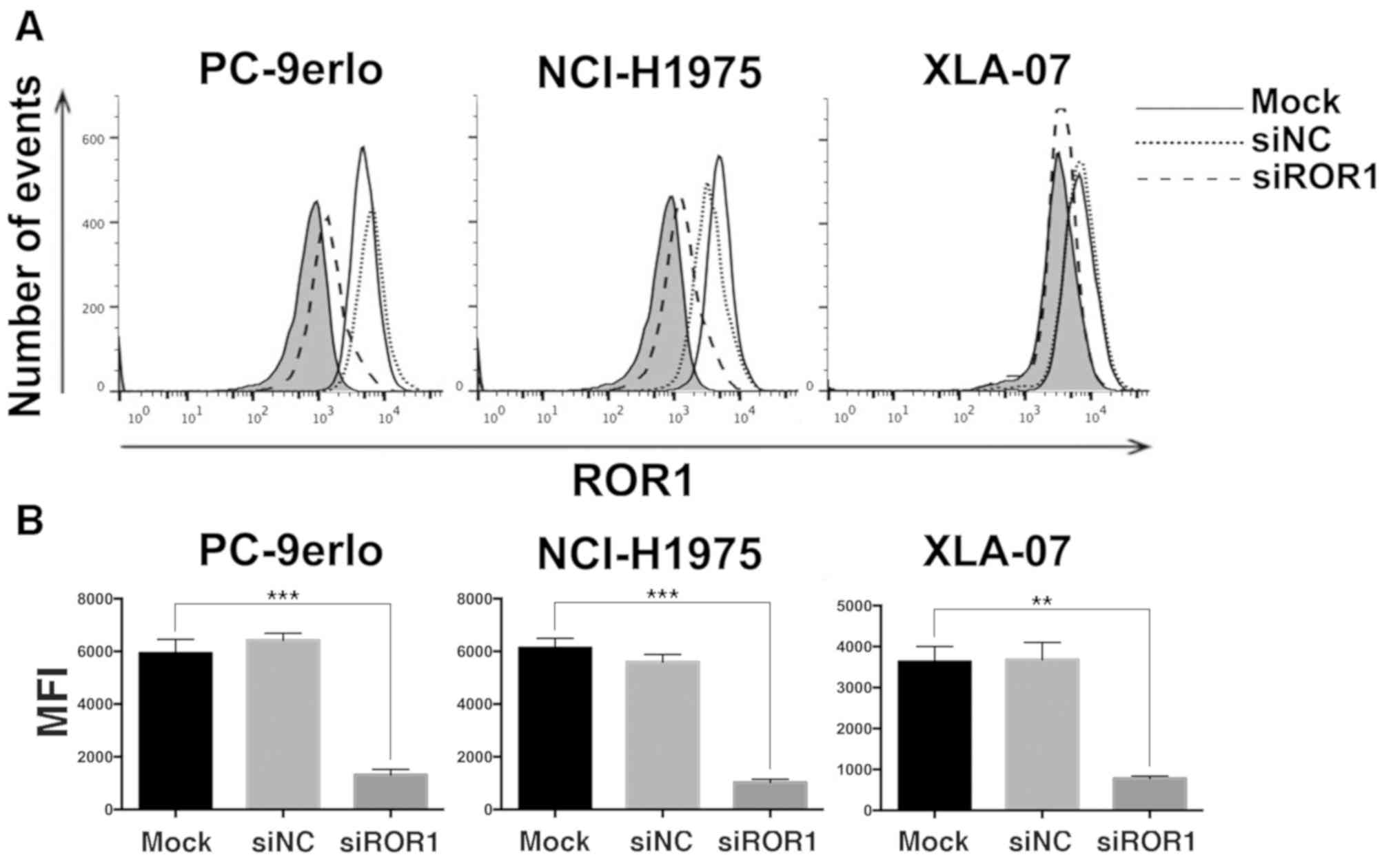
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E and Li QK:
Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical
markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma
(NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 52:103–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reck M, Popat S, Reinmuth N, De Ruysscher
D, Kerr K and Peters S; ESMO Guidelines Working Group, : Metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical practice
guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 25
(Suppl 3):iii27–iii39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nascimento A, Bousbaa H, Ferreira D and
Sarmento B: Non-small cell lung carcinoma: An overview on targeted
therapy. Curr Drug Targets. 16:1448–1463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mitsudomi T and Yatabe Y: Epidermal growth
factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and
cancer. FEBS J. 277:301–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gadgeel SM and Wozniak A: Preclinical
rationale for PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors as therapy for
epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell
lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 14:322–332. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tan CS, Kumarakulasinghe NB, Huang YQ, Ang
YL, Choo JR, Goh BC and Soo RA: Third generation EGFR TKIs: Current
data and future directions. Mol Cancer. 17:292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu SG and Shih JY: Management of acquired
resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin Y, Wang X and Jin H: EGFR-TKI
resistance in NSCLC patients: Mechanisms and strategies. Am J
Cancer Res. 4:411–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morgillo F, Della Corte CM, Fasano M and
Ciardiello F: Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs: Lung
cancer. ESMO Open. 1:e0000602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martinez-Marti A, Felip E, Matito J, Mereu
E, Navarro A, Cedrés S, Pardo N, Martinez de Castro A, Remon J,
Miquel JM, et al: Dual MET and ERBB inhibition overcomes intratumor
plasticity in osimertinib-resistant-advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol. 28:2451–2457. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heydt C, Michels S, Thress KS, Bergner S,
Wolf J and Buettner R: Novel approaches against epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance. Oncotarget.
9:15418–15434. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Q, Yu S, Zhao W, Qin S, Chu Q and Wu
K: EGFR-TKIs resistance via EGFR-independent signaling pathways.
Mol Cancer. 17:532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Westover D, Zugazagoitia J, Cho BC, Lovly
CM and Paz-Ares L: Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and
second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Oncol.
29:i10–i19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Laurila N and Koivunen JP: EGFR inhibitor
and chemotherapy combinations for acquired TKI resistance in
EGFR-mutant NSCLC models. Med Oncol. 32:2052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tricker EM, Xu C, Uddin S, Capelletti M,
Ercan D, Ogino A, Pratilas CA, Rosen N, Gray NS, Wong KK, et al:
Combined EGFR/MEK inhibition prevents the emergence of resistance
in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 5:960–971. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cavazzoni A, La Monica S, Alfieri R,
Ravelli A, Van Der Steen N, Sciarrillo R, Madeddu D, Lagrasta CAM,
Quaini F, Bonelli M, et al: Enhanced efficacy of AKT and FAK kinase
combined inhibition in squamous cell lung carcinomas with stable
reduction in PTEN. Oncotarget. 8:53068–53083. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu X, Shi S, Wang H, Yu X, Wang Q, Jiang
S, Ju D, Ye L and Feng M: Blocking autophagy improves the
anti-tumor activity of afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma with
activating EGFR mutations in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep.
7:45592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang X, Yan L, Zhu L, Jiao D, Chen J and
Chen Q: Salvianolic acid A reverses cisplatin resistance in lung
cancer A549 cells by targeting c-met and attenuating Akt-mTOR
pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 135:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ye M, Wang S, Wan T, Jiang R, Qiu Y, Pei
L, Pang N, Huang Y, Huang Y, Zhang Z and Yang L: Combined
inhibitions of glycolysis and AKT/autophagy can overcome resistance
to EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer. J Cancer. 8:3774–3784.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu Y, Li C, Luo Y, Li L, Liu J and Gui R:
Silencing of long non-coding RNA MIAT sensitizes lung cancer cells
to gefitinib by epigenetically regulating miR-34a. Front Pharmacol.
9:822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ni J, Zhou LL, Ding L, Zhang XQ, Zhao X,
Li H, Cao H, Liu S, Wang Z, Ma R, et al: Efatutazone and T0901317
exert synergistically therapeutic effects in acquired
gefitinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Med.
7:1955–1966. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Dong X, Ren Y, Luo J, Liu P, Su D
and Yang X: Targeting EHMT2 reverses EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC
by epigenetically regulating the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 9:1292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang YC, Wu DW, Wu TC, Wang L, Chen CY and
Lee H: Dioscin overcome TKI resistance in EGFR-mutated lung
adenocarcinoma cells via down-regulation of tyrosine phosphatase
SHP2 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 14:47–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Masiakowski P and Carroll RD: A novel
family of cell surface receptor with tyrosine kinase-like domain. J
Biol Chem. 267:26181–26190. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Borcherding N, Kusner D, Liu GH and Zhang
W: ROR1, an embryonic protein with an emerging role in cancer
biology. Protein Cell. 5:496–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Yang H, Chen T, Luo Y, Xu Z, Li Y
and Yang J: Silencing of receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1 inhibits
tumor-cell proliferation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in
lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01270922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gentile A, Lazzari L, Benvenuti S,
Trusolino L and Comoglio P: The ROR1 pseudokinase diversifies
signaling outputs in MET-addicted cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
135:2305–2316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamaguchi T, Yanagisawa K, Sugiyama R,
Hosono Y, Shimada Y, Arima C, Kato S, Tomida S, Suzuki M, Osada H
and Takahashi T: NKX2-1/TITF1/TTF-1-Induced ROR1 is required to
sustain EGFR survival signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Cell. 21:348–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma LJ, Wang HZ, Bian L, Shao WP, Tang RZ,
Wang QQ and Jin KW: Establishment and characterization of lung
adenocarcinoma cell line XLA-07. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi.
41:335–339. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao YM, Su B, Yang XJ, Shi JY, Tang L,
Zhang J, Li JY and Chen J: Small molecule inhibitor SB203580
enhances the antitumor effect of gefitinib in PC-9 and A549 lung
cancer cell lines. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 35:103–108. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang J, Baskar S, Kwong KY, Kennedy MG,
Wiestner A and Rader C: Therapeutic potential and challenges of
targeting receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1 with monoclonal antibodies
in B-cell malignancies. PLoS One. 6:e210182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang T, Zhang Y, Li Y, Hao Y, Zhou M, Dong
N and Duan X: High amounts of fluoride induce apoptosis/cell death
in matured ameloblast-like LS8 cells by downregulating Bcl-2. Arch
Oral Biol. 58:1165–1173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bonelli MA, Digiacomo G, Fumarola C,
Alfieri R, Quaini F, Falco A, Madeddu D, La Monica S, Cretella D,
Ravelli A, et al: Combined inhibition of CDK4/6 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathways induces a synergistic anti-tumor effect in malignant
pleural mesothelioma cells. Neoplasia. 19:637–648. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Xing Y and Rong L: miR-181
regulates cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer via
downregulation of autophagy through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.
Oncol Rep. 39:1631–1639. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goetsch L, Gonzalez A, Leger O, Beck A,
Pauwels PJ, Haeuw JF and Corvaia N: A recombinant humanized
anti-insulin-like growth factor receptor type I antibody (h7C10)
enhances the antitumor activity of vinorelbine and anti-epidermal
growth factor receptor therapy against human cancer xenografts. Int
J Cancer. 113:316–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cosaceanu D, Carapancea M, Alexandru O,
Budiu R, Martinsson HS, Starborg M, Vrabete M, Kanter L, Lewensohn
R and Dricu A: Comparison of three approaches for inhibiting
insulin-like growth factor I receptor and their effects on NSCLC
cell lines in vitro. Growth Factors. 25:1–8. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu F, Zhang YJ, Li L, Zhang YJ, Han JC, Yu
YY and Ma CN: MicroRNA-214 inhibits the proliferation of non-small
cell lung cancer via the suppression of IRS1. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 9:22–29. 2016.
|