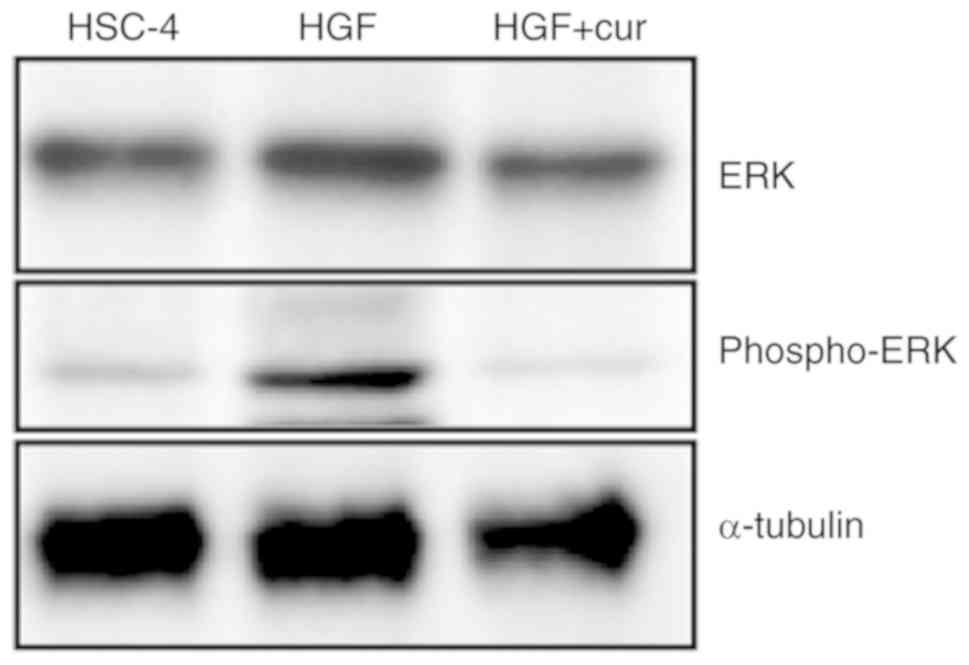
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohen EE, Lingen MW and Vokes EE: The
expanding role of systemic therapy in head and neck cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 22:1743–1752. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kramer RH, Shen X and Zhou H: Tumor cell
invasion and survival in head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 24:35–45. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ziober AF, Falls EM and Ziober BL: The
extracellular matrix in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Friend or
foe? Head Neck. 28:740–749. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K,
Bronner-Fraser M and Nieto MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions:
The importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J
Clin Invest. 119:1438–1449. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumor progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krisanaprakornkit S and Iamaroon A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
ISRN Oncol. 2012:6814692012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scheel C and Weinberg RA: Cancer stem
cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Concepts and molecular
links. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:396–403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morel AP, Lièvre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G,
Ansieau S and Puisieux A: Generation of breast cancer stem cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 3:e28882008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang X, Gan G, Wang X, Xu T and Xie W:
The HGF-MET axis coordinates liver cancer metabolism and autophagy
for chemotherapeutic resistance. Autophagy. 15:1258–1279. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ismail NI, Othman I, Abas F, H Lajis N and
Naidu R: Mechanism of apoptosis induced by curcumin in colorectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:E24542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wong KE, Ngai SC, Chan KG, Lee LH, Goh BH
and Chuah LH: Curcumin nanoformulations for colorectal cancer: A
review. Front Pharmacol. 10:1522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bahrami A, Majeed M and Sahebkar A:
Curcumin: A potent agent to reverse epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Oncol. 42:405–421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Qu C, Xie F, Chen L, Liu L, Liang
X, Wu X, Wang P and Meng Z: Curcumin suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of pancreatic
cancer cells by inhibiting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Am J
Cancer Res. 7:125–133. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang Z, Lu L, Mao J, Li X, Qian H and Xu
W: Curcumin reversed chronic tobacco smoke exposure induced
urocystic EMT and acquisition of cancer stem cells properties via
Wnt/β-catenin. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiao D, Wang J, Lu W, Tang X, Chen J, Mou
H and Chen QY: Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis
through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways
in lung cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 3:160182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohnishi Y, Yasui H, Kakudo K and Nozaki M:
Cetuximab-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma cells become
sensitive in anchorage-independent culture conditions through the
activation of the EGFR/AKT pathway. Int J Oncol. 47:2165–2172.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohnishi Y, Yasui H, Kakudo K and Nozaki M:
Regulation of cell migration via the EGFR signaling pathway in oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 13:930–936. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yasui H, Ohnishi Y, Nakajima M and Nozaki
M: Migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells are induced by
HGF/c-Met signalling via lamellipodia and filopodia formation.
Oncol Rep. 37:3674–3680. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tong W, Wang Q, Sun D and Suo J: Curcumin
suppresses colon cancer cell invasion via AMPK-induced inhibition
of NF-κB, uPA activator and MMP9. Oncol Lett. 12:4139–4146. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locasioa A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shimada S, Mimata A, Sekine M, Mogushi K,
Akiyama Y, Fukamachi H, Jonkers J, Tanaka H, Eishi Y and Yuasa Y:
Synergistic tumour suppressor activity of E-cadherin and p53 in a
conditional mouse model for metastatic diffuse-type gastric cancer.
Gut. 61:344–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Organ SL and Tsao MS: An overview of the
c-MET signaling pathway. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 3:S7–S19. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Baldanzi G and Graziani A: Physiological
signaling and structure of the HGF receptor MET. Biomedicines.
3:1–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Parikh RA, Wang P, Beumer JH, Chu E and
Appleman LJ: The potential roles of hepatocyte growth factor
(HGF)-MET pathway inhibitors in cancer treatment. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:969–983. 2014.
|
|
32
|
Stamenkovic I: Matrix metalloproteinases
in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 10:415–433.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moulik S, Pal S, Biswas J and Chatterjee
A: Role of ERK in modulating MMP 2 and MMP 9 with respect to tumour
invasiveness in human cancer cell line MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. J
Tumor. 2:87–98. 2014.
|
|
34
|
Martin TA, Mason MD and Jiang WG:
Hepatocyte growth factor signaling in cancer metastasis. Curr
Signal Transduct Ther. 6:180–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Grotegut S, von Schweinitz D, Christofori
G and Lehembre F: Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering
through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J.
25:3534–3545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Migliore C and Giordano S: Molecular
cancer therapy: Can our expectation be MET? Eur J Cancer.
44:641–651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ohnishi Y, Lieger O, Attygalla M, Iizuka T
and Kakudo K: Effects of epidermal growth factor on the invasion
activity of the oral cancer cell lines HSC3 and SAS. Oral Oncol.
44:1155–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Davies G, Watkins G, Mason MD and Jiang
WG: Targeting the HGF/SF receptor c-met using a hammerhead ribozyme
transgene reduces in vitro invasion and migration in prostate
cancer cells. Prostate. 60:317–324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Park W, Amin AR, Chen ZG and Shin DM: New
perspectives of curcumin in cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 6:387–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen HW, Lee JY, Huang JY, Wang CC, Chen
WJ, Su SF, Huang CW, Ho CC, Chen JJ, Tsai MF, et al: Curcumin
inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis through the tumor
suppressor HLJ1. Cancer Res. 68:7428–7438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ohnishi Y, Yasui H, Kakudo K and Nozaki M:
Lapatinib-resistant cancer cells possessing epithelial cancer stem
cell properties develop sensitivity during sphere formation by
activation of the ErbB/AKT/cyclin D2 pathway. Oncol Rep.
36:3058–3064. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Siddappa G, Kulsum S, Ravindra DR, Kumar
VV, Raju N, Raghavan N, Sudheendra HV, Sharma A, Sunny SP, Jacob T,
et al: Curcumin and metformin-mediated chemoprevention of oral
cancer is associated with inhibition of cancer stem cells. Mol
Carcinog. 56:2446–2460. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|