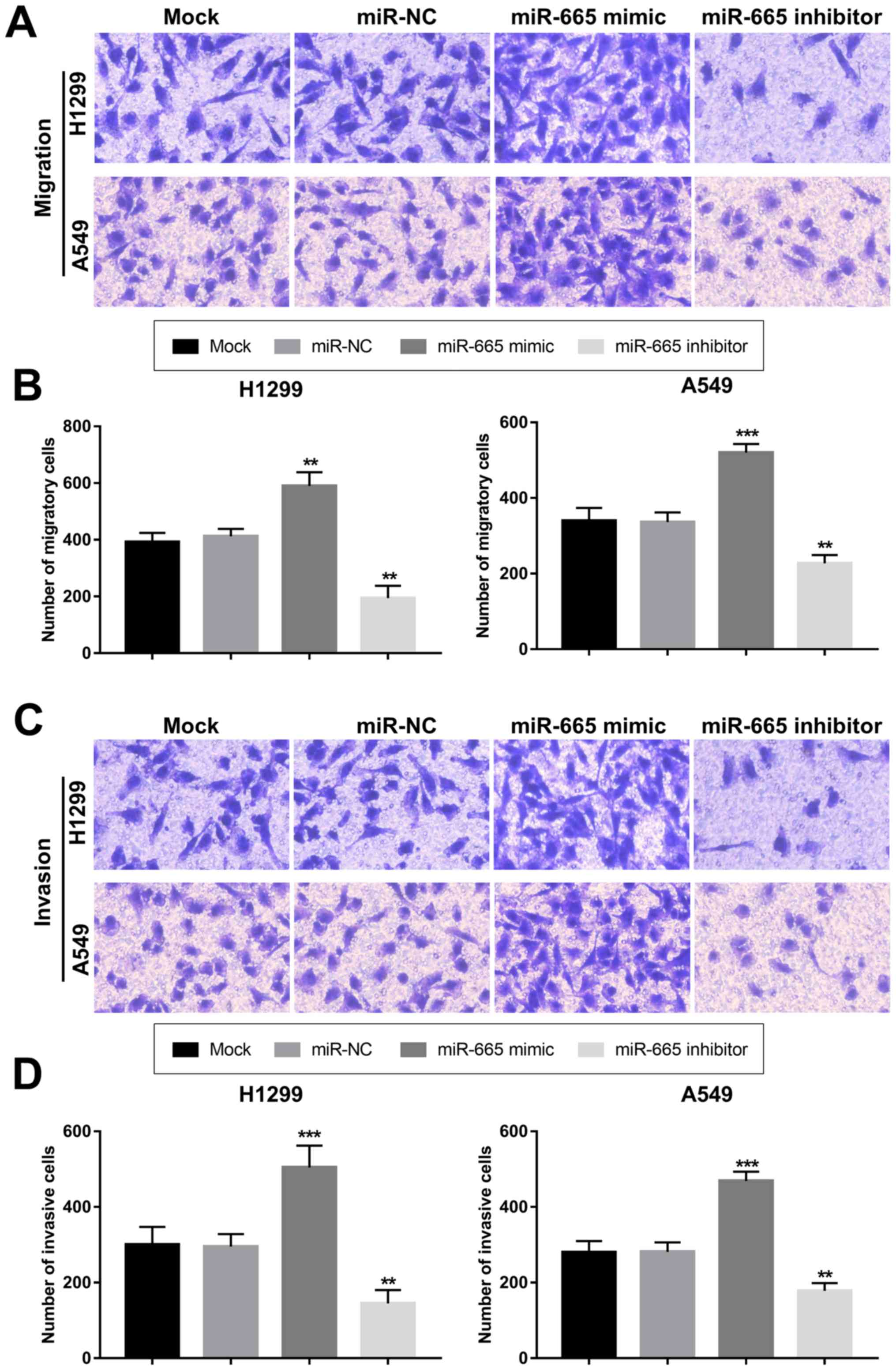
|
1
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akhurst T: Staging of non-small-cell lung
cancer. PET Clin. 13:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Blandin Knight S, Crosbie PA, Balata H,
Chudziak J, Hussell T and Dive C: Progress and prospects of early
detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 7(pii): 1700702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Woodard GA, Jones KD and Jablons DM: Lung
cancer staging and prognosis. Cancer Treat Res. 170:47–75. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu DM, Liu T, Deng SH, Han R and Xu Y:
SLC39A4 expression is associated with enhanced cell migration,
cisplatin resistance, and poor survival in non-small cell lung
cancer. Sci Rep. 7:72112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xue J, Yang J, Luo M, Cho WC and Liu X:
MicroRNA-targeted therapeutics for lung cancer treatment. Expert
Opin Drug Discov. 12:141–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang D, Sun W, Zhou Y, Li P, Chen F, Chen
H, Xia D, Xu E, Lai M, Wu Y and Zhang H: Mutations of key driver
genes in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 37:173–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu J, Zhan Y, Feng J, Luo J and Fan S:
MicroRNAs associated with therapy of non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Biol Sci. 14:390–397. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hwang DW, Kim HY, Li F, Park JY, Kim D,
Park JH, Han HS, Byun JW, Lee YS, Jeong JM, et al: In vivo
visualization of endogenous miR-21 using hyaluronic acid-coated
graphene oxide for targeted cancer therapy. Biomaterials.
121:144–154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Duo Y, Bi J, Zeng X, Mei L, Bao S,
He L, Shan A, Zhang Y and Yu X: Targeted delivery of anti-miR-155
by functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for colorectal
cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 13:1241–1256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu J, Zhang X, Huang Y, Zhang Q, Zhou J,
Zhang X and Wang X: miR-200b and miR-200c co-contribute to the
cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells by targeting DNA
methyltransferases. Oncol Lett. 17:1453–1460. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
An JC, Shi HB, Hao WB, Zhu K and Ma B:
miR-944 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by targeting
STAT1 interaction. Oncol Lett. 17:3790–3798. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong M, Xie Y and Xu Y: miR-7-5p regulates
the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells by
negatively regulating the expression of Krüppel-like factor 4.
Oncol Lett. 17:3241–3246. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang F, Chen L and Wang ZJ: MicroRNA-32
inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human colon
cancer cell lines by targeting E2F transcription factor 5. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:4156–4163. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qiao G, Li J, Wang J, Wang Z and Bian W:
miR-381 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting ETS1 in
pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Med. 44:593–607. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Yu M, Liu Z and Liu B: Clinical
significance of serum miR-25 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J
Biomed Sci. 76:111–116. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin X, Guan Y, Sheng H and Liu Y:
Crosstalk in competing endogenous RNA network reveals the complex
molecular mechanism underlying lung cancer. Oncotarget.
8:91270–91280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li C, Qin F, Hu F, Xu H, Sun G, Han G,
Wang T and Guo M: Characterization and selective incorporation of
small non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer extracellular
vesicles. Cell Biosci. 8:22018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu C, Huang Q and Zhu H: miR-383
inhibited the cell cycle progression of gastric cancer cells via
targeting cyclin E2. DNA Cell Biol. 38:849–856. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao W, Zhang Y, Niu M, Bo Y, Li H, Xue X,
Lu Y, Zheng X, Tang Y, Cui J, et al: Identification of
miR-145-5p-centered competing endogenous RNA network in laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma. Proteomics. 19:e19000202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tao L, Wu YQ and Zhang SP: MiR-21-5p
enhances the progression and paclitaxel resistance in
drug-resistant breast cancer cell lines by targeting PDCD4.
Neoplasma. 66:746–755. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang R, Li G, Zhuang G, Sun S and Song Z:
Overexpression of microRNA-423-3p indicates poor prognosis and
promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung
cancer. Diagn Pathol. 14:532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Wang L, Yao B, Liu Q and Guoa C:
miR-1307-3p promotes tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by repressing DAB2 interacting protein. Biomed
Pharmacother. 117:1090552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu X, Lu Y, Xu Y, Hou S, Huang J, Wang B,
Zhao J, Xia S, Fan S, Yu X, et al: Exosomal transfer of miR-501
confers doxorubicin resistance and tumorigenesis via targeting of
BLID in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 459:122–134. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zou JG, Ma LF, Li X, Xu FL, Fei XZ, Liu Q,
Bai QL and Dong YL: Circulating microRNA array (miR-182, 200b and
205) for the early diagnosis and poor prognosis predictor of
non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:1108–1115. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun Y, Yang B, Lin M, Yu H, Chen H and
Zhang Z: Identification of serum miR-30a-5p as a diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark.
24:299–305. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Du H, Xu Q, Xiao S, Wu Z, Gong J, Liu C,
Ren G and Wu H: MicroRNA-424-5p acts as a potential biomarker and
inhibits proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting TRIM29. Life Sci. 224:1–11. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang SY, Li Y, Jiang YS and Li RZ:
Investigation of serum miR-411 as a diagnosis and prognosis
biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:4092–4097. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang Z, Li X, Liu S, Li C, Wang X and
Xing J: MiR-141-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
invasion by targeting TRAF5 in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 514:699–705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Z, Gao Y, Gao S, Song D and Feng Y:
MiR-135b-5p promotes viability, proliferation, migration and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4
(KLF4). Arch Med Sci. 16:167–176. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Long X, Shi Y, Ye P, Guo J, Zhou Q and
Tang Y: MicroRNA-99a suppresses breast cancer progression by
targeting FGFR3. Front Oncol. 9:14732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu Y, Yang C, Yang S, Cheng F, Rao J and
Wang X: miR-665 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration,
invasion, and proliferation by decreasing Hippo signaling through
targeting PTPRB. Cell Death Dis. 9:9542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao XG, Hu JY, Tang J, Yi W, Zhang MY,
Deng R, Mai SJ, Weng NQ, Wang RQ, Liu J, et al: miR-665 expression
predicts poor survival and promotes tumor metastasis by targeting
NR4A3 in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 10:4792019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Jiang Y, Wan Y, Zhou S, Thapa S and
Cheng W: MicroRNA-665 suppresses the growth and migration of
ovarian cancer cells by targeting HOXA10. Mol Med Rep.
18:2661–2668. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qi Y, Dai Y and Gui S: Protein tyrosine
phosphatase PTPRB regulates Src phosphorylation and tumour
progression in NSCLC. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 43:1004–1012.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|