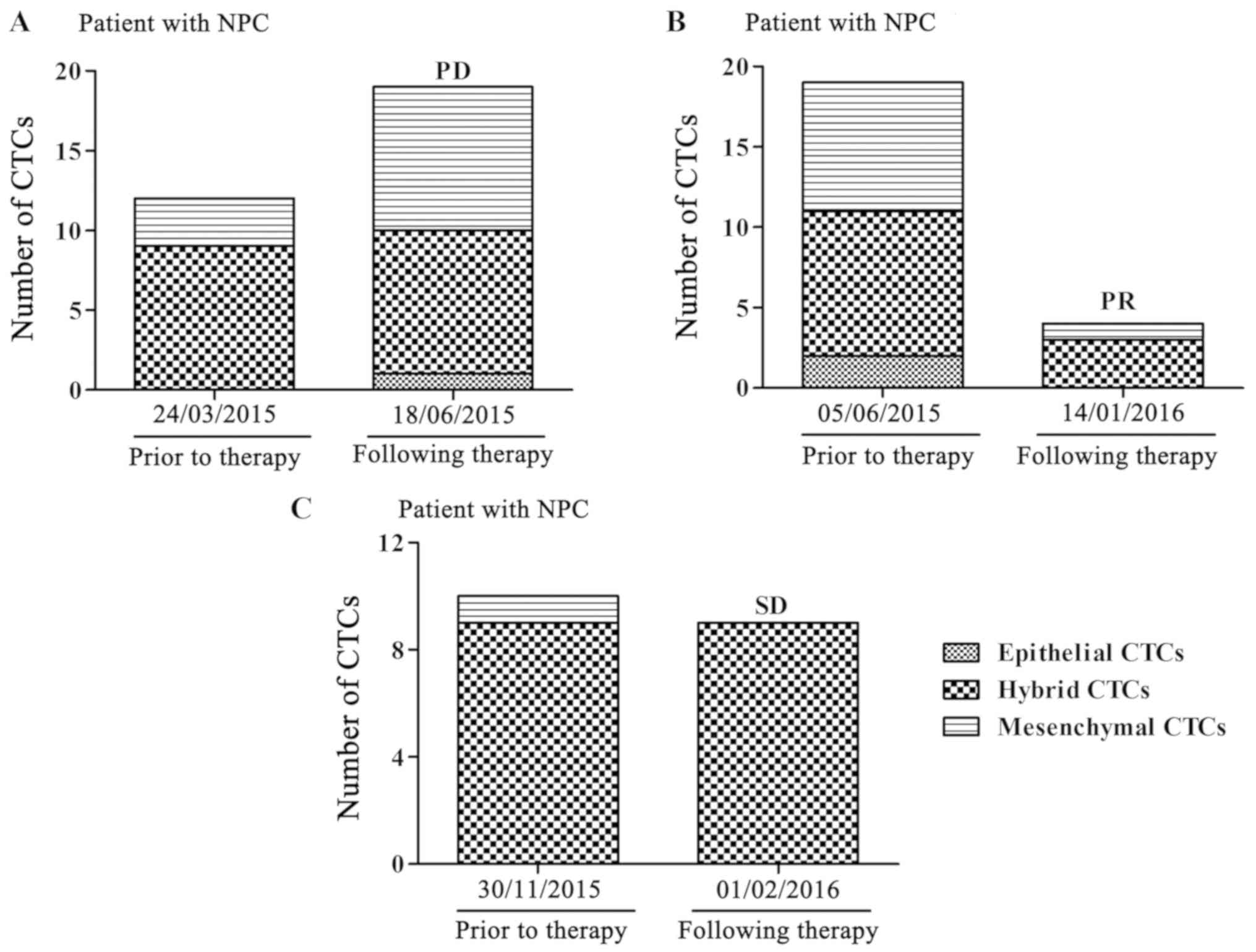
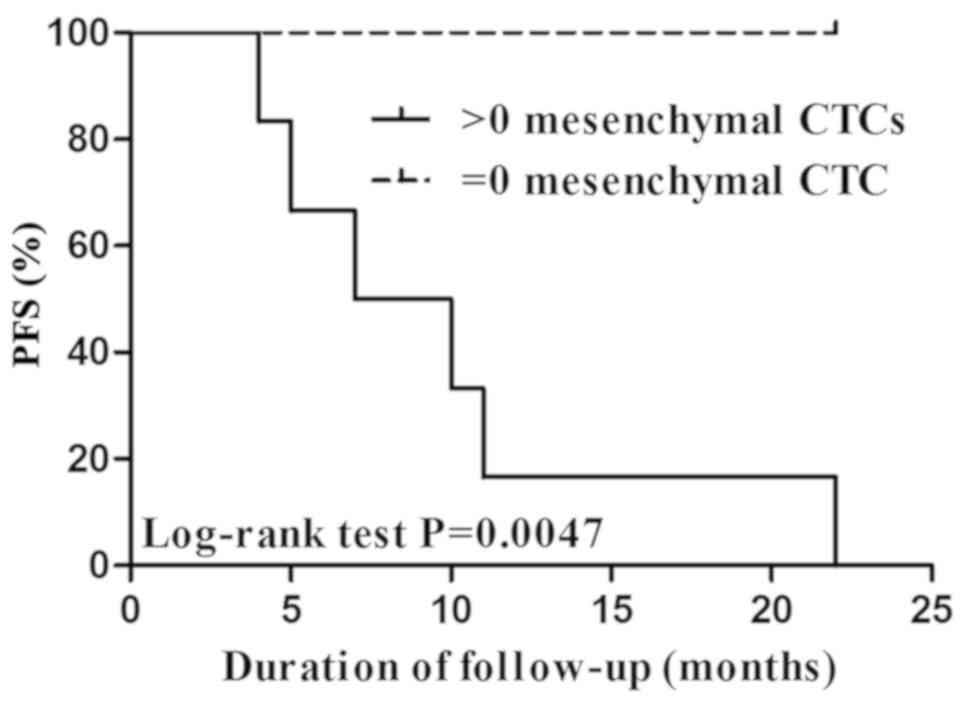
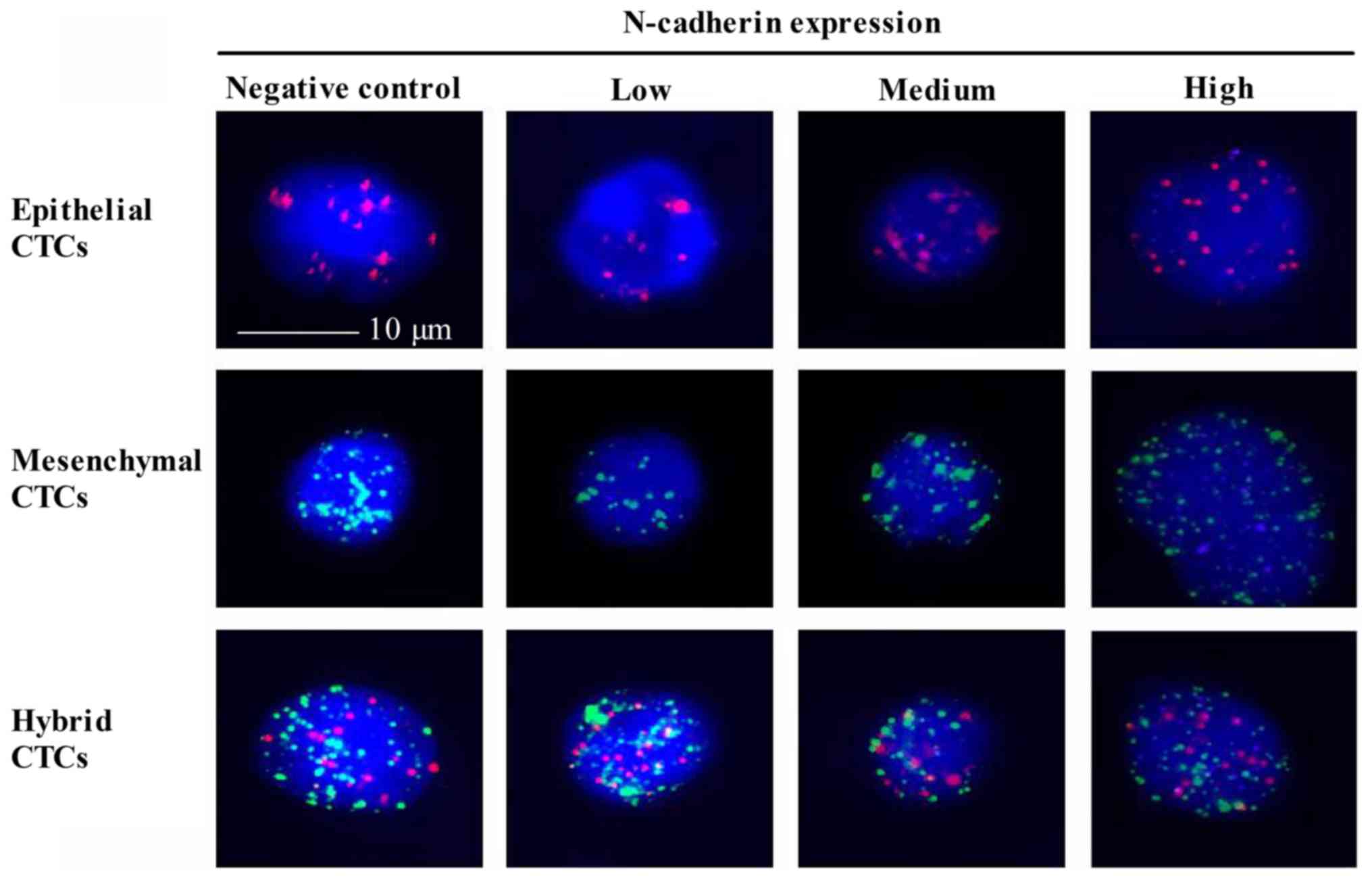
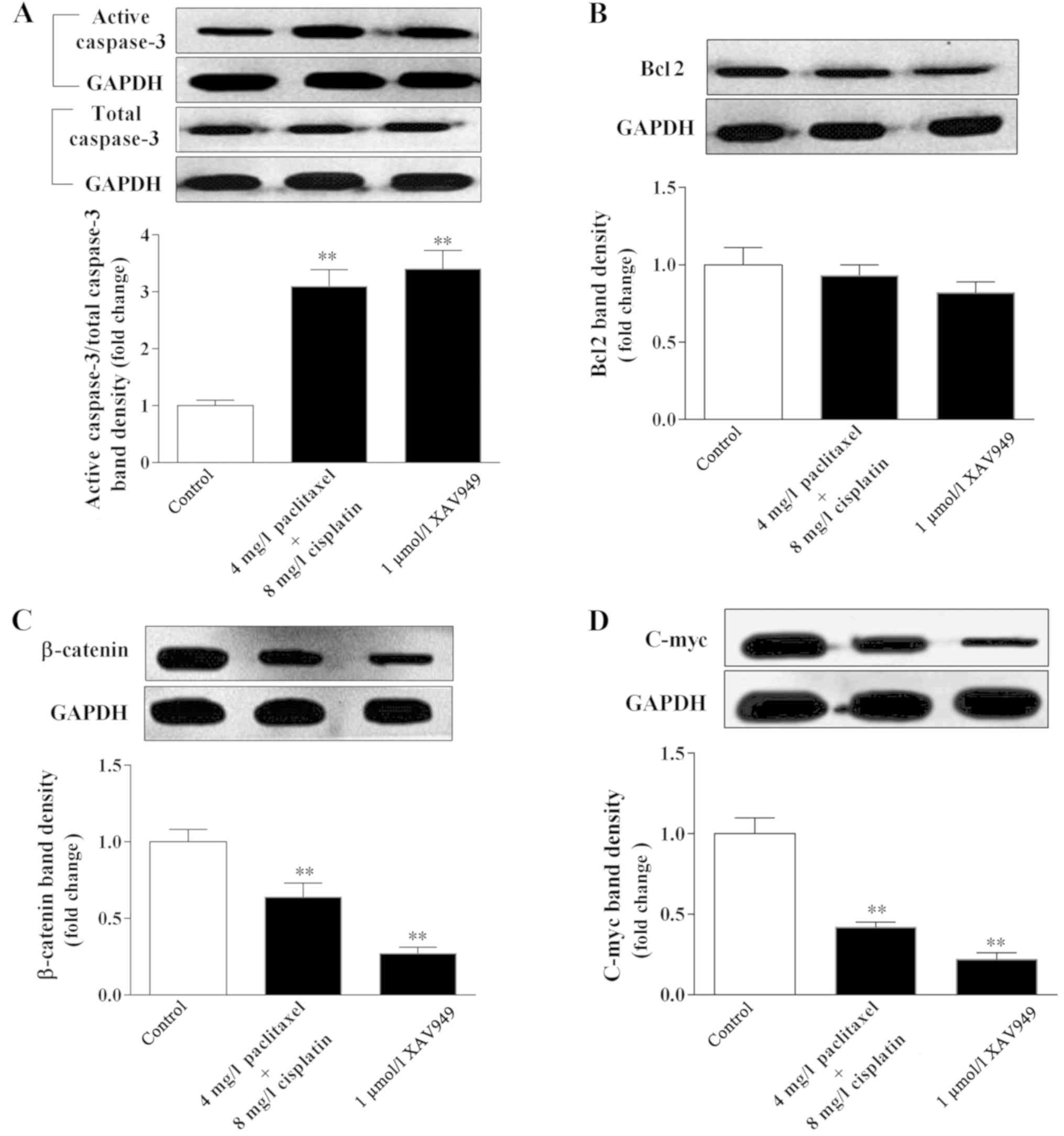
|
1
|
Cao SM, Simons MJ and Qian CN: The
prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China.
Chin J Cancer. 30:114–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Horikawa T, Yoshizaki T, Kondo S, Furukawa
M, Kaizaki Y and Pagano JS: Epstein-Barr Virus latent membrane
protein 1 induces Snail and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 104:1160–1167.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann
Oncol. 21 (Suppl 7):vii308–vii312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin JH, Jiang CQ, Ho SY, Zhang WS, Mai ZM,
Xu L, Lo CM and Lam TH: Smoking and nasopharyngeal carcinoma
mortality: A cohort study of 101,823 adults in Guangzhou, China.
BMC Cancer. 15:9062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sousa H, Mesquita L, Ribeiro J, Catarino
R, Breda E and Medeiros R: Polymorphisms in host immune response
associated genes and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma development
in Portugal. Immunobiology. 221:145–152. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ashworth TR: A case of cancer in which
cells similar to those in the tumours were seen in the blood after
death. Aust Med J. 14:146–149. 1869.
|
|
7
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Książkiewicz M, Markiewicz A and Żaczek
AJ: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A hallmark in metastasis
formation linking circulating tumor cells and cancer stem cells.
Pathobiology. 79:195–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guarino M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and tumour invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:2153–2160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lecharpentier A, Vielh P, Perez-Moreno P,
Planchard D, Soria JC and Farace F: Detection of circulating tumour
cells with a hybrid (epithelial/mesenchymal) phenotype in patients
with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer.
105:1338–1341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Economopoulou P, Georgoulias V and
Kotsakis A: Classifying circulating tumor cells to monitor cancer
progression. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 17:153–165. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai LL, Ye HM, Zheng LM, Ruan RS and Tzeng
CM: Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) as a liquid biopsy material and
drug target. Curr Drug Targets. 15:965–972. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cristofanilli M: Circulating tumor cells,
disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer.
Semin Oncol 33 (3 Suppl 9). S9–S14. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Nolé F, Munzone E, Zorzino L, Minchella I,
Salvatici M, Botteri E, Medici M, Verri E, Adamoli L, Rotmensz N,
et al: Variation of circulating tumor cell levels during treatment
of metastatic breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic
implications. Ann Oncol. 19:891–897. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cohen SJ, Punt CJ, Iannotti N, Saidman BH,
Sabbath KD, Gabrail NY, Picus J, Morse M, Mitchell E, Miller MC, et
al: Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response,
progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:3213–3221. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fina E, Necchi A, Giannatempo P, Colecchia
M, Raggi D, Daidone MG and Cappelletti V: Clinical significance of
early changes in circulating tumor cells from patients receiving
first-line cisplatin-based chemotherapy for metastatic urothelial
carcinoma. Bladder Cancer. 2:395–403. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hirose T, Oki Y, Kusumoto S, Sugiyama T,
Shirai T, Nakashima M, Yamaoka T, Okuda K, Ohnishi T, Ohmori T and
Adachi M: Circulating tumor cells as a predictive marker for
chemotherapy and prognostic marker in patients with metastatic
non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29 (Suppl 15):e210202011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hall C, Valad L and Lucci A: Circulating
tumor cells in breast cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncog. 21:125–139.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alva A, Friedlander T, Clark M, Huebner T,
Daignault S, Hussain M, Lee C, Hafez K, Hollenbeck B, Weizer A, et
al: Circulating tumor cells as potential biomarkers in bladder
cancer. J Urol. 194:790–798. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Derycke LD and Bracke ME: N-cadherin in
the spotlight of cell-cell adhesion, differentiation,
embryogenesis, invasion and signalling. Int J Dev Bio. 48:463–476.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Craig SE and Brady-Kalnay SM: Cancer cells
cut homophilic cell adhesion molecules and run. Cancer Res.
71:303–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nieman MT, Prudoff RS, Johnson KR and
Wheelock MJ: N-cadherin promotes motility in human breast cancer
cells regardless of their E-cadherin expression. J Cell Biol.
147:631–644. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Araki K, Shimura T, Suzuki H, Tsutsumi S,
Wada W, Yajima T, Kobayahi T, Kubo N and Kuwano H: E/N-cadherin
switch mediates cancer progression via TGF-β-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:1885–1893. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li S and Jiao J: Effects of N-cadherin
expression on cell cycle, cell apoptosis and invasiveness and
metastasis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell line Tca8113
cells. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 46:365–369. 2011.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF, Norton L
and Aaronson SA: Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast
cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. J
Cell Biol. 148:779–790. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Valkenburg KC, Graveel CR, Zylstra-Diegel
CR, Zhong Z and Williams BO: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in normal and
cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 3:2050–2079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen K, Huang Y and Chen J: Understanding
and targeting cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications and
challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:732–740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin QQ, Jin-Tian LI and Wang M: Role of
Wnt/β-catenin pathway in differentiation of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Sun Yat-sen Univ (Med Sci). 4:384–387. 2005.(In
Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Wu S, Liu Z, Liu S, Lin L, Yang W and Xu
J: Enrichment and enumeration of circulating tumor cells by
efficient depletion of leukocyte fractions. Clin Chem Lab Med.
52:243–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu S, Liu S, Liu Z, Huang J, Pu X, Li J,
Yang D, Deng H, Yang N and Xu J: Classification of circulating
tumor cells by epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers. PLoS One.
10:e01239762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsongalis GJ: Branched DNA technology in
molecular diagnostics. Am J Clin Pathol. 126:448–453. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Horn T, Chang CA and Urdea MS: Chemical
synthesis and characterization of branched
oligodeoxyribonucleotides (bDNA) for use as signal amplifiers in
nucleic acid quantification assays. Nucleic Acids Res.
25:4842–4849. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann
Oncol. 21 (Suppl 7):vii308–vii312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei KR, Xu Y, Liu J, Zhang WJ and Liang
ZH: Histopathological classification of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1141–1147. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hui EP, Ma BB, King AD, Mo F, Chan SL, Kam
MK, Loong HH, Ahuja AT, Zee BC and Chan AT: Hemorrhagic
complications in a phase ii study of sunitinib in patients of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma who has previously received high-dose
radiation. Ann Oncol. 22:1280–1287. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luo WR, Wu AB, Fang WY, Li SY and Yao KT:
Nuclear expression of N-cadherin correlates with poor prognosis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Histopathology. 61:237–246. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi L, Wu YX, Yu JH, Chen X, Luo XJ and
Yin YR: Research of the relationship between β-catenin and
c-myc-mediated Wnt pathway and laterally spreading tumors
occurrence. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:252–257. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
OuYang PY, Su Z, Ma XH, Mao YP, Liu MZ and
Xie FY: Comparison of TNM staging systems for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma, and proposal of a new staging system. Br J Cancer.
109:2987–2997. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mehta S, Shelling A, Muthukaruppan A,
Lasham A, Blenkiron C, Laking G and Print C: Predictive and
prognostic molecular markers for cancer medicine. Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 2:125–148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Micalizzi DS, Haber DA and Maheswaran S:
Cancer metastasis through the prism of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in circulating tumor cells. Mol Oncol. 11:770–780. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alix-Panabieres C and Pantel K: The
circulating tumor cells: Liquid biopsy of cancer. Klin Lab Diagn.
60–64. 2014.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Si Y, Lan G, Deng Z, Wang Y, Lu Y, Qin Y,
Huang B, Yang Y, Weng J, Han X, et al: Distribution and clinical
significance of circulating tumor cells in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:622–630. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen X and Tang Q: The impact of
radiotherapy course length on the treatment results of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Chin J Cancer Res. 7:130–133. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ren JH, Dai XF, Yan GL, Jin M, Liu CW,
Yang KY, Wu G and Ma CM: Acute oral mucositis in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy: association with
genetic polymorphism in DNA DSB repair genes. Int J Radiat Biol.
90:256–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lengyel E, Baricza K, Somogyi A, Olajos J,
Pápai Z, Godény M, Németh G and Esik O: Reirradiation of locally
recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol.
179:298–305. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kong FF, Ying H, Du CR, Huang S, Zhou JJ
and Hu CS: Effectiveness and toxicities of intensity-modulated
radiation therapy for patients with T4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
PLoS One. 9:e913622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Paterlini-Brechot P and Benali NL:
Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future
directions. Cancer Lett. 253:180–204. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hatta K, Nose A, Nagafuchi A and Takeichi
M: Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a neural
calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecule: Its identity in the
cadherin gene family. J Cell Biol. 106:873–881. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H,
Beppu T, Nakamori S, Baba H and Mori M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer development and its clinical significance.
Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Drocaş AI, Tomescu PI, Mitroi G, Drăgoescu
PO, Mărgăritescu C, Stepan AE, Şurlin V, CrăiŢoiu Ş, Drocaş I,
Ungureanu AM, et al: The cadherin switch assessment in the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of urothelial bladder carcinomas.
Rom J Morphol Embryol. 57:1037–1044. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|