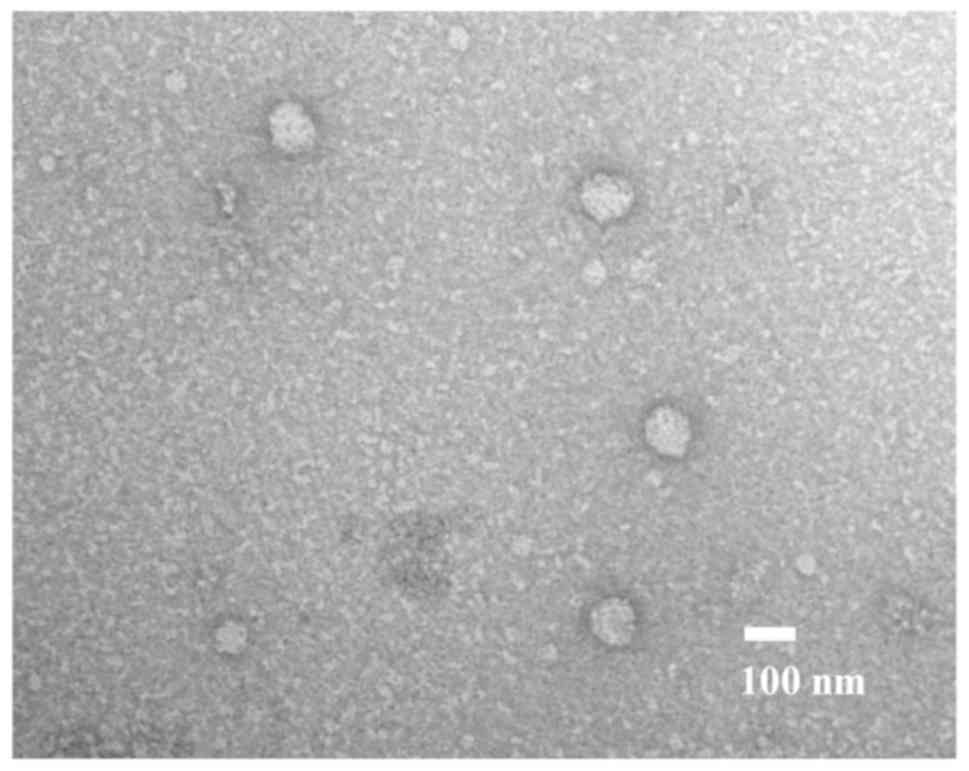
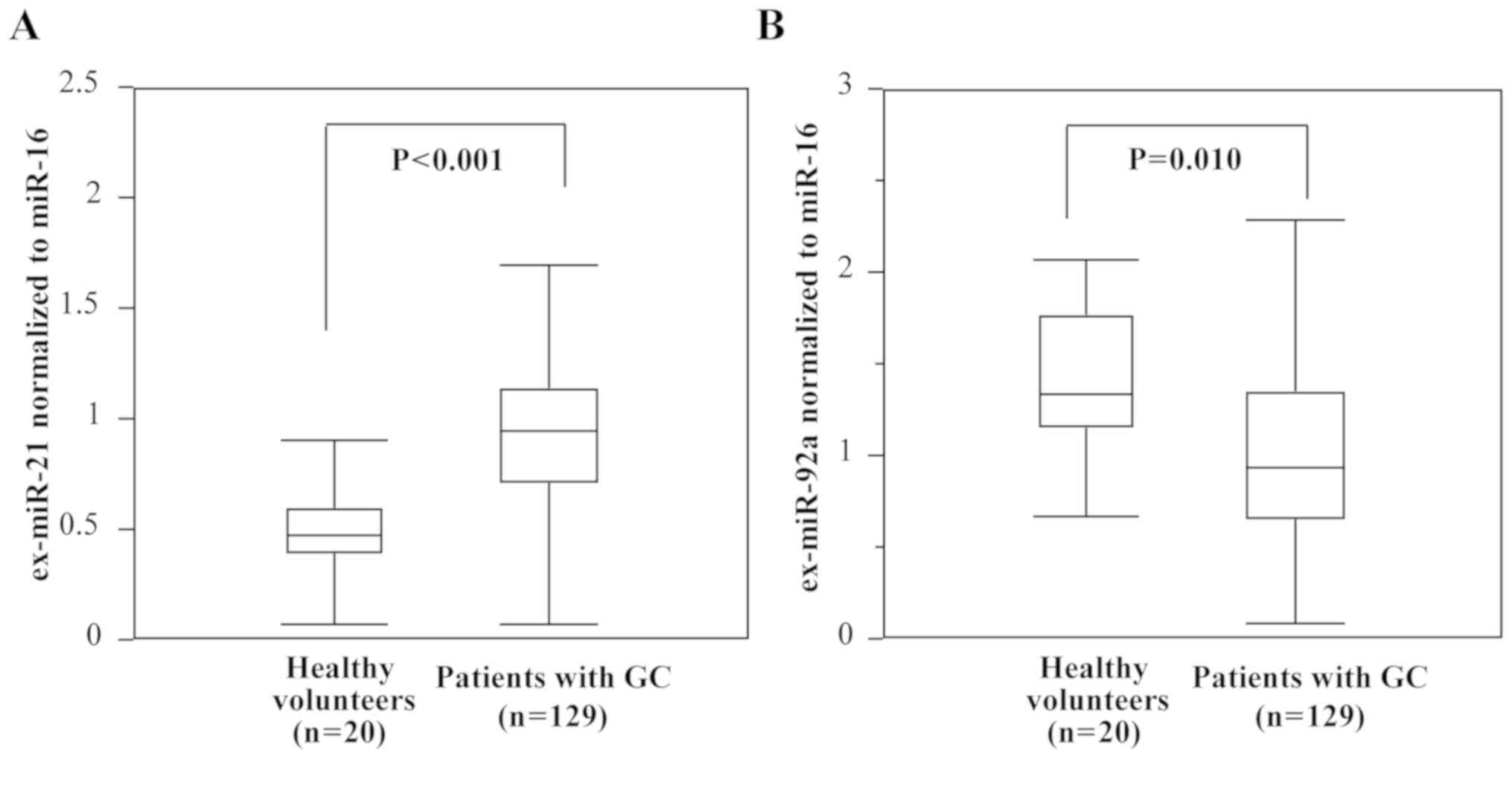
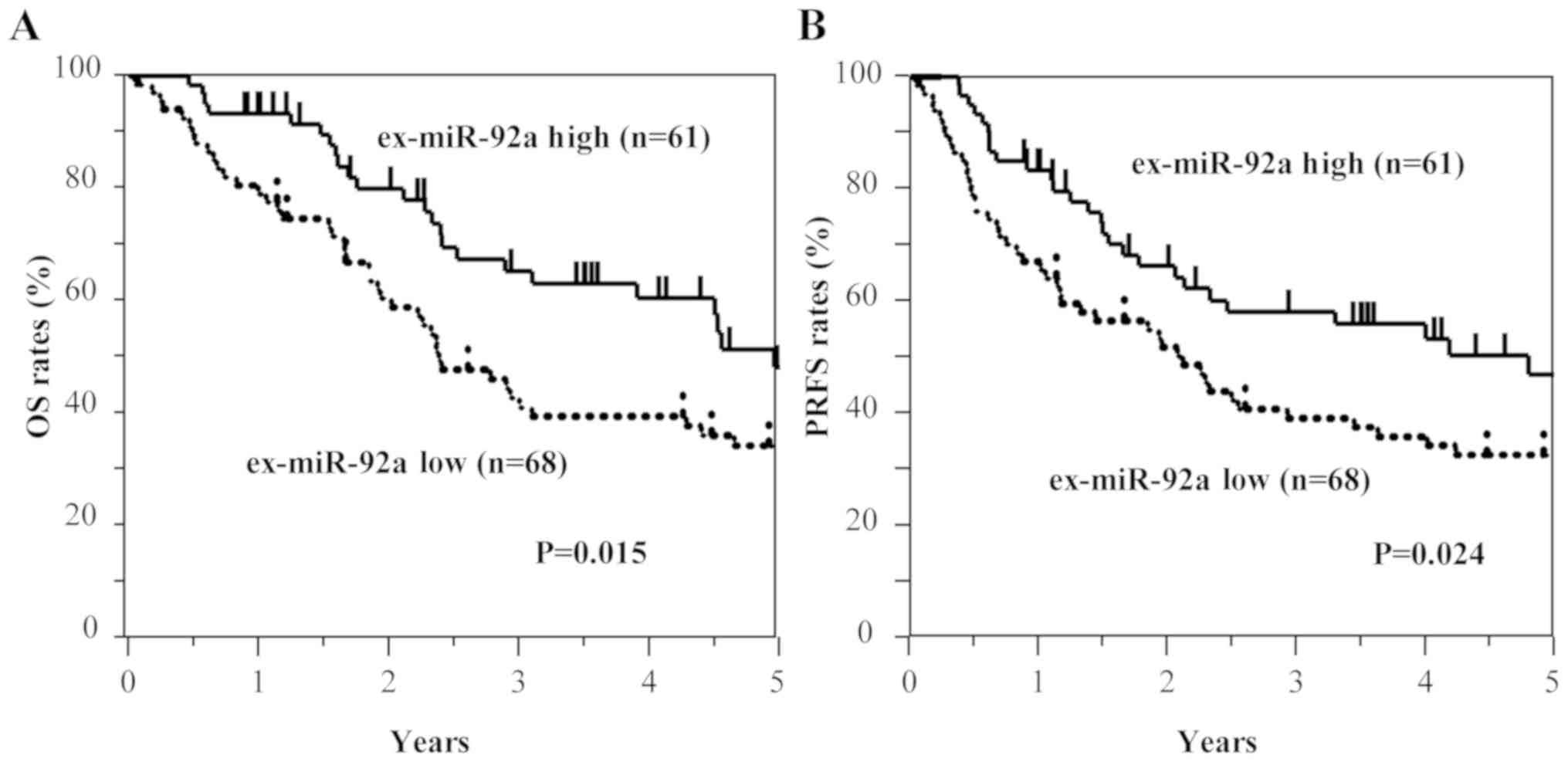
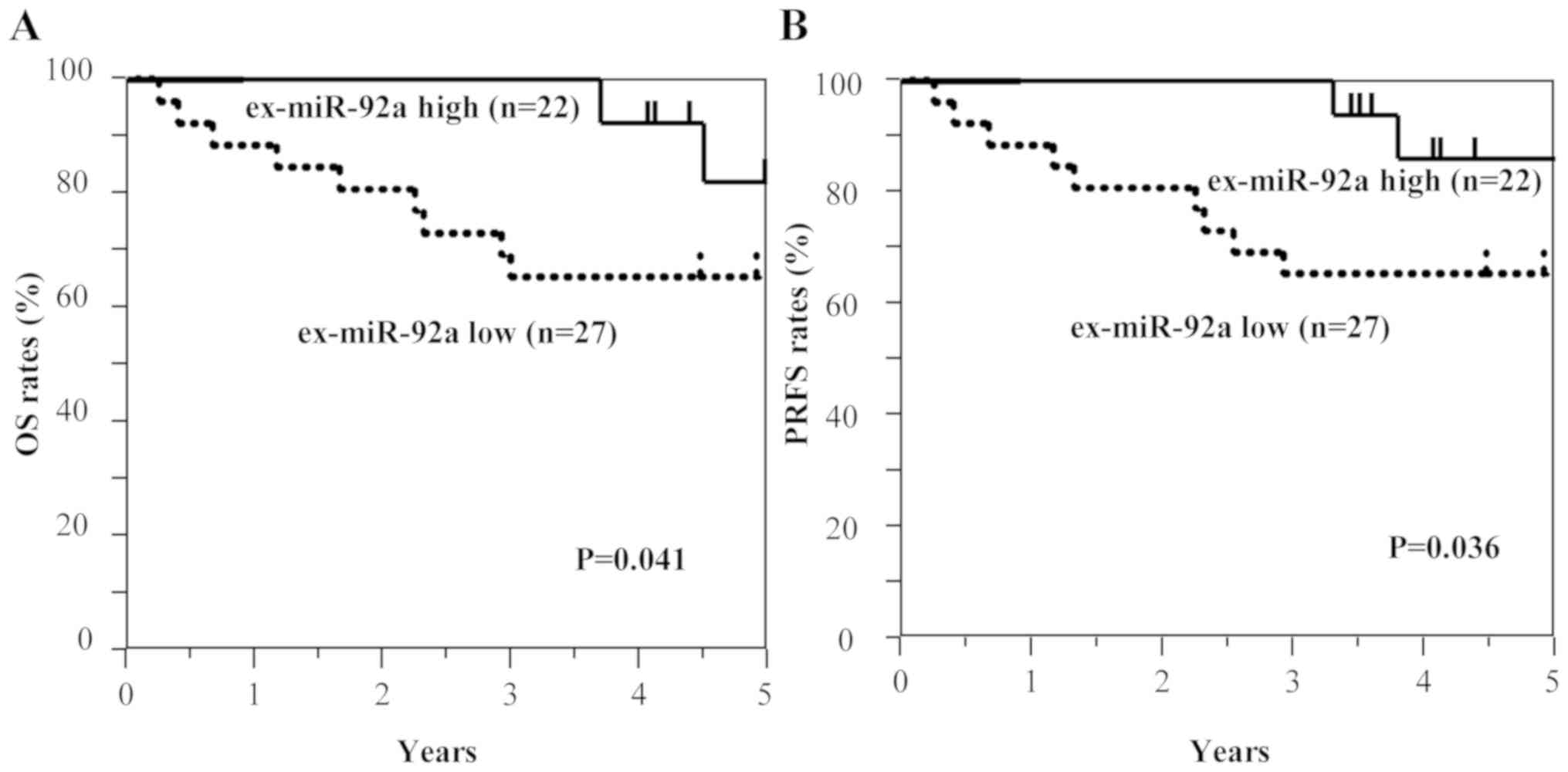
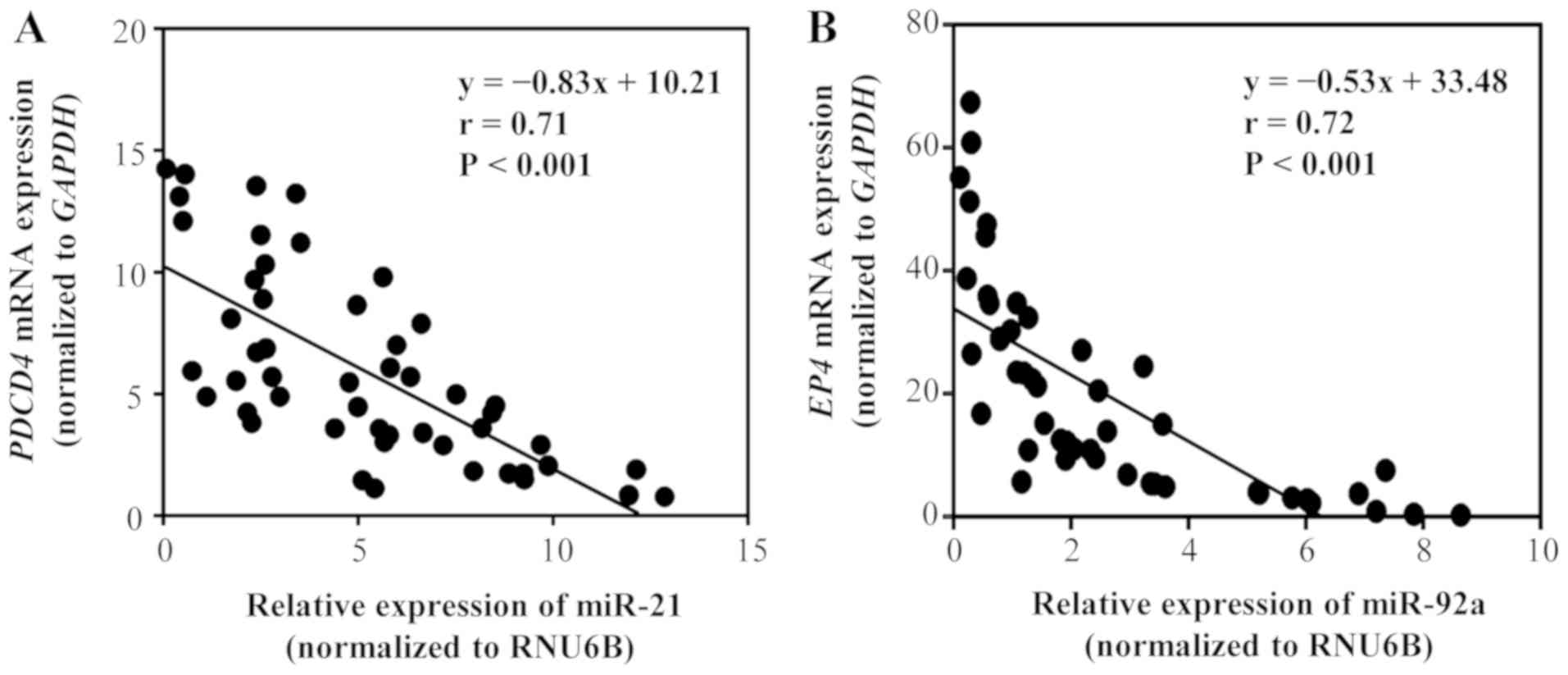
|
1
|
Hundahl SA, Menck HR, Mansour EG and
Winchester DP: The National Cancer Data Base report on gastric
carcinoma. Cancer. 80:2333–2341. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura
N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N and Schlemper RJ:
Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric
cancer. N Engl J Med. 345:784–789. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sasako M, Sakuramoto S, Katai H, Kinoshita
T, Furukawa H, Yamaguchi T, Nashimoto A, Fujii M, Nakajima T and
Ohashi Y: Five-year outcomes of a randomized phase III trial
comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 versus surgery alone in
stage II or III gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:4387–4393. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bando E, Yonemura Y, Takeshita Y,
Taniguchi K, Yasui T, Yoshimitsu Y, Fushida S, Fujimura T,
Nishimura G and Miwa K: Intraoperative lavage for cytological
examination in 1,297 patients with gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg.
178:256–262. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen KB, Chen J, Jin XL, Huang Y, Su QM
and Chen L: Exosome-mediated peritoneal dissemination in gastric
cancer and its clinical applications. Biomed Rep. 8:503–509.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sugarbaker PH and Yonemura Y: Clinical
pathway for the management of resectable gastric cancer with
peritoneal seeding: Best palliation with a ray of hope for cure.
Oncology. 58:96–107. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishigami H, Fujiwara Y, Fukushima R,
Nashimoto A, Yabusaki H, Imano M, Imamoto H, Kodera Y, Uenosono Y,
Amagai K, et al: Phase III trial comparing intraperitoneal and
intravenous paclitaxel plus S-1 versus cisplatin plus S-1 in
patients with gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis: PHOENIX-GC
trial. J Clin Oncol. 36:1922–1929. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jeung HC, Rha SY, Jang WI, Noh SH and
Chung HC: Treatment of advanced gastric cancer by palliative
gastrectomy, cytoreductive therapy and postoperative
intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Br J Surg. 89:460–466. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuramoto M, Shimada S, Ikeshima S, Matsuo
A, Yagi Y, Matsuda M, Yonemura Y and Baba H: Extensive
intraoperative peritoneal lavage as a standard prophylactic
strategy for peritoneal recurrence in patients with gastric
carcinoma. Ann Surg. 250:242–246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang P and Hu X: Strategies of diagnosis
and treatment for peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. Zhonghua
Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 20:500–503. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
La Torre M, Rossi Del Monte S, Ferri M,
Cosenza G, Mercantini P and Ziparo V: Peritoneal washing cytology
in gastric cancer. How, when and who will get a benefit? A review.
Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 57:43–51. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abe S, Yoshiwara H, Tabata H, Tachibana M,
Monden N, Nakamura T and Nagaoka S: Curative resection of gastric
cancer: Limitation of peritoneal lavage cytolology in predicating
the outcome. J Surg Oncol. 59:226–229. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Wang L, Wu Z, Sun R, Jin H, Ma J,
Liu L, Ling R, Yi J, Wang L, et al: Three dysregulated microRNAs in
serum as novel biomarkers for gastric cancer screening. Med Oncol.
31:2982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma GJ, Gu RM, Zhu M, Wen X, Li JT, Zhang
YY, Zhang XM and Chen SQ: Plasma post-operative miR-21 expression
in the prognosis of gastric cancers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:7551–7554. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng D, Liu Z and Du Y: Epigenetic
alterations as cancer diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive
biomarkers. Adv Genet. 71:125–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grady WM and Tewai M: The next thing in
prognostic molecular markers: MicroRNA signatures of cancer. Gut.
59:706–708. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kowal J, Tkach M and Thery C: Biogenesis
and secretion of exosome. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 29:116–125. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Palma J, Yaddannapudi SC, Pigati L, Havens
MA, Jeong S, Weiner GA, Weimer KM, Stern B, Hastings ML and Duelli
DM: MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized
particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:9125–9138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Silva M and Melo SA: Non-coding RNAs in
exosomes: New players in cancer biology. Curr Genomics. 16:295–303.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simons M and Raposo G: Exosomes-vesicular
carriers for intercelluar communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
21:575–581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ge Q, Zhou Y, Lu J, Bai Y, Xie X and Lu Z:
MiRNA in plasma exosome is stable under different storage
conditions. Molecules. 19:1567–1575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hannafon BN and Ding WQ: Intercellular
communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:14240–14269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dejima H, Iinuma H, Kanaoka R, Matsutani N
and Kawamura K: Exosomal microRNA in plasma as a non-invasive
biomarker for the recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol
Lett. 13:1256–1263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsukamoto M, Iinuma H, Yagi T, Matsuda K
and Hashiguchi Y: Circulating exosomal microRNA-21 as a biomarker
in each tumor stage of colorectal cancer. Oncology. 92:360–370.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanaoka R, Iinuma H, Dejima H, Sakai T,
Uehara H, Matsutani N and Kawamura M: Usefulness of plasma exosomal
microRNA-451a as a noninvasive biomarker for early prediction of
recurrence and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology.
94:311–323. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takahasi K, Iinuma H, Wada K, Minezaki S,
Kawamura S, Kainuma M, Ikeda Y, Shibuya M, Miura F and Sano K:
Usefulness of exosome-encapsulated microRNA-451a as a minimally
invasive biomarker for prediction of recurrence and prognosis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci.
25:155–161. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kumata Y, Iinuma H, Suzuki Y, Tsukahara D,
Midorikawa H, Igarashi Y, Soeda N, Kiyokawa T, Horikawa M and
Fukushima R: Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-23b as a minimally
invasive liquid biomarker for the prediction of recurrence and
prognosis of gastric cancer patients in each tumor stage. Oncol
Rep. 40:319–330. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bertero L, Massa F, Metovic J, Zanetti R,
Castellano I, Ricardi U, Papotti M and Cassoni P: Eighth edition of
the UICC classification of malignant tumours: An overview of the
changes in the pathological TNM classification criteria-what has
changed and why? Virchows Arch. 472:519–531. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng L, Sharples RA, Scicluna BJ and Hill
AF: Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for
biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood.
J Extracell Vesicles. 3:237432014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sun Z, Chen C, Su Y, Wang W, Yang S, Zhou
Q, Wang G, Li Z, Song J, Zhang Z, et al: Regulatory mechanisms and
clinical perspectives of circRNA in digestive system neoplasms. J
Cancer. 10:2885–2891. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang S, Wang J, Li J, Luo Q, Zhao M,
Zheng L, Dong X, Chen C, Che Y, Liu P, et al: Serum microRNA
expression profile as a diagnostic panel for gastric cancer. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 46:811–818. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu C, Ren C, Han J, Ding Y, Du J, Dai N,
Dai J, Ma H, Hu Z, Shen H, et al: A five-microRNA panel in plasma
was identified as a potential biomarker for early detection of
gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:2291–2299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao G, Jiang T, Liu Y, Huai G, Lan C, Li
G, Jia G, Wang K and Yang M: Droplet digital PCR-based circulating
microRNA detection serves as a promising diagnostic method for
gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:6762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang Z, Zhu D, Wu L, He M, Zhou X, Zhang
L, Zhang H, Wang W, Zhu J, Cheng W, et al: Six serum-based miRNAs
as potential diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 26:188–196. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Tsujiura M, Konishi
H, Takeshita H, Nagata H, Kawaguchi T, Hirajima S, Arita T,
Shiozaki A, et al: Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 in the
plasma of patients with gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
33:271–276. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng Y, Cui L, Sun W, Zhou H, Yuan X, Huo
M, Chen J, Lou Y and Guo J: MicroRNA-21 is a new marker of
circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark.
10:71–77. 2011-2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu HN, Wu H, Tseng YJ, Chen YJ, Zhang DY,
Zhu L, Dong L and Shen XZ: Serum microRNA signatures and
metabolomics have high diagnostic value in gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 18:4152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rana S, Malinowska K and Zöller M:
Exosomal tumor microRNA modulates premetastatic organ cells.
Neoplasia. 15:281–295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu Y, Luo F, Liu Y, Shi L, Lu X, Xu W and
Liu Q: Exosomal miR-21 derived from arsenite-transformed human
bronchial epithelial cells promotes cell proliferation associated
with arsenite carcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol. 89:1071–1082. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang J, Yang P, Guo Z, Yang R, Yang H,
Yang F, Li L and Xiang B: Overexpression of microRNA-21 strengthens
stem cell-like characteristics in a hepatocellular carcinoma cell
line. World J Surg Oncol. 14:2782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shin VY, Siu MT, Liu X, Ng EKO, Kwong A
and Chu KM: MiR-92 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis
by targeting EP4/Notch1 axis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
9:24209–24220. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mattick JS and Makunin IV: Non-coding RNA.
Hum Mol Genet. 15:R17–R29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon
T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, Labourier E and Hahn SA: MicroRNA
expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and
non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Oncogene. 26:4442–4452. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Mimori K, Tanaka F,
Kojima K, Uetake H, Sugihara K and Mori M: Clinicopathological and
prognostic significance of PDCD4 and microRNA-21 in human gastric
cancer. Int J Oncol. 36:1089–1095. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao Z, Yoon JH, Nam SW, Lee JY and Park
WS: PDCD4 expression inversely correlated with miR-21 levels in
gastric cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:611–619. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|