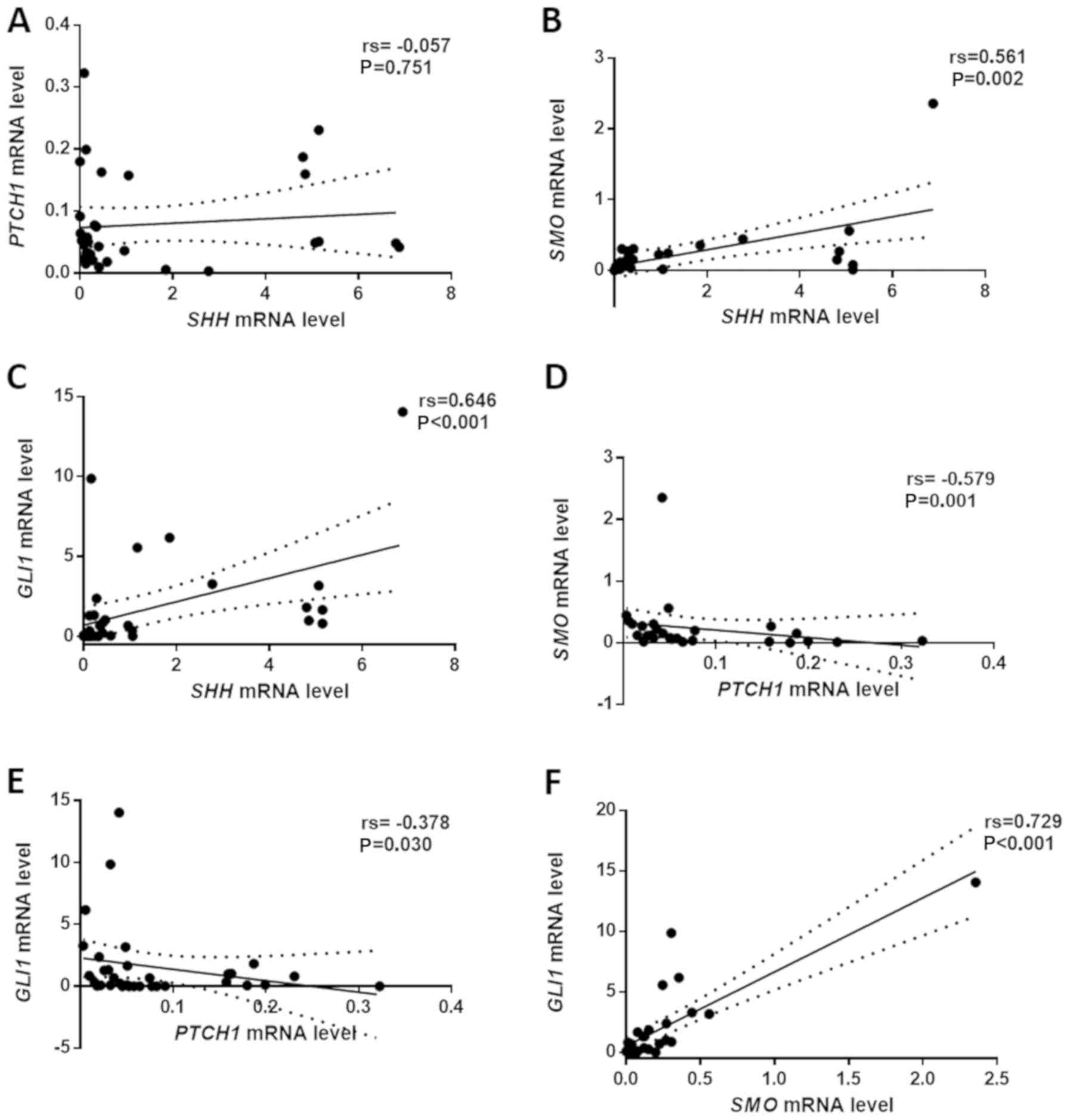
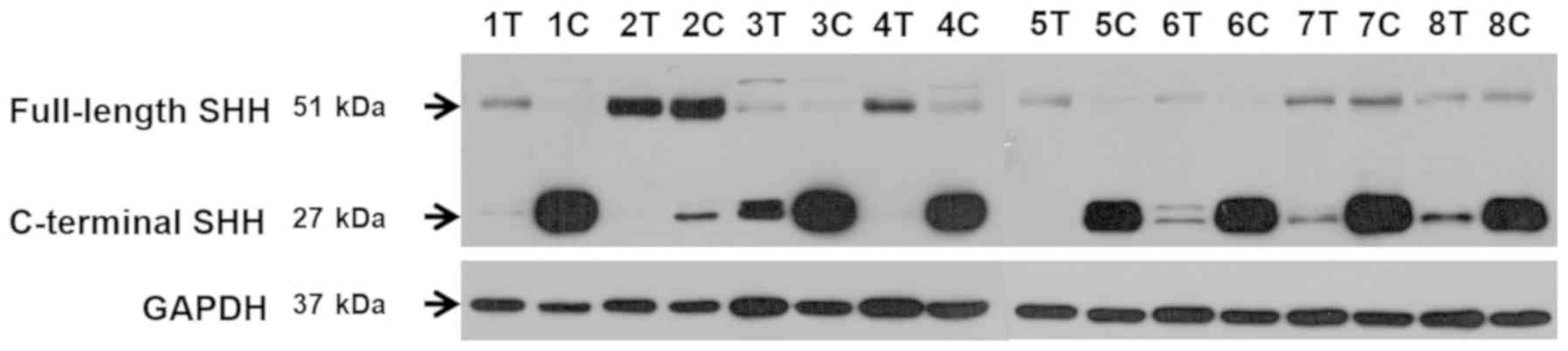
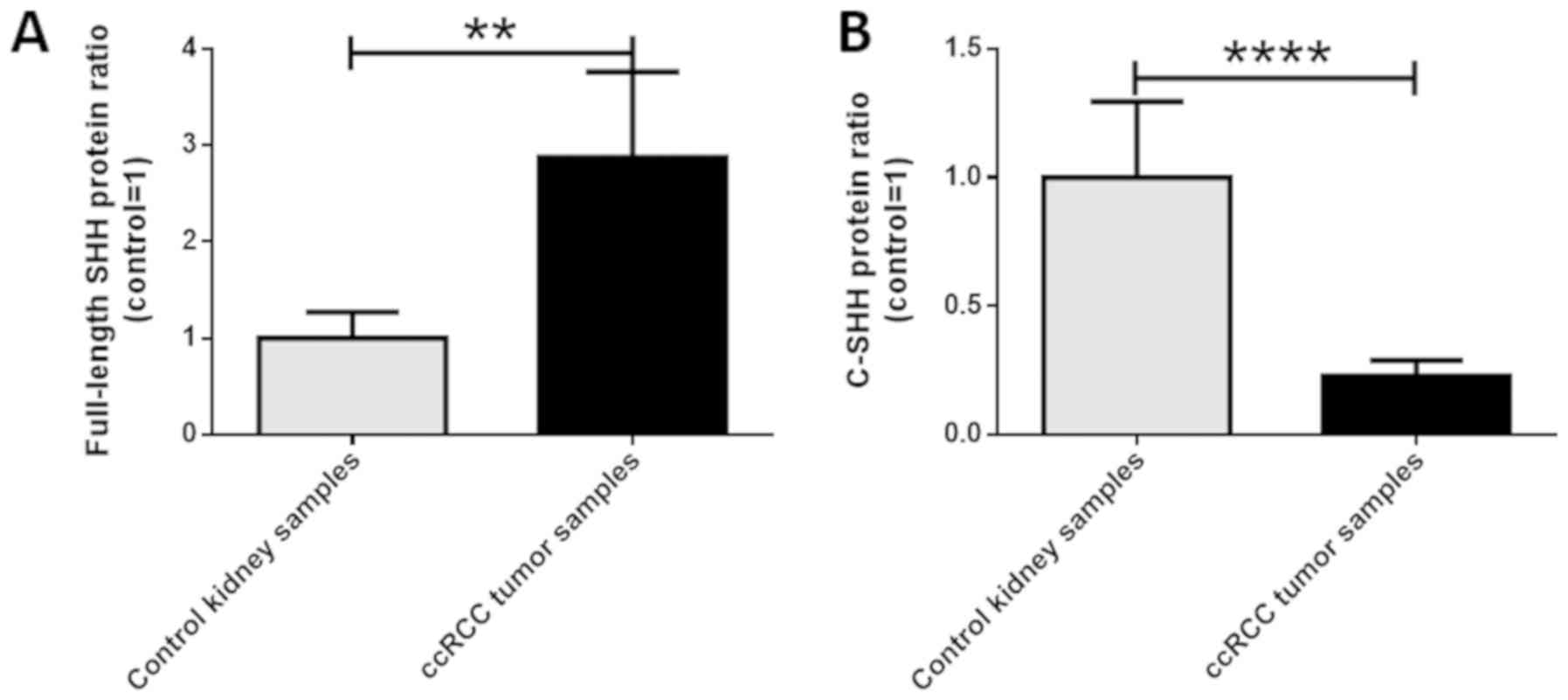
|
1
|
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton
C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M, Heng DY, Larkin J and Ficarra V: Renal
cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu J, Zhu L, Zheng LP, Cui Q, Zhu HH, Zhao
H, Shen ZJ, Dong HY, Chen SS, Wu WZ and Tan JM: Overexpression of
ULK1 represents a potential diagnostic marker for clear cell renal
carcinoma and the antitumor effects of SBI-0206965. EBioMedicine.
34:85–93. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sanchez DJ and Simon MC: Genetic and
metabolic hallmarks of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1870:23–31. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M,
Rioux-Leclercq N, Bex A, Khoo V, Grünwald V, Gillessen S and
Horwich A; ESMO Guidelines Committee, : Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO
clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
follow-up†. Ann Oncol. 30:706–720. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gupta S, Takebe N and LoRusso P: Targeting
the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2:237–250.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fattahi S, Pilehchian Langroudi M and
Akhavan-Niaki H: Hedgehog signaling pathway: Epigenetic regulation
and role in disease and cancer development. J Cell Physiol.
233:5726–5735. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choudhry Z, Rikani AA, Choudhry AM, Tariq
S, Zakaria F, Asghar MW, Sarfraz MK, Haider K, Shafiq AA and
Mobassarah NJ: Sonic hedgehog signalling pathway: A complex
network. Ann Neurosci. 21:28–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giroux Leprieur E, Tolani B, Li H, Leguay
F, Hoang NT, Acevedo LA, Jin JQ, Tseng HH, Yue D, Kim IJ, et al:
Membrane-bound full-length sonic hedgehog identifies cancer stem
cells in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
8:103744–103757. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Skoda AM, Simovic D, Karin V, Kardum V,
Vranic S and Serman L: The role of the hedgehog signaling pathway
in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 18:8–20.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Didiasova M, Schaefer L and Wygrecka M:
Targeting GLI transcription factors in cancer. Molecules.
23:E10032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buetti-Dinh A, Jensen R and Friedman R: A
computational study of hedgehog signalling involved in basal cell
carcinoma reveals the potential and limitation of combination
therapy. BMC Cancer. 18:5692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kubo M, Nakamura M, Tasaki A, Yamanaka N,
Nakashima H, Nomura M, Kuroki S and Katano M: Hedgehog signaling
pathway is a new therapeutic target for patients with breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 64:6071–6074. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu M, Li X, Liu T, Leng A and Zhang G:
Prognostic value of hedgehog signaling pathway in patients with
colon cancer. Med Oncol. 29:1010–1016. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saze Z, Terashima M, Kogure M, Ohsuka F,
Suzuki H and Gotoh M: Activation of the sonic hedgehog pathway and
its prognostic impact in patients with gastric cancer. Dig Surg.
29:115–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dormoy V, Danilin S, Lindner V, Thomas L,
Rothhut S, Coquard C, Helwig JJ, Jacqmin D, Lang H and Massfelder
T: The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is reactivated in human
renal cell carcinoma and plays orchestral role in tumor growth. Mol
Cancer. 8:1232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou J, Zhu G, Huang J, Li L, Du Y, Gao Y,
Wu D, Wang X, Hsieh JT, He D and Wu K: Non-canonical GLI1/2
activation by PI3K/AKT signaling in renal cell carcinoma: A novel
potential therapeutic target. Cancer Lett. 370:313–323. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Behnsawy HM, Shigemura K, Meligy FY,
Yamamichi F, Yamashita M, Haung WC, Li X, Miyake H, Tanaka K,
Kawabata M, et al: Possible role of sonic hedgehog and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell cancer progression.
Korean J Urol. 54:547–554. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eble JN; Weltgesundheitsorganisation and
International Agency for Research on Cancer, : Pathology and
genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs:
Editorial and consensus conference in Lyon, FranceDecember
14-18–2002, IARC Press; Lyon: 2006
|
|
19
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Nature. 499:43–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wierzbicki PM, Klacz J, Rybarczyk A,
Slebioda T, Stanislawowski M, Wronska A, Kowalczyk A, Matuszewski M
and Kmiec Z: Identification of a suitable qPCR reference gene in
metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol.
35:12473–12487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma Y, Zhang P, Wang F, Yang J, Yang Z and
Qin H: The relationship between early embryo development and
tumourigenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 14:2697–2701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang WG, Ye L, Ruge F, Sun PH, Sanders
AJ, Ji K, Lane J, Zhang L, Satherley L, Weeks HP, et al: Expression
of sonic hedgehog (SHH) in human lung cancer and the impact of
YangZheng XiaoJi on SHH-mediated biological function of lung cancer
cells and tumor growth. Anticancer Res. 35:1321–1331.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bian X, Sun H, Xue H, Zhang G, Zhang CH,
Liu XL, Su J and Li SJ: Expression and clinical significance of
Shh/Gli-1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
35:10523–10528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choe JY, Yun JY, Jeon YK, Kim SH, Choung
HK, Oh S, Park M and Kim JE: Sonic hedgehog signalling proteins are
frequently expressed in retinoblastoma and are associated with
aggressive clinicopathological features. J Clin Pathol. 68:6–11.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qi X, Schmiege P, Coutavas E, Wang J and
Li X: Structures of human patched and its complex with native
palmitoylated sonic hedgehog. Nature. 560:128–132. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin T and Matsui W: Hedgehog pathway as a
drug target: Smoothened inhibitors in development. Onco Targets
Ther. 5:47–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xin M, Ji X, De La Cruz LK, Thareja S and
Wang B: Strategies to target the Hedgehog signaling pathway for
cancer therapy. Med Res Rev. 38:870–913. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ding YL, Wang QS, Zhao WM and Xiang L:
Expression of smoothened protein in colon cancer and its prognostic
value for postoperative liver metastasis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:4001–4005. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Furukawa J, Miyake H and Fujisawa M: GLI2
expression levels in radical nephrectomy specimens as a predictor
of disease progression in patients with metastatic clear cell renal
cell carcinoma following treatment with sunitinib. Mol Clin Oncol.
5:186–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
ten Haaf A, Bektas N, von Serenyi S, Losen
I, Arweiler EC, Hartmann A, Knüchel R and Dahl E: Expression of the
glioma-associated oncogene homolog (GLI) 1 in human breast cancer
is associated with unfavourable overall survival. BMC Cancer.
9:2982009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He HC, Chen JH, Chen XB, Qin GQ, Cai C,
Liang YX, Han ZD, Dai QS, Chen YR, Zeng GH, et al: Expression of
hedgehog pathway components is associated with bladder cancer
progression and clinical outcome. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:349–355.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ciucci A, De Stefano I, Vellone VG, Lisi
L, Bottoni C, Scambia G, Zannoni GF and Gallo D: Expression of the
glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 (Gli1) in advanced serous
ovarian cancer is associated with unfavorable overall survival.
PLoS One. 8:e601452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carballo GB, Honorato JR, de Lopes GPF and
Spohr TCLSE: A highlight on Sonic hedgehog pathway. Cell Commun
Signal. 16:112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mukherjee S, Frolova N, Sadlonova A, Novak
Z, Steg A, Page GP, Welch DR, Lobo-Ruppert SM, Ruppert JM, Johnson
MR and Frost AR: Hedgehog signaling and response to cyclopamine
differ in epithelial and stromal cells in benign breast and breast
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:674–683. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Singh S, Wang Z, Liang Fei D, Black KE,
Goetz JA, Tokhunts R, Giambelli C, Rodriguez-Blanco J, Long J, Lee
E, et al: Hedgehog-producing cancer cells respond to and require
autocrine hedgehog activity. Cancer Res. 71:4454–4463. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maréchal R, Bachet JB, Calomme A, Demetter
P, Delpero JR, Svrcek M, Cros J, Bardier-Dupas A, Puleo F, Monges
G, et al: Sonic hedgehog and Gli1 expression predict outcome in
resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1215–1224.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Q, Zhang Y, Zhan H, Yuan Z, Lu P, Zhan
L and Xu W: The Hedgehog signalling pathway and its prognostic
impact in human gliomas. ANZ J Surg. 81:440–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cheng J, Gao J and Tao K: Prognostic role
of Gli1 expression in solid malignancies: A meta-analysis. Sci Rep.
6:221842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|