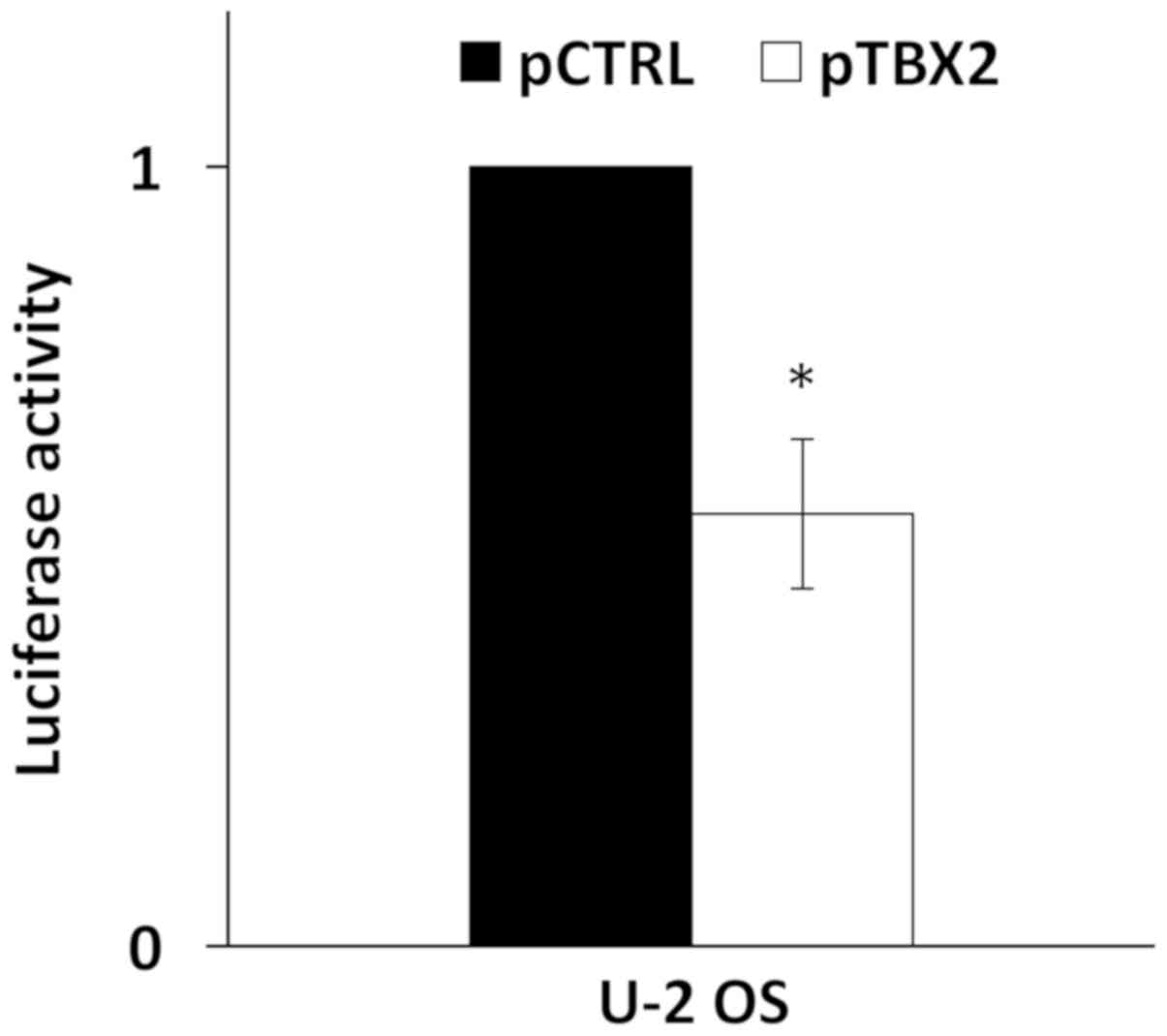
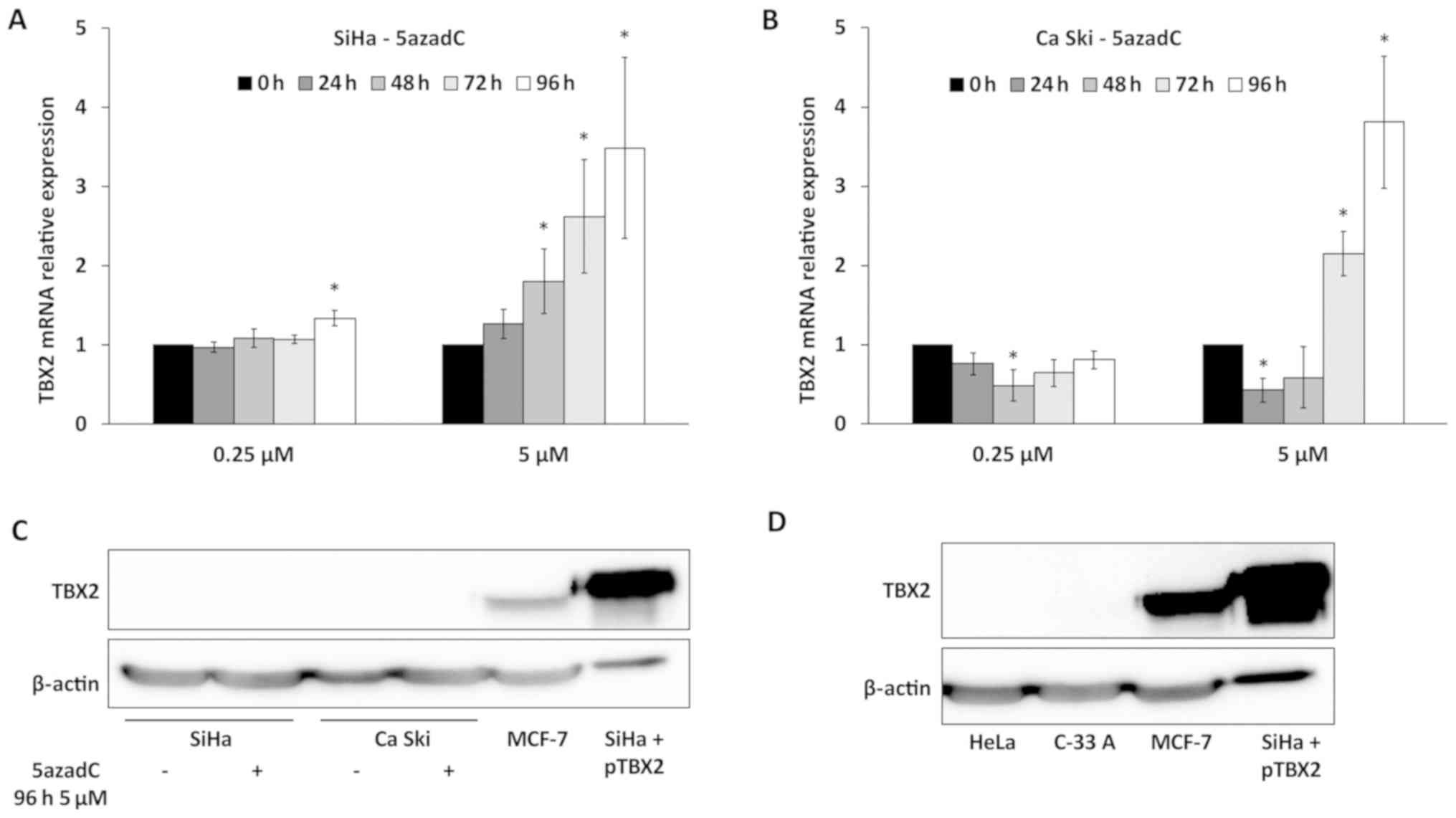
|
1
|
Doorbar J, Egawa N, Griffin H, Kranjec C
and Murakami I: Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease
association. Rev Med Virol. 25 (Suppl 1):S2–S23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM,
Levine AJ and Howley PM: The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human
papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53.
Cell. 63:1129–1136. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Münger K, Scheffner M, Huibregtse JM and
Howley PM: Interactions of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with tumour
suppressor gene products. Cancer Surv. 12:197–217. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huh K, Zhou X, Hayakawa H, Cho JY,
Libermann TA, Jin J, Harper JW and Munger K: Human papillomavirus
type 16 E7 oncoprotein associates with the cullin 2 ubiquitin
ligase complex, which contributes to degradation of the
retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. J Virol. 81:9737–9747. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
zur Hausen H: Human papillomaviruses in
the pathogenesis of anogenital cancer. Virology. 184:9–13. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jacquin E, Baraquin A, Ramanah R,
Carcopino X, Morel A, Valmary-Degano S, Bravo IG, de Sanjosé S,
Riethmuller D, Mougin C and Prétet JL: Methylation of human
papillomavirus Type 16 CpG sites at E2-binding site 1 (E2BS1),
E2BS2, and the Sp1-binding site in cervical cancer samples as
determined by high-resolution melting analysis-PCR. J Clin
Microbiol. 51:3207–3215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang C, Deng Z, Pan X, Uehara T, Suzuki M
and Xie M: Effects of methylation status of CpG sites within the
HPV16 long control region on HPV16-positive head and neck cancer
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01412452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stich M, Ganss L, Puschhof J, Prigge ES,
Reuschenbach M, Guiterrez A, Vinokurova S and von Knebel Doeberitz
M: 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (DAC) treatment downregulates the HPV E6
and E7 oncogene expression and blocks neoplastic growth of
HPV-associated cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:52104–52117.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morel A, Baguet A, Perrard J, Demeret C,
Jacquin E, Guenat D, Mougin C and Prétet JL: 5azadC treatment
upregulates miR-375 level and represses HPV16 E6 expression.
Oncotarget. 8:46163–46176. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung HM, Phillips BL and Chan EK: miR-375
activates p21 and suppresses telomerase activity by coordinately
regulating HPV E6/E7, E6AP, CIP2A, and 14-3-3ζ. Mol Cancer.
13:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schneider MA, Scheffer KD, Bund T,
Boukhallouk F, Lambert C, Cotarelo C, Pflugfelder GO, Florin L and
Spoden GA: The transcription factors TBX2 and TBX3 interact with
human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) L2 and repress the long control
region of HPVs. J Virol. 87:4461–4474. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wansleben S, Peres J, Hare S, Goding CR
and Prince S: T-box transcription factors in cancer biology.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:380–391. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abrahams A, Parker MI and Prince S: The
T-box transcription factor Tbx2: Its role in development and
possible implication in cancer. IUBMB Life. 62:92–102.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du WL, Fang Q, Chen Y, Teng JW, Xiao YS,
Xie P, Jin B and Wang JQ: Effect of silencing the T-Box
transcription factor TBX2 in prostate cancer PC3 and LNCaP cells.
Mol Med Rep. 16:6050–6058. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khalil A, Dekmak B, Boulos F, Kantrowitz
J, Spira A, Fujimoto J, Kadara H, El-Hachem N and Nemer G:
Transcriptomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma unveil new
mechanisms targeted by the TBX2 subfamily of tumor suppressor
genes. Front Oncol. 8:4822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khalil AA, Sivakumar S, Lucas FAS,
McDowell T, Lang W, Tabata K, Fujimoto J, Yatabe Y, Spira A, Scheet
P, et al: TBX2 subfamily suppression in lung cancer pathogenesis: A
high-potential marker for early detection. Oncotarget.
8:68230–68241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rani L, Mathur N, Gupta R, Gogia A, Kaur
G, Dhanjal JK, Sundar D, Kumar L and Sharma A: Genome-wide DNA
methylation profiling integrated with gene expression profiling
identifiesPAX9as a novel prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. Clin Epigenetics. 9:572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Farkas SA, Sorbe BG and Nilsson TK:
Epigenetic changes as prognostic predictors in endometrial
carcinomas. Epigenetics. 12:19–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kandimalla R, van Tilborg AA, Kompier LC,
Stumpel DJ, Stam RW, Bangma CH and Zwarthoff EC: Genome-wide
analysis of CpG island methylation in bladder cancer identified
TBX2, TBX3, GATA2, and ZIC4 as pTa-specific prognostic markers. Eur
Urol. 61:1245–1256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gangat N, Patnaik MM and Tefferi A:
Myelodysplastic syndromes: Contemporary review and how we treat. Am
J Hematol. 91:76–89. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nieto M, Demolis P, Béhanzin E, Moreau A,
Hudson I, Flores B, Stemplewski H, Salmonson T, Gisselbrecht C,
Bowen D and Pignatti F: The european medicines agency review of
decitabine (Dacogen) for the treatment of adult patients with acute
myeloid leukemia: Summary of the scientific assessment of the
committee for medicinal products for human use. Oncologist.
21:692–700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Biktasova A, Hajek M, Sewell A, Gary C,
Bellinger G, Deshpande HA, Bhatia A, Burtness B, Judson B, Mehra S,
et al: Demethylation therapy as a targeted treatment for human
papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
23:7276–7287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Prince S, Carreira S, Vance KW, Abrahams A
and Goding CR: Tbx2 directly represses the expression of the
p21(WAF1) cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res.
64:1669–1674. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jacobs JJ, Keblusek P, Robanus-Maandag E,
Kristel P, Lingbeek M, Nederlof PM, van Welsem T, van de Vijver MJ,
Koh EY, Daley GQ and van Lohuizen M: Senescence bypass screen
identifies TBX2, which represses Cdkn2a (p19(ARF)) and is amplified
in a subset of human breast cancers. Nat Genet. 26:291–299. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vance KW, Carreira S, Brosch G and Goding
CR: Tbx2 is overexpressed and plays an important role in
maintaining proliferation and suppression of senescence in
melanomas. Cancer Res. 65:2260–2268. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harrelson Z, Kelly RG, Goldin SN,
Gibson-Brown JJ, Bollag RJ, Silver LM and Papaioannou VE: Tbx2 is
essential for patterning the atrioventricular canal and for
morphogenesis of the outflow tract during heart development.
Development. 131:5041–5052. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lüdtke TH, Rudat C, Wojahn I, Weiss AC,
Kleppa MJ, Kurz J, Farin HF, Moon A, Christoffels VM and Kispert A:
Tbx2 and Tbx3 act downstream of shh to maintain canonical wnt
signaling during branching morphogenesis of the murine lung. Dev
Cell. 39:239–253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu B, Zhang M, Williams EM, Keller C,
Mansoor A and Davie JK: TBX2 represses PTEN in rhabdomyosarcoma and
skeletal muscle. Oncogene. 35:4212–4224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Redmond KL, Crawford NT, Farmer H, D'Costa
ZC, O'Brien GJ, Buckley NE, Kennedy RD, Johnston PG, Harkin DP and
Mullan PB: T-box 2 represses NDRG1 through an EGR1-dependent
mechanism to drive the proliferation of breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 29:3252–3262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|