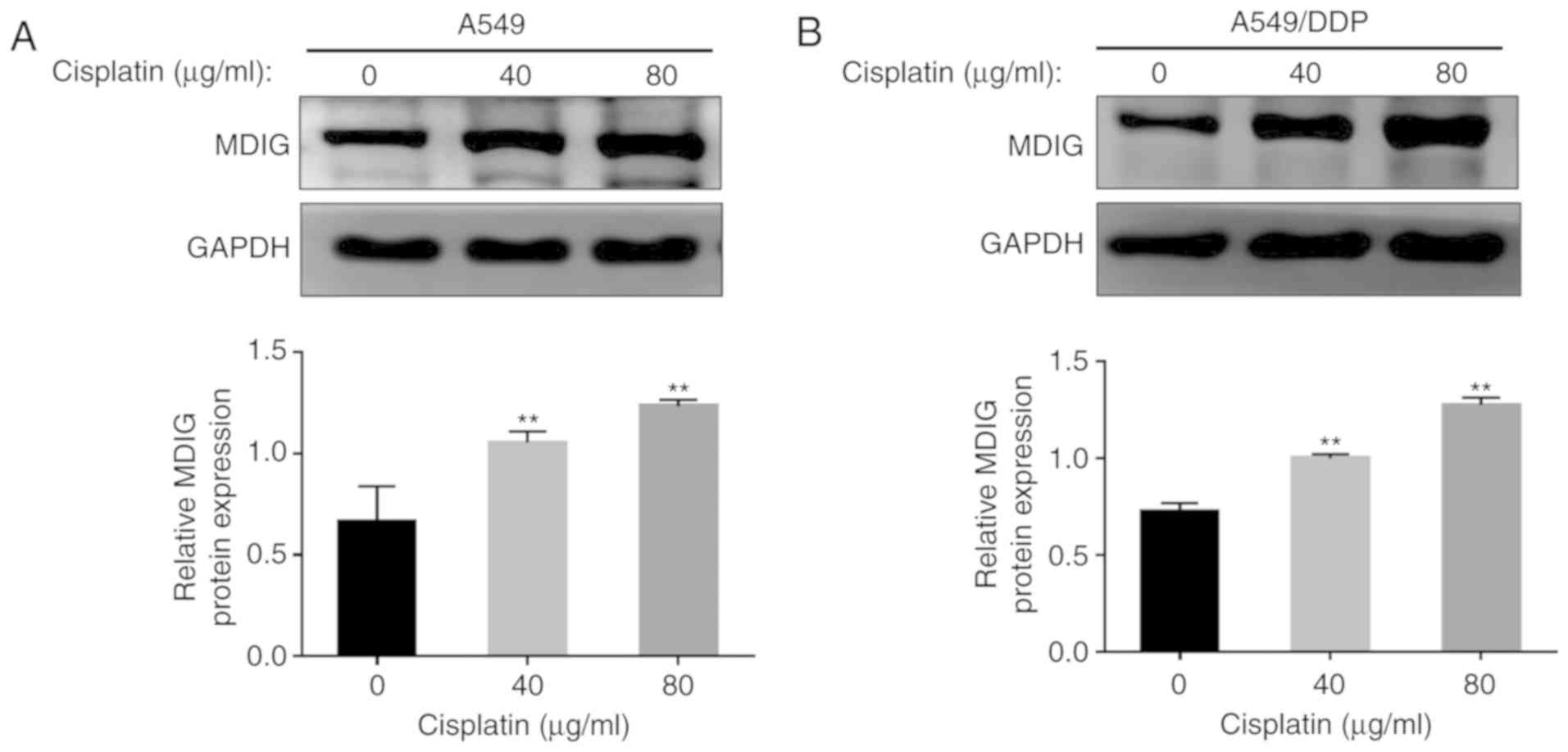
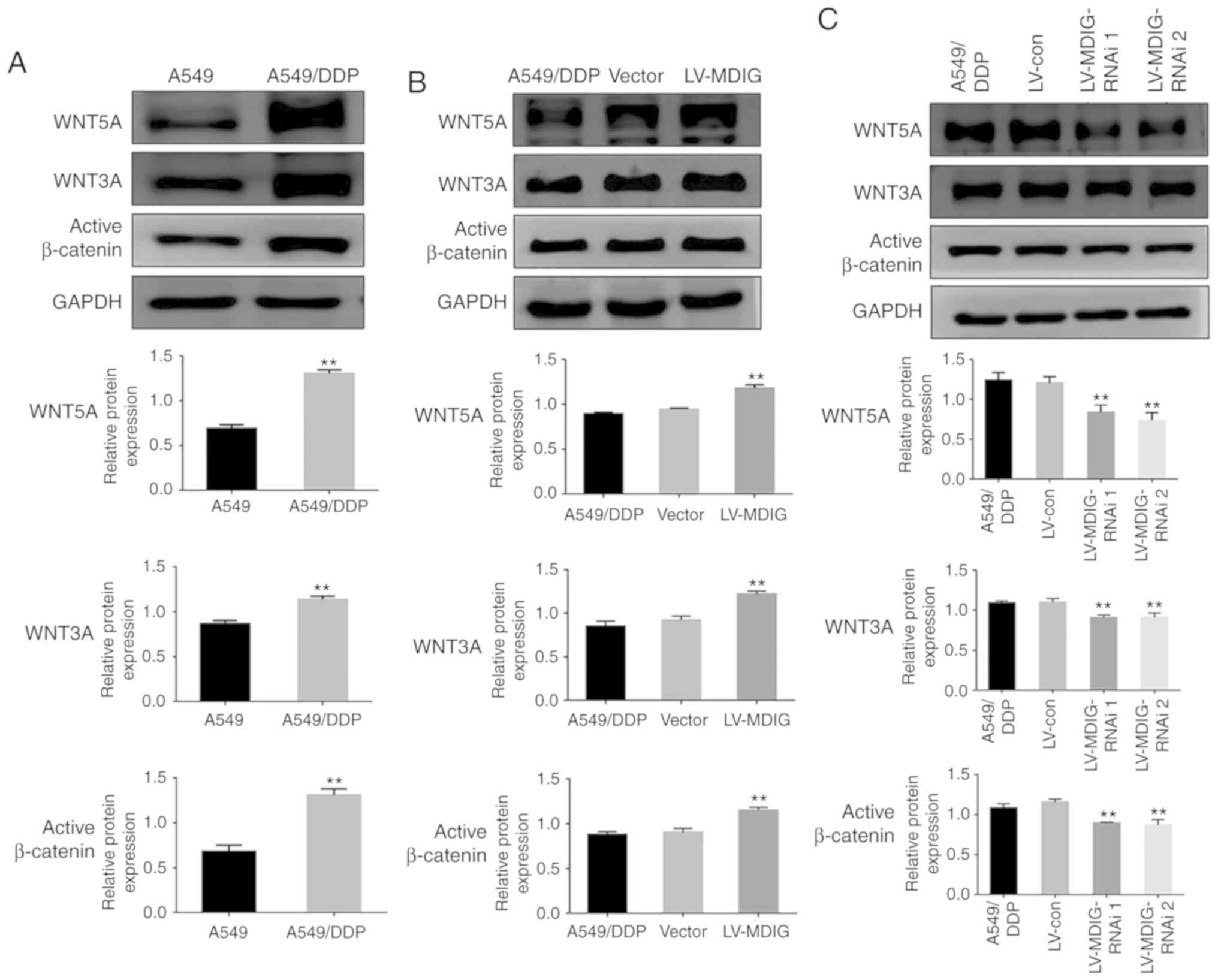
|
1
|
de Groot P and Munden RF: Lung cancer
epidemiology, risk factors, and prevention. Radiol Clin North Am.
50:863–876. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma D, Guo D, Li W and Zhao H: MDIG, a lung
cancer-associated gene, regulates cell cycle progression through
p27(KIP1). Tumour Biol. 36:6909–6917. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu HY, Wang XJ and Mao WM: Targeted
therapies in small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 5:3–11.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo Y, Chu M, Tan S, Zhao S, Liu H, Otieno
BO, Yang X, Xu C and Zhang Z: Chitosan-g-TPGS nanoparticles for
anticancer drug delivery and overcoming multidrug resistance. Mol
Pharm. 11:59–70. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, Nie Y, Shi Y and Fan D:
Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and
lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 347:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calatozzolo C, Gelati M, Ciusani E,
Sciacca FL, Pollo B, Cajola L, Marras C, Silvani A,
Vitellaro-Zuccarello L, Croci D, et al: Expression of drug
resistance proteins Pgp, MRP1, MRP3, MRP5 and GST-pi in human
glioma. J Neurooncol. 74:113–121. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui H, Zhang AJ, Chen M and Liu JJ: ABC
transporter inhibitors in reversing multidrug resistance to
chemotherapy. Curr Drug Targets. 16:1356–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mohammad IS, He W and Yin L: Understanding
of human ATP binding cassette superfamily and novel multidrug
resistance modulators to overcome MDR. Biomed Pharmacother.
100:335–348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hung TH, Hsu SC, Cheng CY, Choo KB, Tseng
CP, Chen TC, Lan YW, Huang TT, Lai HC, Chen CM and Chong KY: WNT5A
regulates ABCB1 expression in multidrug-resistant cancer cells
through activation of the non-canonical PKA/β-catenin pathway.
Oncotarget. 5:12273–12290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen B, Zhang D, Kuai J, Cheng M, Fang X
and Li G: Upregulation of miR-199a/b contributes to cisplatin
resistance via WNT/β-catenin-ABCG2 signaling pathway in
ALDHA1+ colorectal cancer stem cells. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177151552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Lu Y, Yuan BZ, Castranova V, Shi
X, Stauffer JL, Demers LM and Chen F: The Human mineral
dust-induced gene, MDIG, is a cell growth regulating gene
associated with lung cancer. Oncogene. 24:4873–4882. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsuneoka M, Koda Y, Soejima M, Teye K and
Kimura H: A novel myc target gene, mina53, that is involved in cell
proliferation. J Biol Chem. 277:35450–35459. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eilbracht J, Kneissel S, Hofmann A and
Schmidt-Zachmann MS: Protein NO52-a constitutive nucleolar
component sharing high sequence homologies to protein NO66. Eur J
Cell Biol. 84:279–294. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu M, Sun J, Thakur C, Chen B, Lu Y, Zhao
H and Chen F: Paradoxical roles of mineral dust induced gene on
cell proliferation and migration/invasion. PLoS One. 9:e879982014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thakur C, Wolfarth M, Sun J, Zhang Y, Lu
Y, Battelli L, Porter DW and Chen F: Oncoprotein MDIG contributes
to silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by altering balance between
Th17 and Treg T cells. Oncotarget. 6:3722–3736. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen B, Yu M, Chang Q, Lu Y, Thakur C, Ma
D, Yi Z and Chen F: MDIG de-represses H19 large intergenic
non-coding RNA (lincRNA) by down-regulating H3K9me3 and
heterochromatin. Oncotarget. 4:1427–1437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu K, Tan MY, Jiang JT, Mu XY, Wang JR,
Zhou WJ, Wang X, Li MQ, He YY and Liu ZH: Cisplatin inhibits the
progression of bladder cancer by selectively depleting G-MDSCs: A
novel chemoimmunomodulating strategy. Clin Immunol. 193:60–69.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo K, Gu X, Liu J, Zeng G, Peng L, Huang
H, Jiang M, Yang P, Li M, Yang Y, et al: Inhibition of disheveled-2
resensitizes cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells through
down-regulating WNT/β-catenin signaling. Exp Cell Res. 347:105–113.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Corrêa S, Binato R, Du Rocher B,
Castelo-Branco MT, Pizzatti L and Abdelhay E: WNT/β-catenin pathway
regulates ABCB1 transcription in chronic myeloid leukemia. BMC
Cancer. 12:3032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou C: Lung cancer molecular epidemiology
in China: Recent trends. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:270–279.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC and
Rabe KF: Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent
developments. Lancet. 382:709–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thakur C, Lu Y, Sun J, Yu M, Chen B and
Chen F: Increased expression of MDIG predicts poorer survival of
the breast cancer patients. Gene. 535:218–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Teye K, Tsuneoka M, Arima N, Koda Y,
Nakamura Y, Ueta Y, Shirouzu K and Kimura H: Increased expression
of a Myc target gene Mina53 in human colon cancer. Am J Pathol.
164:205–216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ogasawara S, Komuta M, Nakashima O, Akiba
J, Tsuneoka M and Yano H: Accelerated expression of a Myc target
gene Mina53 in aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res.
40:330–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ishizaki H, Yano H, Tsuneoka M, Ogasawara
S, Akiba J, Nishida N, Kojiro S, Fukahori S, Moriya F, Matsuoka K
and Kojiro M: Overexpression of the myc target gene Mina53 in
advanced renal cell carcinoma. Pathol Int. 57:672–680. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukahori S, Yano H, Tsuneoka M, Tanaka Y,
Yagi M, Kuwano M, Tajiri T, Taguchi T, Tsuneyoshi M and Kojiro M:
Immunohistochemical expressions of Cap43 and Mina53 proteins in
neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 42:1831–1840. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huo Q, Ge C, Tian H, Sun J, Cui M, Li H,
Zhao F, Chen T, Xie H, Cui Y, et al: Dysfunction of IKZF1/MYC/MDIG
axis contributes to liver cancer progression through regulating
H3K9me3/p21 activity. Cell Death Dis. 8:e27662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Robey RW, Shukla S, Finley EM, Oldham RK,
Barnett D, Ambudkar SV, Fojo T and Bates SE: Inhibition of
P-glycoprotein (ABCB1)- and multidrug resistance-associated protein
1 (ABCC1)-mediated transport by the orally administered inhibitor,
CBT-1((R)). Biochem Pharmacol. 75:1302–1312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi Z, Parmar S, Peng XX, Shen T, Robey
RW, Bates SE, Fu LW, Shao Y, Chen YM, Zang F and Chen ZS: The
epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 and
erlotinib reverse ABCG2-mediated drug resistance. Oncol Rep.
21:483–489. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoh K, Ishii G, Yokose T, Minegishi Y,
Tsuta K, Goto K, Nishiwaki Y, Kodama T, Suga M and Ochiai A: Breast
cancer resistance protein impacts clinical outcome in
platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:1691–1697. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li A, Song J, Lai Q, Liu B, Wang H, Xu Y,
Feng X, Sun X and Du Z: Hypermethylation of ATP-binding cassette B1
(ABCB1) multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1) is associated with cisplatin
resistance in the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Int J Exp
Pathol. 97:412–421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pei K, Zhu JJ, Wang CE, Xie QL and Guo JY:
MicroRNA-185-5p modulates chemosensitivity of human non-small cell
lung cancer to cisplatin via targeting ABCC1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 20:4697–4704. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang L, Jin Y, Feng S, Zou Y, Xu S, Qiu
S, Li L and Zheng J: Role of WNT/β-catenin, WNT/c-Jun N-terminal
kinase and WNT/Ca2+ pathways in cisplatin-induced
chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Exp Ther Med. 12:3851–3858.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Z, Zhao L and Wang Q: Overexpression of
long non-coding RNA HOTTIP increases chemoresistance of
osteosarcoma cell by activating the WNT/β-catenin pathway. Am J
Transl Res. 8:2385–2393. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|