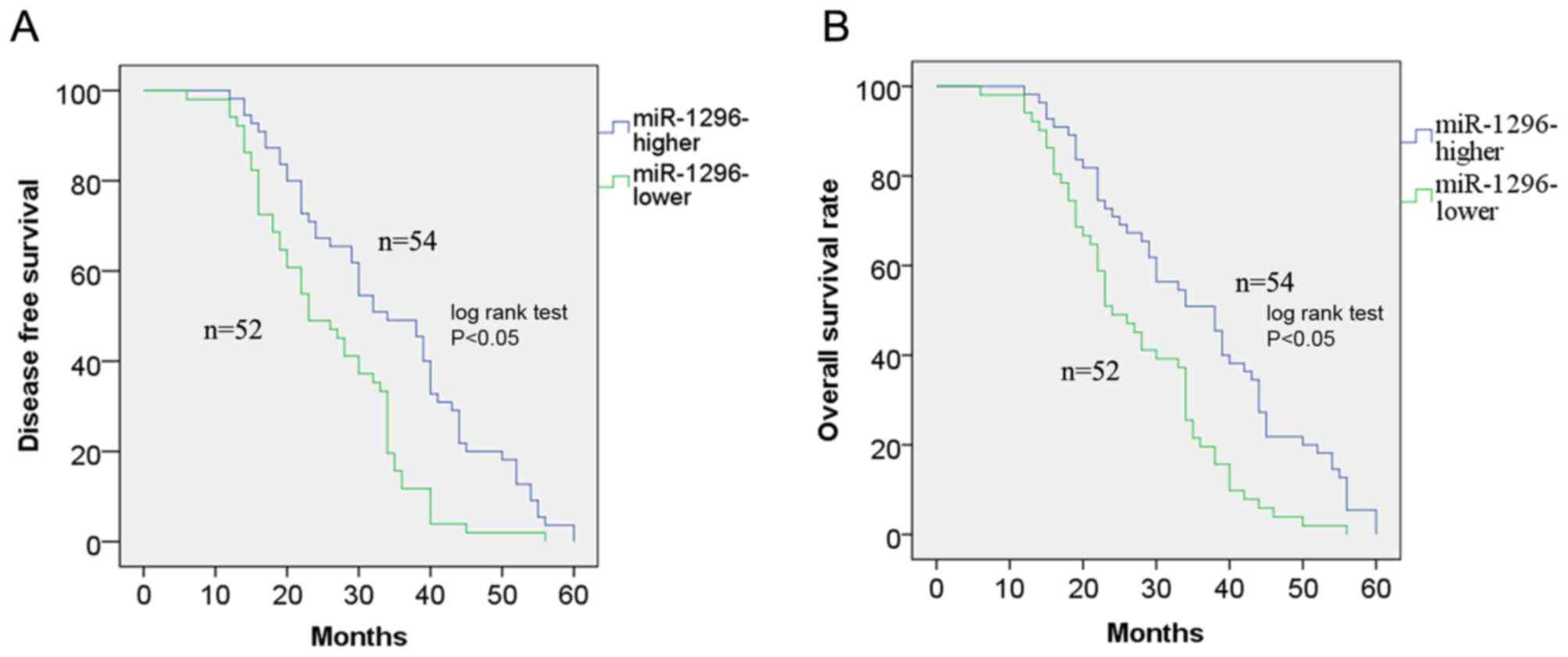
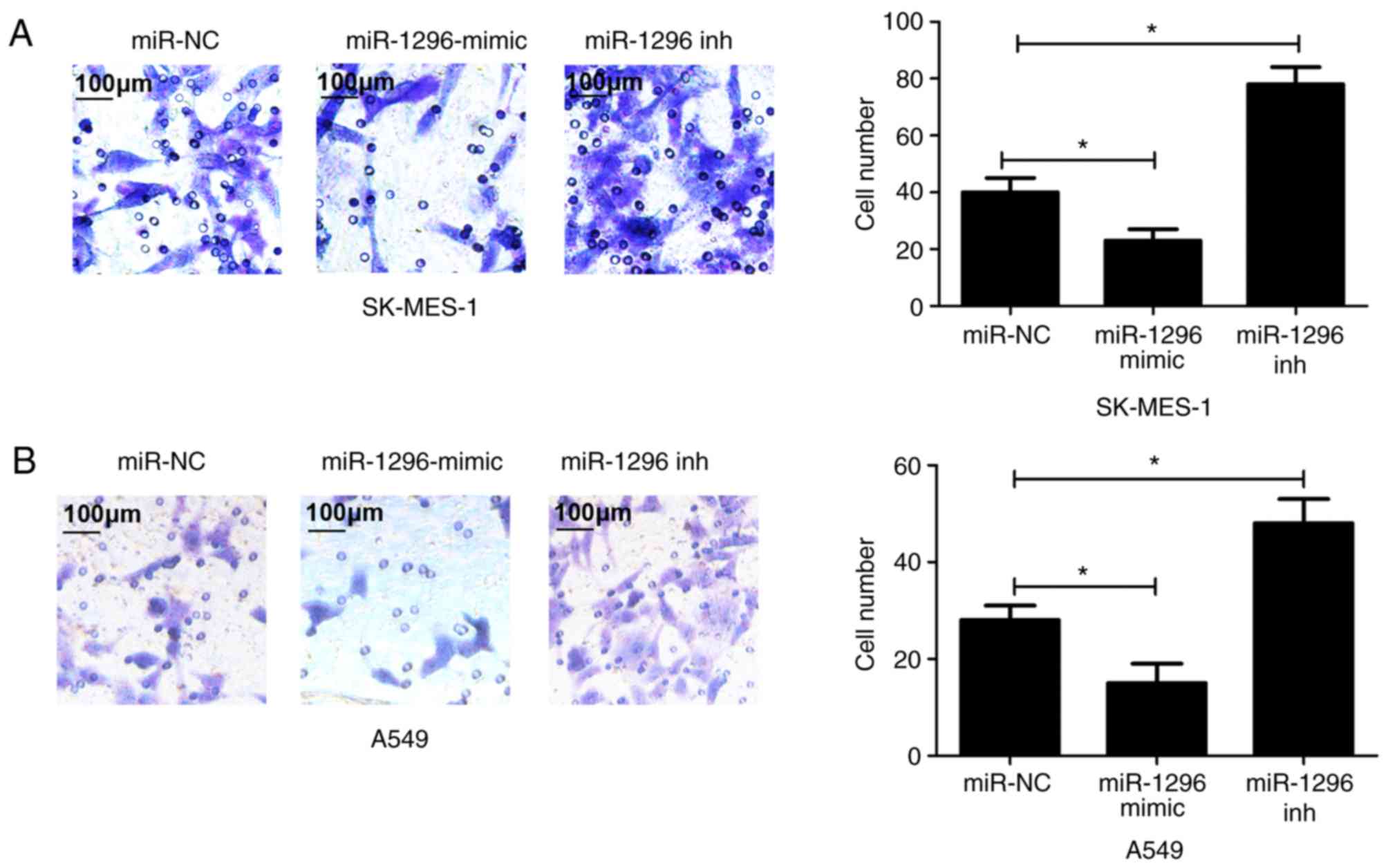
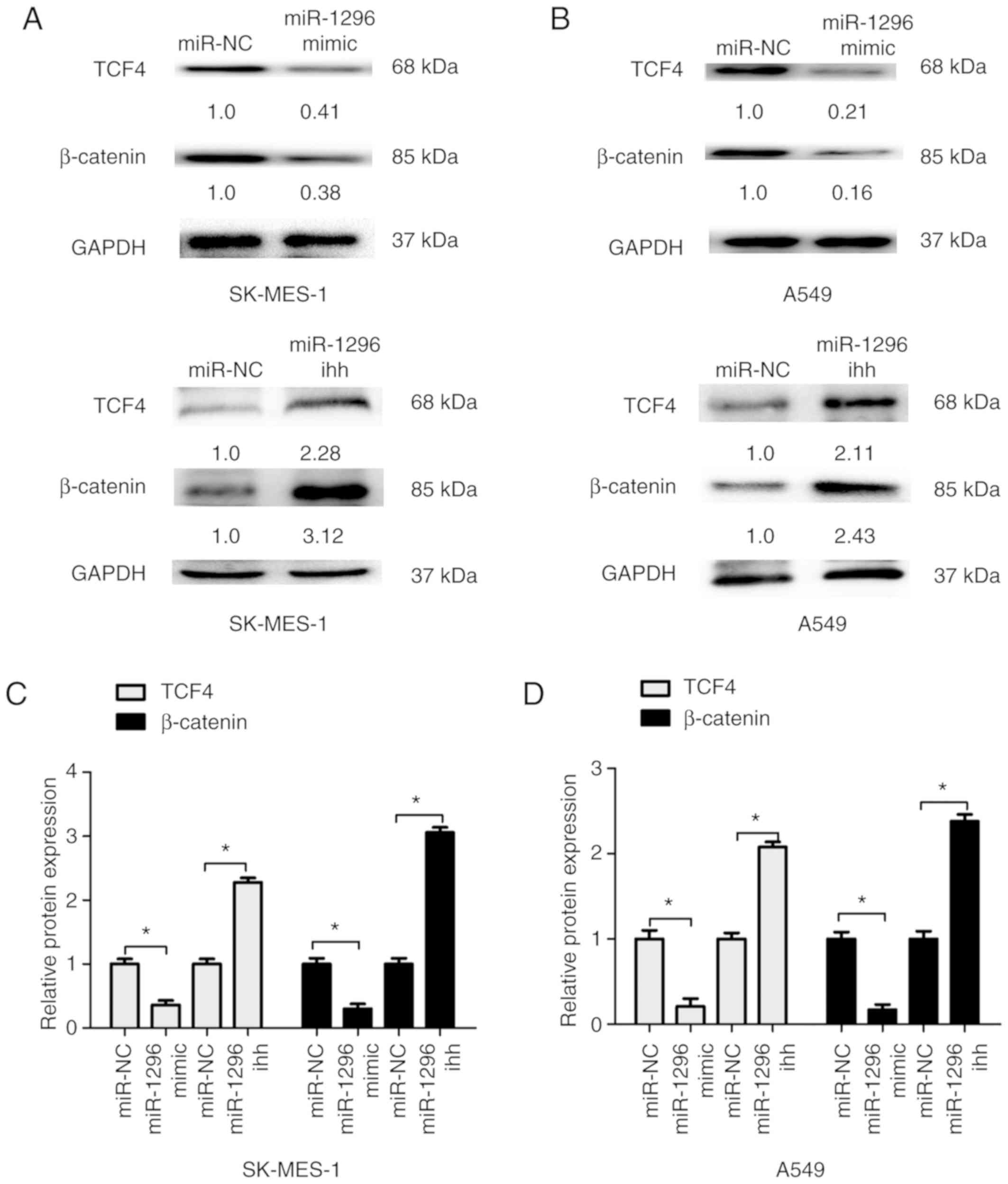
|
1
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carney DN and Hansen HH: Non-small-cell
lung cancer-stalemate or progress? N Engl J Med. 343:1261–1262.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sánchez de Cos J, Sojo González MA,
Montero MV, Pérez Calvo MC, Vicente MJ and Valle MH: Non-small cell
lung cancer and silent brain metastasis. Survival and prognostic
factors. Lung Cancer. 63:140–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suresh R, Ali S, Ahmad A, Philip PA and
Sarkar FH: The role of cancer stem cells in recurrent and
drug-resistant lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 890:57–74. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 96
(Suppl):R40–R44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu X, Zhu S, Tao Z and Ye S: High
circulating miR-18a, miR-20a, and miR-92a expression correlates
with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Med. 7:21–31. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang Z, Kong R, He Z, Lin LY, Qin SS,
Chen CY, Xie ZQ, Yu F, Sun GQ, Li CG, et al: High expression of
miR-493-5p positively correlates with clinical prognosis of non
small cell lung cancer by targeting oncogene ITGB1. Oncotarget.
8:47389–47399. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang X, Ke X, Pu Q, Yuan Y, Yang W, Luo
X, Jiang Q, Hu X, Gong Y, Tang K, et al: MicroRNA-410 acts as
oncogene in NSCLC through downregulating SLC34A2 via activating
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 7:14569–14585. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Okuyemi OT, Piccirillo JF and Spitznagel
E: TNM staging compared with a new clinicopathological model in
predicting oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma survival. Head Neck.
36:1481–1489. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Skrzypski M, Dziadziuszko R and Jassem J:
MicroRNA in lung cancer diagnostics and treatment. Mutat Res.
717:25–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gu Y, Cheng Y, Song Y, Zhang Z, Deng M,
Wang C, Zheng G and He Z: MicroRNA-493 suppresses tumor growth,
invasion and metastasis of lung cancer by regulating E2F1. PLoS
One. 9:e1026022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Min L, Wang F, Hu S, Chen Y, Yang J, Liang
S and Xu X: Aberrant microRNA-137 promoter methylation is
associated with lymph node metastasis and poor clinical outcomes in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:7744–7750.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanaoka R, Iinuma H, Dejima H, Sakai T,
Uehara H, Matsutani N and Kawamura M: Usefulness of plasma exosomal
MicroRNA-451a as a noninvasive biomarker for early prediction of
recurrence and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology.
94:311–323. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Wang T, Zhang Y, Wang H, Wu Y,
Liu K and Pei C: Upregulation of serum miR-494 predicts poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Biomark.
21:763–768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shan X, Wen W, Zhu D, Yan T, Cheng W,
Huang Z, Zhang L, Zhang H, Wang T, Zhu W, et al: miR 1296-5p
inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by
repressing ERBB2 expression. PLoS One. 12:e01702982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen G, He M, Yin Y, Yan T, Cheng W, Huang
Z, Zhang L, Zhang H, Liu P, Zhu W and Zhu Y: miR-1296-5p decreases
ERBB2 expression to inhibit the cell proliferation in
ERBB2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 17:952017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Tu J,
Li L, Bao H, Yang L and Tu K: MicroRNA-1296 inhibits metastasis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting SRPK1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cancer. 16:1032017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stewart DJ: Wnt signaling pathway in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt3562014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|