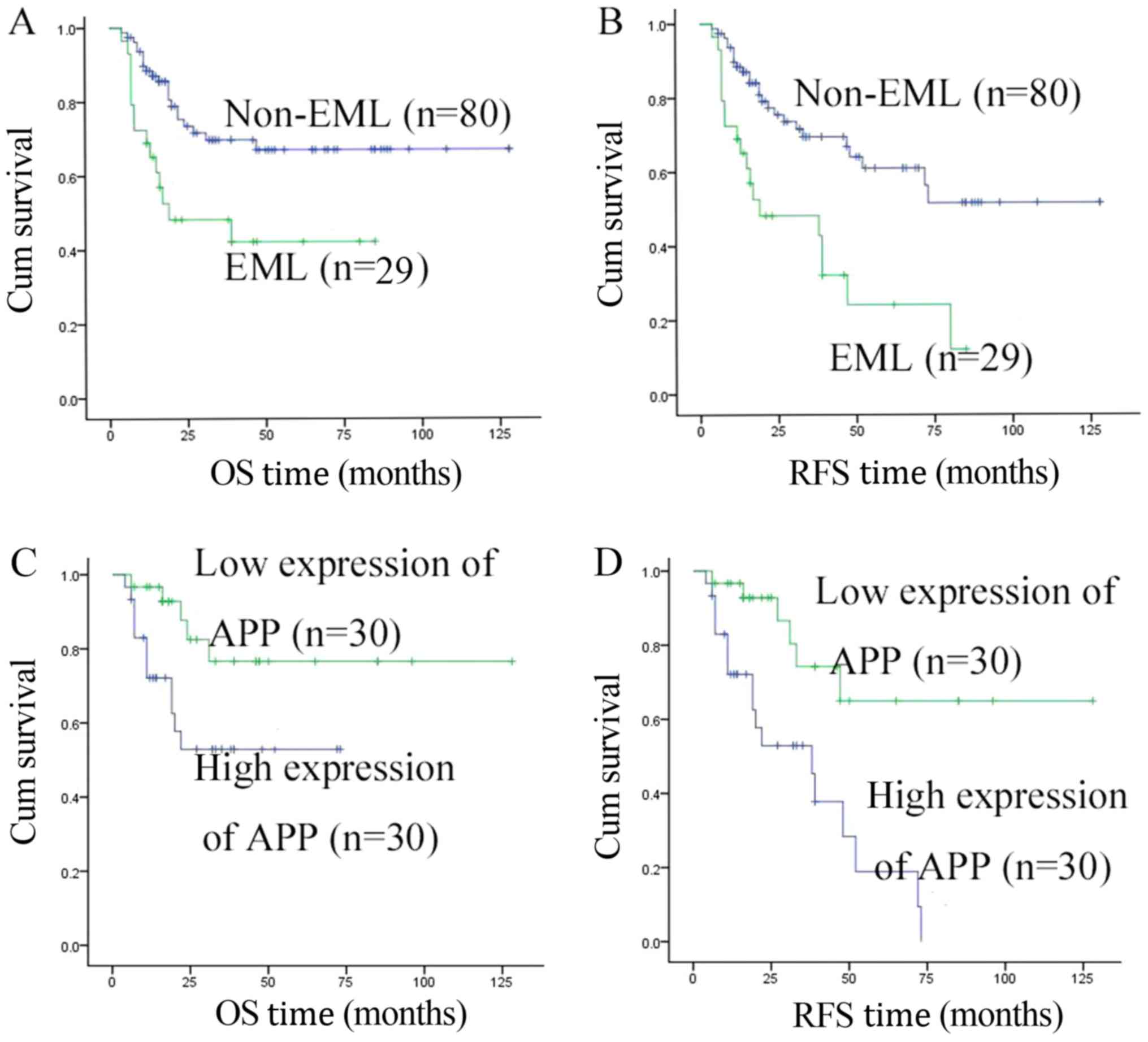
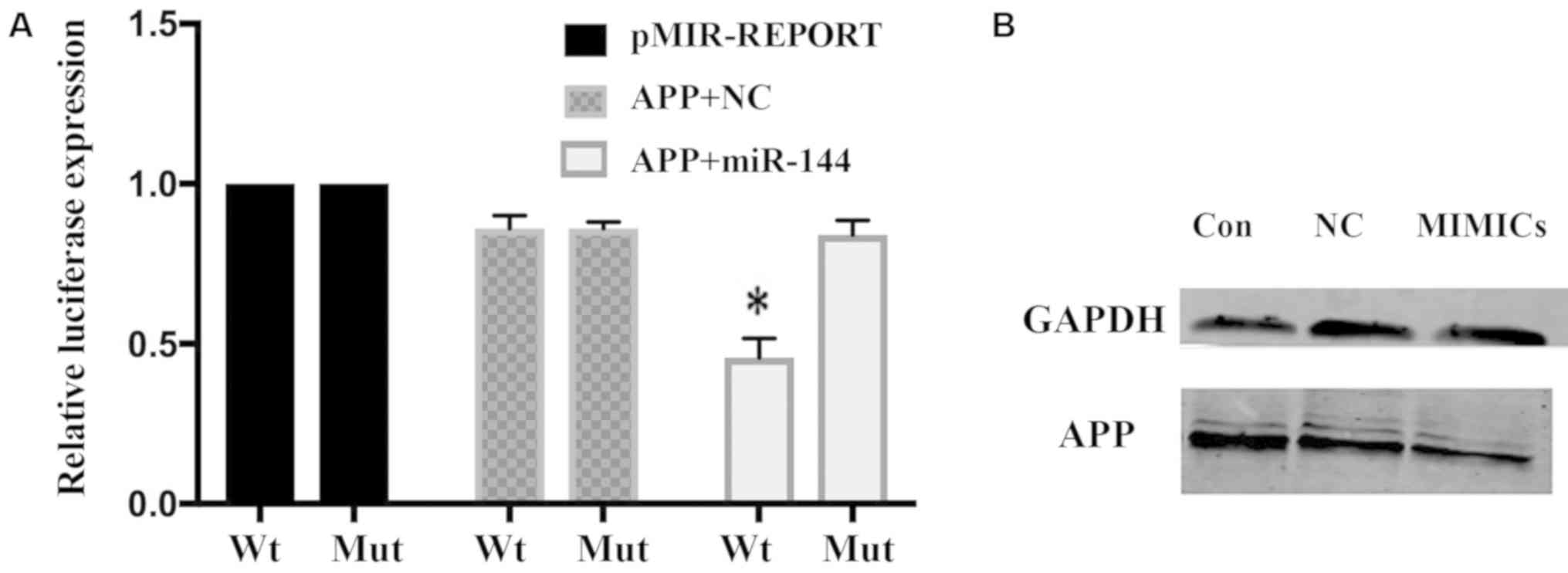
|
1
|
Wang L, Xu J, Tian X, Lv T and Yuan G:
Analysis of efficacy and prognostic factors of CLAG treatment in
chinese patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid
leukemia. Acta Haematol. 141:43–53. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Low M, Lee D, Coutsouvelis J, Patil S,
Opat S, Walker P, Schwarer A, Salem H, Avery S, Spencer A and Wei
A: High-dose cytarabine (24 g/m2) in combination with
idarubicin (HiDAC-3) results in high first-cycle response with
limited gastro- intestinal toxicity in adult acute myeloid
leukaemia. Intern Med J. 43:294–297. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sasine JP and Schiller GJ: Emerging
strategies for high-risk and relapsed/refractory acute myeloid
leukemia: Novel agents and approaches currently in clinical trials.
Blood Rev. 29:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pui CH: Central nervous system disease in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Prophylaxis and treatment. Hematology
Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006:142–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Boissel N, Leroy H, Brethon B, Philippe N,
de Botton S, Auvrignon A, Raffoux E, Leblanc T, Thomas X, Hermine
O, et al: Incidence and prognostic impact of c-Kit, FLT3 and Ras
gene mutations in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia
(CBF-AML). Leukemia. 20:965–970. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prébet T, Boissel N, Reutenauer S, Thomas
X, Delaunay J, Cahn JY, Pigneux A, Quesnel B, Witz F, Thépot S, et
al: Acute myeloid leukemia with translocation (8;21) or inversion
(16) in elderly patients treated with conventional chemotherapy: A
collaborative study of the French CBF-AML intergroup. J Clin Oncol.
27:4747–4753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Byrd JC, Mrózek K, Dodge RK, Carroll AJ,
Edwards CG, Arthur DC, Pettenati MJ, Patil SR, Rao KW, Watson MS,
et al: Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of
induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse and overall
survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia:
Results from cancer and leukemia group B. Blood. 100:4325–4336.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Slovak ML, Kopecky KJ, Cassileth PA,
Harrington DH, Theil KS, Mohamed A, Paietta E, Willman CL, Head DR,
Rowe JM, et al: Karyotypic analysis predicts outcome of pre-
remission and postremission therapy in adult acute myeloid leuke-
mia: A Southwest Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
Study. Blood. 96:4075–4083. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley
K, Harrison C, Harrison G, Rees J, Hann I, Stevens R, Burnett A and
Goldstone A: The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome
in AML: Analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10
trial. Blood. 92:2322–2333. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang L, Yu G, Meng W, Wang Z, Meng F and
Ma W: Overexpression of amyloid precursor protein in acute myeloid
leukemia enhances extramedullary infiltration by MMP-2. Tumor Biol.
34:629–636. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Campbell JJ, Qin S, Bacon KB, Mackay CR
and Butcher EC: Biology of chemokine and classical chemoattractant
receptors: Differential requirements for adhesion-triggering versus
chemotactic responses in lymphoid cells. J Cell Biol. 134:255–266.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu SH, Gu Y, Pascual B, Yan Z, Hallin M,
Zhang C, Fan C, Wang W, Lam J, Spilker ME, et al: A novel CXCR4
antagonist IgG1 antibody (PF-06747143) for the treatment of
hematologic malignancies. Blood Adv. 1:1088–1100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tavor S, Petit I, Porozov S, Goichberg P,
Avigdor A, Sagiv S, Nagler A, Naparstek E and Lapidot T: Motility,
proliferation, and egress to the circulation of human AML cells are
elastase dependent in NOD/SCID chimeric mice. Blood. 106:2120–2127.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Klein G, Vellenga E, Fraaije MW, Kamps WA
and de Bont ES: The possible role of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in cancer, e.g. acute leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 50:87–100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Suminoe A, Matsuzaki A, Hattori H, Koga Y,
Ishii E and Hara T: Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)
and tissue inhibitor of MMP (TIMP) genes in blasts of infant acute
lymphoblastic leukemia with organ involvement. Leuk Res.
31:1437–1440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su Z, Si W, Li L, Zhou B, Li X, Xu Y, Xu
C, Jia H and Wang QK: MiR-144 regulates hematopoiesis and vascular
development by targeting meis1 during zebrafish development. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 49:53–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Papapetrou EP, Korkola JE and Sadelain M:
A genetic strategy for single and combinatorial analysis of miRNA
function in mammalian hematopoietic stem cells. Stem cells.
28:287–296. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li B, Zhu X, Ward CM, Starlard-Davenport
A, Takezaki M, Berry A, Ward A, Wilder C, Neunert C, Kutlar A and
Pace BS: MiR-144-mediated NRF2 gene silencing inhibits fetal
hemoglobin expression in sickle cell disease. Exp Hematol.
70:85–96.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trecul A, Morceau F, Gaigneaux A,
Schnekenburger M, Dicato M and Diederich M: Valproic acid regulates
erythro-megakaryocytic differentiation through the modulation of
transcription factors and microRNA regulatory micro-networks.
Biochem Pharmacol. 92:299–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu L, Wang S, Chen R, Wu Y, Zhang B,
Huang S, Zhang J, Xiao F, Wang M and Liang Y: Myc induced
miR-144/451 contributes to the acquired imatinib resistance in
chronic myelogenous leukemia cell K562. Biochem biophys Res Commun.
425:368–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang Y, Lin Q, Luo F, Wu W, Yang T and
Wan S: Requirement of miR-144 in CsA induced proliferation and
invasion of human trophoblast cells by targeting titin. J cell
Biochem. 115:690–696. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning
RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM,
Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A and Bloomfield CD: The 2008
revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of
myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important
changes. Blood. 114:937–951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker
H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH, Wheatley K, Harrison CJ and Burnett
AK; National Cancer Research Institute Adult Leukaemia Working
Group, : Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid
leukemia: Determination of prognostic significance of rare
recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult
patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council
trials. Blood. 116:354–365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhen T, Wu CF, Liu P, Wu HY, Zhou GB, Lu
Y, Liu JX, Liang Y, Li KK and Wang YY: Targeting of AML1-ETO in
t(8;21) leukemia by oridonin generates a tumor suppressor-like
protein. Sci Transl Med. 4:127ra382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abdel Rahman H, Farrag SA and EI-Attar IA:
AML1/ETO fusion gene in de novo pediatric acute myeloid leukemia:
Clinical significance and prognostic implications. J Egypt Natl
Canc Inst. 19:39–47. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan YX, Yang L, Wen SP, Liu XJ and Luo JM:
Expression and clinical significance of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in B acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
22:640–643. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Itoh Y, Takamura A, Ito N, Maru Y, Sato H,
Suenaga N, Aoki T and Seiki M: Homophilic complex formation of
MT1-MMP facilitates proMMP-2 activation on the cell surface and
promotes tumor cell invasion. EMBO J. 20:4782–4793. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takayama K, Tsutsumi S, Suzuki T,
Horie-Inoue K, Ikeda K, Kaneshiro K, Fujimura T, Kumagai J, Urano
T, Sakaki Y, et al: Amyloid precursor protein is a primary androgen
target gene that promotes prostate cancer growth. Cancer Res.
69:137–142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Krause K, Karger S, Sheu SY, Aigner T,
Kursawe R, Gimm O, Schmid KW, Dralle H and Fuhrer D: Evidence for a
role of the amyloid precursor protein in thyroid carcinogenesis. J
Endocrinol. 198:291–299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iannetti A, Ledoux AC, Tudhope SJ, Sellier
H, Zhao B, Mowla S, Moore A, Hummerich H, Gewurz BE, Cockell SJ, et
al: Regulation of p53 and Rb links the alternative NF-kB pathway to
EZH2 expression and cell senescence. PLoS Genet. 10:e10046422014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakahara F, Kitaura J, Uchida T, Nishida
C, Togami K, Inoue D, Matsukawa T, Kagiyama Y, Enomoto Y, Kawabata
KC, et al: Hes1 promotes blast crisis in chronic myelogenous
leukemia through MMP-9 upregulation in leukemic cells. Blood.
123:3932–3942. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ugarte-Berzal E, Bailón E, Amigo-Jiménez
I, Albar JP, García-Marco JA and García-Pardo A: A novel
CD44-binding peptide from the pro-matrix metalloproteinase-9
hemopexin domain impairs adhesion and migration of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 289:15340–15349. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Douglass S, Meeson AP, Overbeck-Zubrzycka
D, Brain JG, Bennett MR, Lamb CA, Lennard TW, Browell D, Ali S and
Kirby JA: Breast cancer metastasis: Demonstration that FOXP3
regulates CXCR4 expression and the response to CXCL12. J Pathol.
234:74–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Möhle R, Bautz F, Rafii S, Moore MA,
Brugger W and Kanz L: The chemokine receptor CXCR-4 is expressed on
CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors and leukemic cells and
mediates transendothelial migration induced by stromal cell-derived
factor-1. Blood. 91:4523–4530. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vlad A, Deglesne PA, Letestu R,
Saint-Georges S, Chevallier N, Baran-Marszak F, Varin-Blank N,
Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F and Ledoux D: Down-regulation of CXCR4 and
CD62 L in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells is triggered by B-cell
receptor ligation and associated with progressive disease. Cancer
Res. 69:6387–6395. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sarkissyan S, Sarkissyan M, Wu Y, Cardenas
J, Koeffler HP and Vadgama JV: IGF-1 regulates cyr61 induced breast
cancer cell proliferation and invasion. PLoS One. 9:e1035342014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jin W, Lu Y, Li Q, Wang J, Zhang H, Chang
G, Lin Y and Pang T: Down-regulation of the P-glycoprotein relevant
for multidrug resistance by intracellular acidification through the
crosstalk of MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
54:111–121. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Liu D, Zhang J, Fong C and Yang
M: Gold nanoparticles stimulate differentiation and mineralization
of primary osteoblasts through the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway.
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 42:70–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Verykokakis M, Papadaki C, Vorgia E, Le
Gallic L and Mavrothalassitis G: The RAS-dependent ERF control of
cell proliferation and differentiation is mediated by c-Myc
repression. J Biol Chem. 282:30285–942. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gao Z, Zhang P, Xie M, Gao H, Yin L and
Liu R: miR-144/451 cluster plays an oncogenic role in esophageal
cancer by inhibiting cell invasion. Cancer Cell Int. 18:1842018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Witten LW, Cheng CJ and Slack FJ: miR-155
drives oncogenesis by promoting and cooperating with mutations in
the c-kit oncogene. Oncogene. 38:2151–2161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shirafkan N, Shomali N, Kazemi T,
Shanehbandi D, Ghasabi M, Baghbani E, Ganji M, Khaze V, Mansoori B
and Baradaran B: microRNA-193a-5p inhibits migration of human HT-29
colon cancer cells via suppression of metastasis pathway. J Cell
Biochem. Dec 2–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1002/jcb.28164.
|
|
45
|
Garcia TY, Gutierrez M, Reynolds J and
Lamba DA: Modeling the dynamic AMD-associated chronic oxidative
stress changes in human ESC and iPSC-derived RPE cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:7480–7482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|