|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC,
Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR and
Winchester DP: The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual:
Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more
‘personalized’ approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:93–99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, Paradis
V, Rugge M, Schirmacher P, Washington KM, Carneiro F and Cree IA;
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, : The 2019 WHO
classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology.
76:182–188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
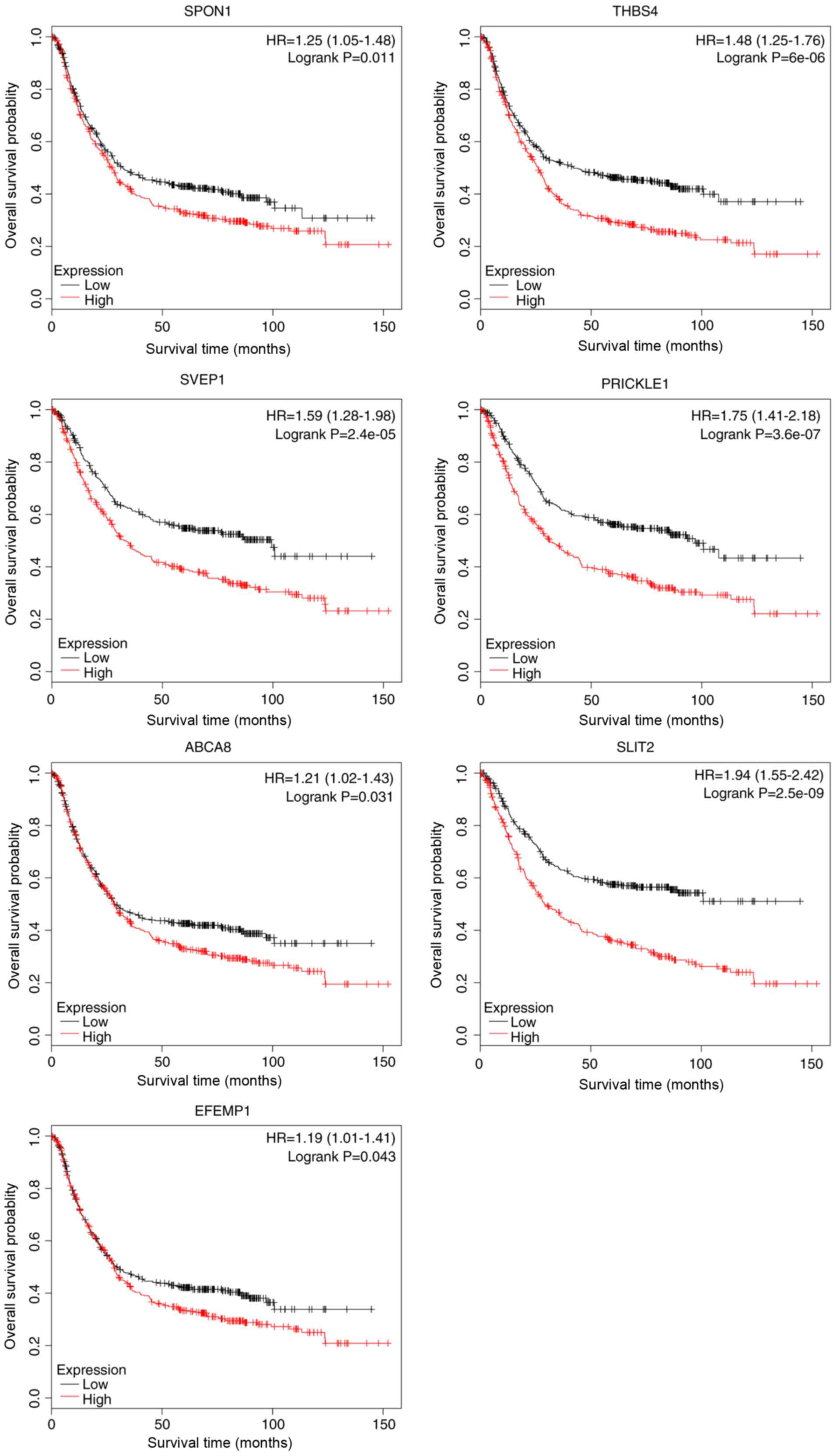
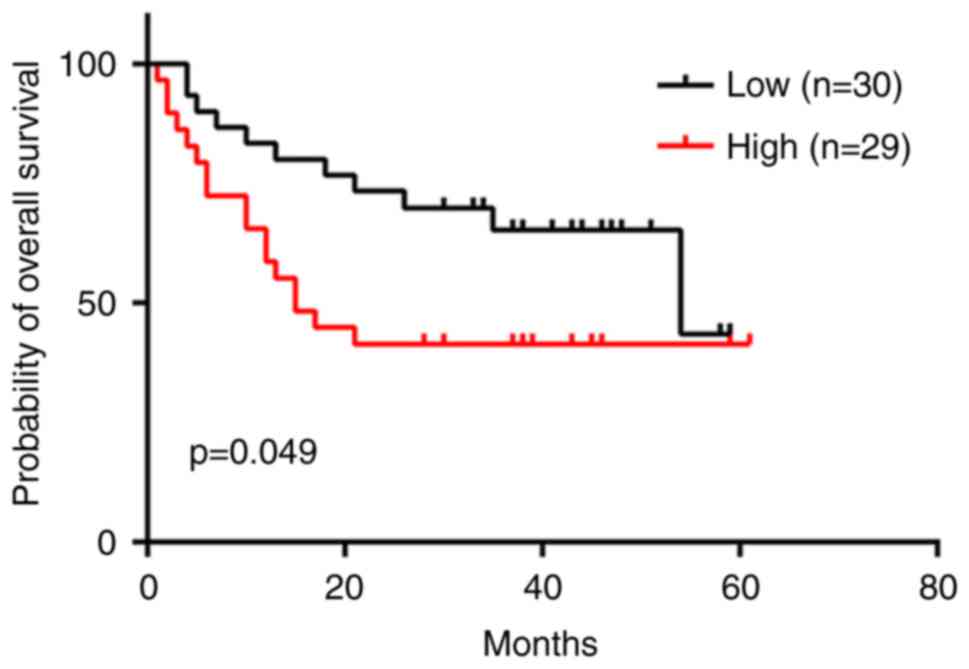
|
|
4
|
Jørgensen JT and Hersom M: HER2 as a
prognostic marker in gastric cancer-A systematic analysis of data
from the literature. J Cancer. 3:137–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jørgensen JT: Role of human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 in gastric cancer: Biological and
pharmacological aspects. World J Gastroenterol. 20:4526–4535. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oh SY, Kwon HC, Kim SH, Jang JS, Kim MC,
Kim KH, Han JY, Kim CO, Kim SJ, Jeong JS and Kim HJ:
Clinicopathologic significance of HIF-1alpha, p53, and VEGF
expression and preoperative serum VEGF level in gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 8:1232008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:(Database Issue).
D991–D995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang P, Wang Y, Hang B, Zou X and Mao JH:
A novel gene expression-based prognostic scoring system to predict
survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55343–55351.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
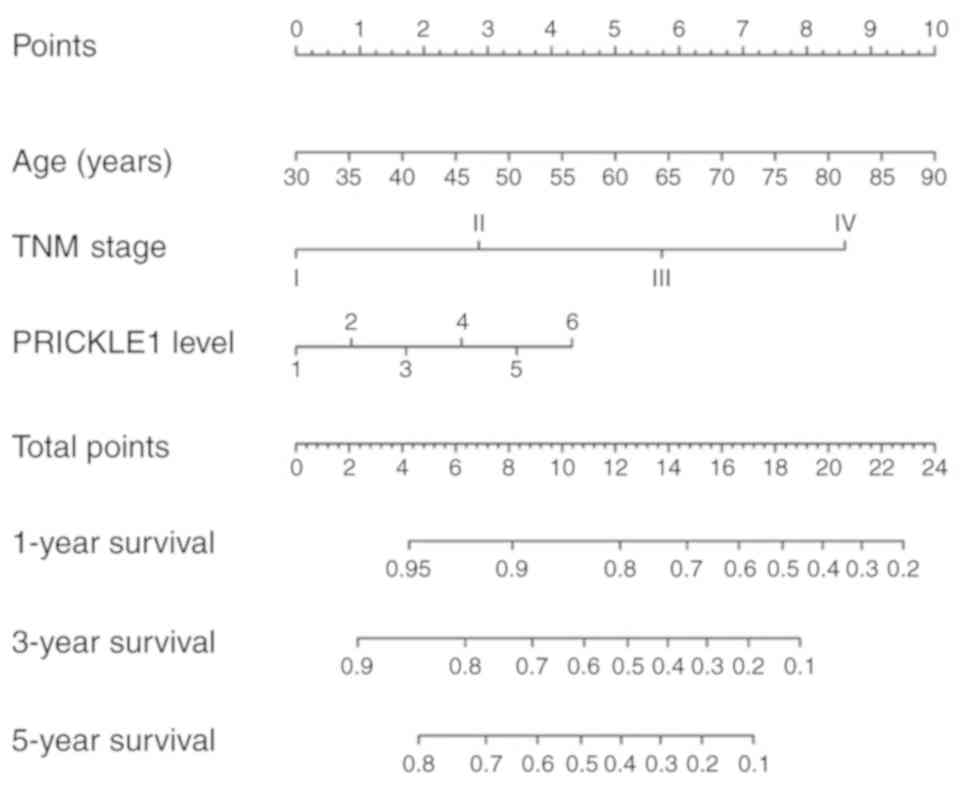
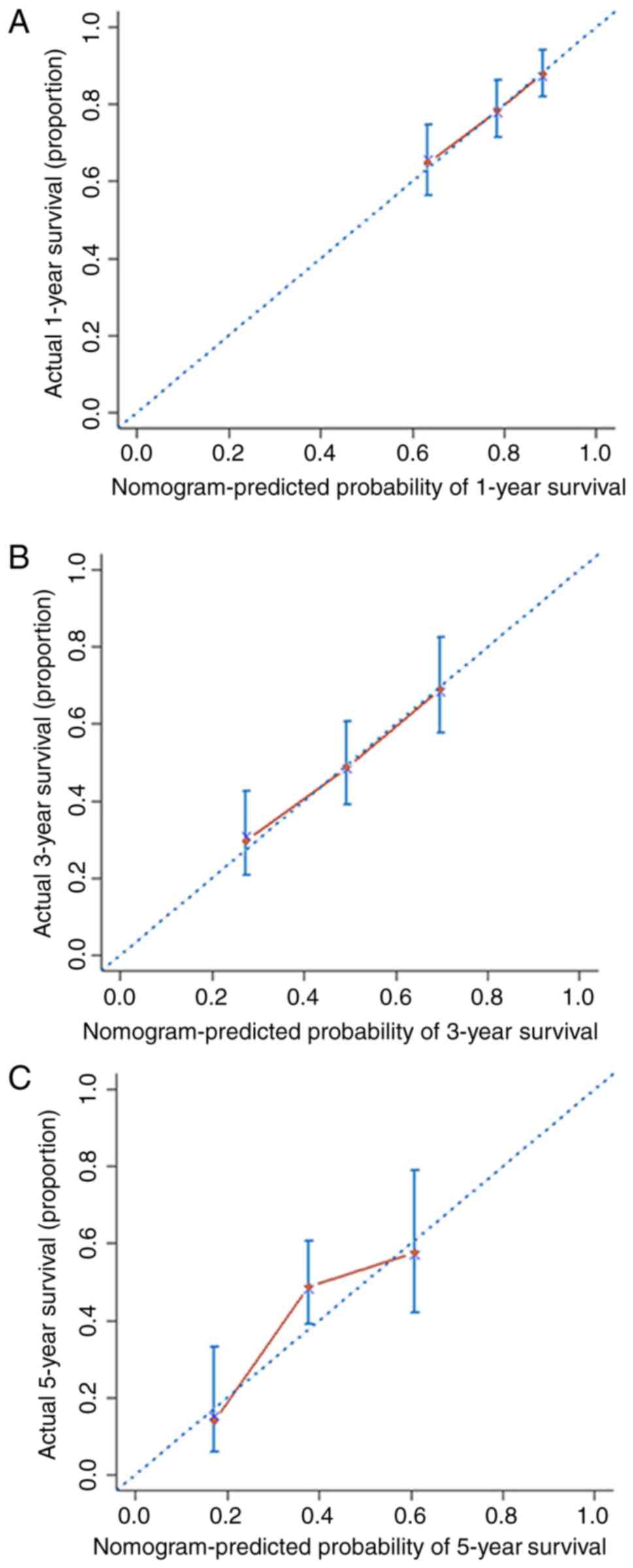
Iasonos A, Schrag D, Raj GV and Panageas
KS: How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J
Clin Oncol. 26:1364–1370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ and
DeMatteo RP: Nomograms in oncology: More than meets the eye. Lancet
Oncol. 16:e173–e180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lai JF, Kim S, Kim K, Li C, Oh SJ, Hyung
WJ, Rha SY, Chung HC, Choi SH, Wang LB and Noh SH: Prediction of
recurrence of early gastric cancer after curative resection. Ann
Surg Oncol. 16:1896–1902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim JH, Kim HS, Seo WY, Nam CM, Kim KY,
Jeung HC, Lai JF, Chung HC, Noh SH and Rha SY: External validation
of nomogram for the prediction of recurrence after curative
resection in early gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 23:361–367. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen D, Jiang B, Xing J, Liu M, Cui M, Liu
Y, Wang Z, Chen L, Yang H, Zhang C, et al: Validation of the
memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center nomogram to predict
disease-specific survival after R0 resection in a Chinese gastric
cancer population. PLoS One. 8:e760412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng Q, He B, Liu X, Yue J, Ying H, Pan Y,
Sun H, Chen J, Wang F, Gao T, et al: Prognostic value of
pre-operative inflammatory response biomarkers in gastric cancer
patients and the construction of a predictive model. J Transl Med.
13:662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han DS, Suh YS, Kong SH, Lee HJ, Choi Y,
Aikou S, Sano T, Park BJ, Kim WH and Yang HK: Nomogram predicting
long-term survival after d2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 30:3834–3840. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Zhang H, He H, Shen Z, Tang Z, Xu
J and Sun Y: Prognostic value of stromal cell-derived factor 1
expression in patients with gastric cancer after surgical
resection. Cancer Sci. 105:1447–1456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Zhang H, Shen Z, Wang X, Wang Z, Xu
J and Sun Y: Expression of Jagged1 predicts postoperative clinical
outcome of patients with gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:14782–14792. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu Y, Qiu P and Ji Y: TCGA-assembler:
Open-source software for retrieving and processing TCGA data. Nat
Methods. 11:599–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anders S and Huber W: Differential
expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol.
11:R1062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M and Rimm DL:
X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and
outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7252–7259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szász AM, Lánczky A, Nagy Á, Förster S,
Hark K, Green JE, Boussioutas A, Busuttil R, Szabó A and Győrffy B:
Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric
cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget.
7:49322–49333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harrell FE Jr: Rms: Regression modeling
strategies. R Package version 5.1–0. http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=rms
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Daulat AM, Bertucci F, Audebert S, Sergé
A, Finetti P, Josselin E, Castellano R, Birnbaum D, Angers S and
Borg JP: PRICKLE1 contributes to cancer cell dissemination through
its interaction with mTORC2. Dev Cell. 37:311–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang GM, Xu W, Du J, Zhang KS, Zhang QG,
Wang XW, Liu ZG, Liu SQ, Xie WY, Liu HF, et al: The application of
the fibroblast activation protein α-targeted immunotherapy
strategy. Oncotarget. 7:33472–33482. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang RF, Zhang LH, Shan LH, Sun WG, Chai
CC, Wu HM, Ibla JC, Wang LF and Liu JR: Effects of the fibroblast
activation protein on the invasion and migration of gastric cancer.
Exp Mol Pathol. 95:350–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan L, Li W, Ying S, Shi L, Wang Z, Chen
G, Ye H, Wu X, Wu J, Liang G and Li X: A peptide derivative serves
as a fibroblast growth factor 2 antagonist in human gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 36:7233–7241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Xu L, Li C, Zhao L, Ma Y, Zheng H,
Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang R, Liu Y and Qu X: Ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b
represses IGF-I-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via ZEB2
and microRNA-200c regulation in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
13:1362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ge J and Chen Z, Wu S, Chen J, Li X, Li J,
Yin J and Chen Z: Expression levels of insulin-like growth factor-1
and multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 indicate poor
prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Digestion. 80:148–158.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang H, Dong T, Ma X, Zhang T, Chen Z,
Yang Z and Zhang Y: Spondin 1 promotes metastatic progression
through Fak and Src dependent pathway in human osteosarcoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:45–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stenina OI, Desai SY, Krukovets I, Kight
K, Janigro D, Topol EJ and Plow EF: Thrombospondin-4 and its
variants: Expression and differential effects on endothelial cells.
Circulation. 108:1514–1519. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McCart Reed AE, Song S, Kutasovic JR, Reid
LE, Valle JM, Vargas AC, Smart CE and Simpson PT: Thrombospondin-4
expression is activated during the stromal response to invasive
breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 463:535–545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Förster S, Gretschel S, Jöns T, Yashiro M
and Kemmner W: THBS4, a novel stromal molecule of diffuse-type
gastric adenocarcinomas, identified by transcriptome-wide
expression profiling. Mod Pathol. 24:1390–1403. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shur I, Socher R, Hameiri M, Fried A and
Benayahu D: Molecular and cellular characterization of SEL-OB/SVEP1
in osteogenic cells in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Physiol.
206:420–427. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Samuelov L, Li Q, Bochner R, Najor NA,
Albrecht L, Malchin N, Goldsmith T, Grafi-Cohen M, Vodo D, Fainberg
G, et al: SVEP1 plays a crucial role in epidermal differentiation.
Exp Dermatol. 26:423–430. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takeuchi M, Nakabayashi J, Sakaguchi T,
Yamamoto TS, Takahashi H, Takeda H and Ueno N: The prickle-related
gene in vertebrates is essential for gastrulation cell movements.
Curr Biol. 13:674–679. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Veeman MT, Slusarski DC, Kaykas A, Louie
SH and Moon RT: Zebrafish prickle, a modulator of noncanonical
Wnt/Fz signaling, regulates gastrulation movements. Curr Biol.
13:680–685. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM,
Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, Buchanan M, Hosein AN, Basik M and
Wrana JL: Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine
Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell.
151:1542–1556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hedditch EL, Gao B, Russell AJ, Lu Y,
Emmanuel C, Beesley J, Johnatty SE, Chen X, Harnett P, George J, et
al: ABCA transporter gene expression and poor outcome in epithelial
ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106(pii): dju1492014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dunaway CM, Hwang Y, Lindsley CW, Cook RS,
Wu JY, Boothby M, Chen J and Brantley-Sieders DM: Cooperative
signaling between Slit2 and Ephrin-A1 regulates a balance between
angiogenesis and angiostasis. Mol Cell Biol. 31:404–416. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang B, Xiao Y, Ding BB, Zhang N, Yuan XB,
Gui L, Qian KX, Duan S, Chen Z, Rao Y and Geng JG: Induction of
tumor angiogenesis by Slit-Robo signaling and inhibition of cancer
growth by blocking Robo activity. Cancer Cell. 4:19–29. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang QQ, Zhou DL, Lei Y, Zheng L, Chen
SX, Gou HJ, Gu QL, He XD, Lan T, Qi CL, et al: Slit2/Robo1
signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through Src-mediated
activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 6:3123–3135.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen J, Wei D, Zhao Y, Liu X and Zhang J:
Overexpression of EFEMP1 correlates with tumor progression and poor
prognosis in human ovarian carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e787832013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Seeliger H, Camaj P, Ischenko I, Kleespies
A, De Toni EN, Thieme SE, Blum H, Assmann G, Jauch KW and Bruns CJ:
EFEMP1 expression promotes in vivo tumor growth in human pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 7:189–198. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song EL, Hou YP, Yu SP, Chen SG, Huang JT,
Luo T, Kong LP, Xu J and Wang HQ: EFEMP1 expression promotes
angiogenesis and accelerates the growth of cervical cancer in vivo.
Gynecol Oncol. 121:174–180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Katoh M: WNT/PCP signaling pathway and
human cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 14:1583–1588. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ding J, Wu K and
Fan D: Survival prediction of gastric cancer by a seven-microRNA
signature. Gut. 59:579–585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li YF, Wang DD, Zhao BW, Wang W, Huang CY,
Chen YM, Zheng Y, Keshari RP, Xia JC and Zhou ZW: High level of
COP1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in primary
gastric cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 8:1168–1177. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang Y, Li J, Xia Y, Gong R, Wang K, Yan
Z, Wan X, Liu G, Wu D, Shi L, et al: Prognostic nomogram for
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after partial hepatectomy. J Clin
Oncol. 31:1188–1195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|