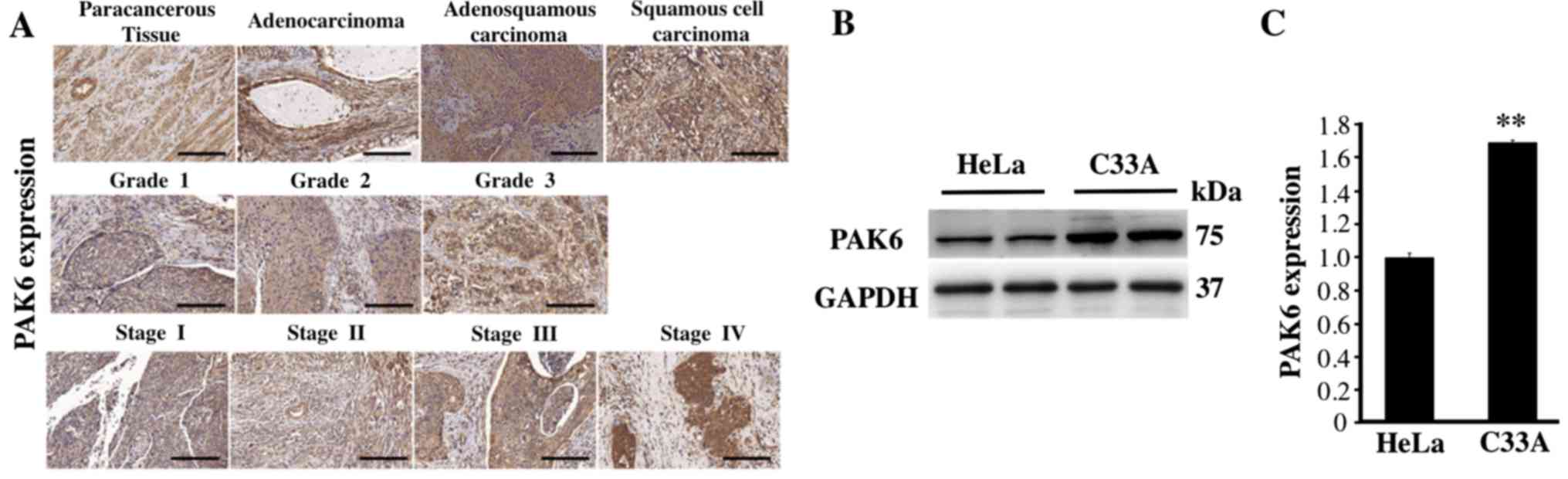
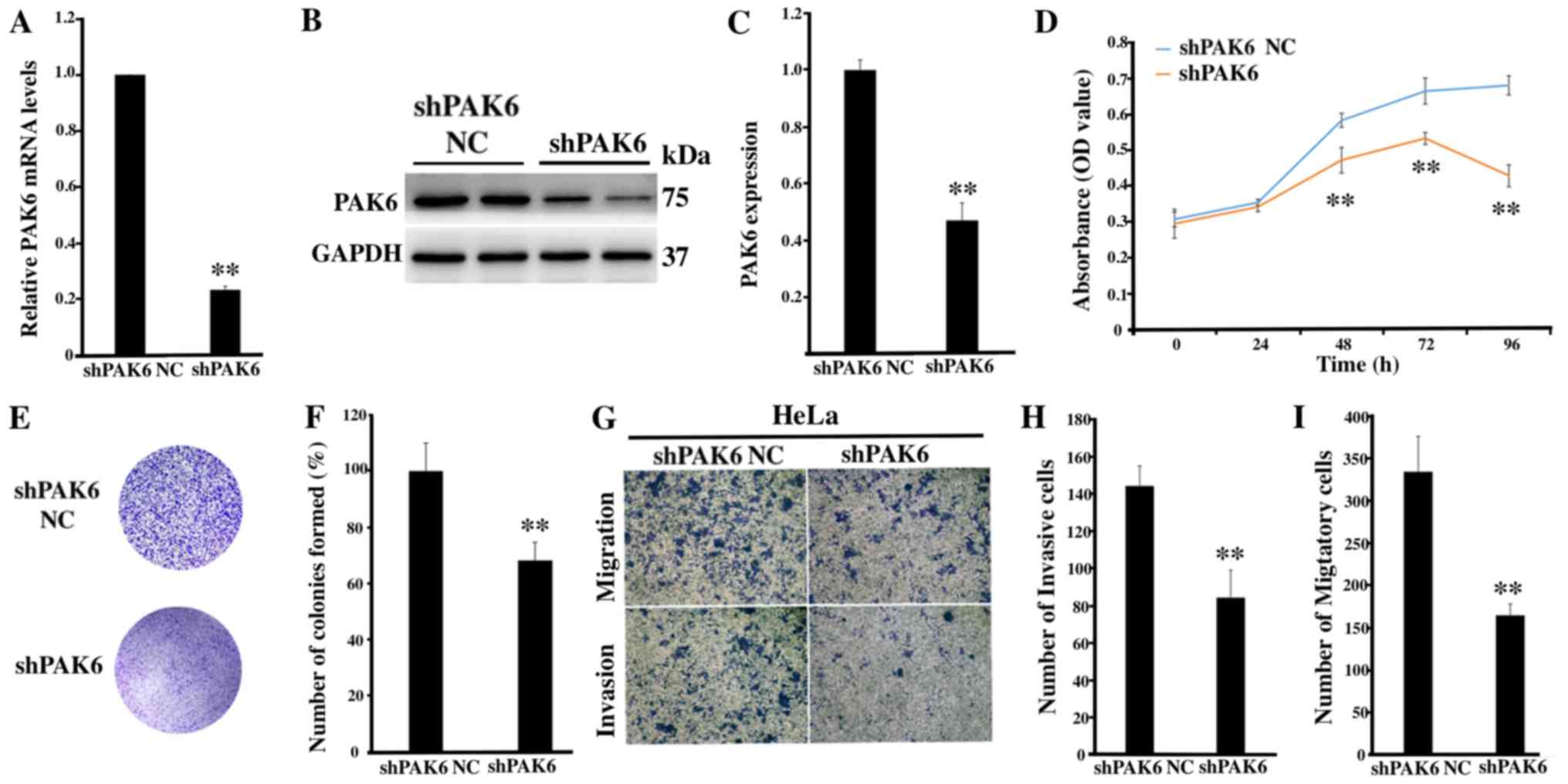
|
1
|
Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé
S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J and Bray F: Estimates of incidence and
mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet
Glob Health. 8:e191–e203. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whitham HK, Hawes SE, Chu H, Oakes JM,
Lifson AR, Kiviat NB, Sow PS, Gottlieb GS, Ba S, Sy MP and
Kulasingam SL: A comparison of the natural history of hpv infection
and cervical abnormalities among HIV-positive and HIV-negative
women in Senegal, Africa. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
26:886–894. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gomih A, Smith JS, North KE, Hudgens MG,
Brewster WR, Huang Z, Skaar D, Valea F, Bentley RC, Vidal AC, et
al: DNA methylation of imprinted gene control regions in the
regression of low-grade cervical lesions. Int J Cancer.
143:552–560. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu X, Busby J, John C, Wei J, Yuan X and
Lu ML: Direct interaction between AR and PAK6 in
androgen-stimulated PAK6 activation. PLoS One. 8:e773672013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang K, Baldwin GS, Nikfarjam M and He H:
p21-activated kinase signalling in pancreatic cancer: New insights
into tumour biology and immune modulation. World J Gastroenterol.
24:3709–3723. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chow HY, Dong B, Valencia CA, Zeng CT,
Koch JN, Prudnikova TY and Chernoff J: Group I Paks are essential
for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in an Apc-driven model of
colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. 9:34732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu H, Liu S, Zhang G, Bin Wu, Zhu Y,
Frederick DT, Hu Y, Zhong W, Randell S, Sadek N, et al: PAK
signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in
BRAF-mutant melanomas. Nature. 550:133–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han K, Zhou Y, Tseng KF, Hu H, Li K, Wang
Y, Gan Z, Lin S, Sun Y and Min D: PAK5 overexpression is associated
with lung metastasis in osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 15:2202–2210.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Siekmann IK, Dierck K, Prall S, Klokow M,
Strauss J, Buhs S, Wrzeszcz A, Bockmayr M, Beck F, Trochimiuk M, et
al: Combined inhibition of receptor tyrosine and p21-activated
kinases as a therapeutic strategy in childhood ALL. Blood Adv.
2:2554–2567. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sabra H, Brunner M, Mandati V,
Wehrle-Haller B, Lallemand D, Ribba AS, Chevalier G, Guardiola P,
Block MR and Bouvard D: β1 integrin-dependent Rac/group I PAK
signaling mediates YAP activation of Yes-associated protein 1
(YAP1) via NF2/merlin. J Biol Chem. 292:19179–19197. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Raghavan S, Venkatraman G and Rayala SK:
Cloning and functional characterization of human Pak1 promoter by
steroid hormones. Gene. 646:120–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Si W, Liu X, He L, Ren J, Yang Z,
Yang J, Li W, Liu S, Pei F, et al: JMJD6 promotes melanoma
carcinogenesis through regulation of the alternative splicing of
PAK1, a key MAPK signaling component. Mol Cancer. 16:1752017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rane CK and Minden A: P21 activated kinase
signaling in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 54:40–49. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kumar R, Sanawar R, Li X and Li F:
Structure, biochemistry, and biology of PAK kinases. Gene.
605:20–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang M, Siedow M, Saia G and Chakravarti
A: Inhibition of p21-activated kinase 6 (PAK6) increases
radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 70:807–816.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee EJ, McClelland M, Wang YP, Long F,
Choi SH and Lee JH: Distinct DNA methylation profiles between
adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of human uterine cervix.
Oncol Res. 18:401–408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN and
Sankaranarayanan R: Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 143 (Suppl 2):S2–S36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee DW, Ryu HS, Jin MS, Lee KH, Suh KJ,
Youk J, Kim JY, Min A, Lee HB, Moon HG, et al: Immune recurrence
score using 7 immunoregulatory protein expressions can predict
recurrence in stage I–III breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
121:230–236. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Zhao ZS
and Lim L: A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by
Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 367:40–46. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao ZS and Manser E: PAK family kinases:
Physiological roles and regulation. Cell Logist. 2:59–68. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu G, Li X, Guo B, Ke Q, Dong M and Li F:
PAK5-mediated E47 phosphorylation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene. 35:1943–1954.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramos-Alvarez I and Jensen RT:
P21-activated kinase 4 in pancreatic acinar cells is activated by
numerous gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth
factors by novel signaling, and its activation stimulates
secretory/growth cascades. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
315:G302–G317. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dou Q, Chen HN, Wang K, Yuan K, Lei Y, Li
K, Lan J, Chen Y, Huang Z, Xie N, et al: Ivermectin induces
cytostatic autophagy by blocking the PAK1/Akt axis in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 76:4457–4469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aburatani T, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y,
Ishikawa T, Okuno K, Gokita K, Tomii C, Tanioka T, Murase H, Otsuki
S, et al: High expression of P21-activated kinase 5 protein is
associated with poor survival in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett.
14:404–410. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang F, Li X, Sharma M, Zarnegar M, Lim B
and Sun Z: Androgen receptor specifically interacts with a novel
p21-activated kinase, PAK6. J Biol Chem. 276:15345–15353. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee SR, Ramos SM, Ko A, Masiello D,
Swanson KD, Lu ML and Balk SP: AR and ER interaction with a
p21-activated kinase (PAK6). Mol Endocrinol. 16:85–99. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bompard G, Rabeharivelo G, Cau J, Abrieu
A, Delsert C and Morin N: P21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) is required
for metaphase spindle positioning and anchoring. Oncogene.
32:910–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Wang D, Zhang H, Wang C, Dai W,
Cheng Z, Wang G and Li F: P21-activated kinase 4 regulates the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57(kip2) in human breast cancer.
Anat Rec (Hoboken). 296:1561–1567. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tyagi N, Bhardwaj A, Singh AP, McClellan
S, Carter JE and Singh S: p-21 activated kinase 4 promotes
proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells through AKT-
and ERK-dependent activation of NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget.
5:8778–8789. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He W, Zhao Z, Anees A, Li Y, Ashraf U,
Chen Z, Song Y, Chen H, Cao S and Ye J: p21-activated kinase 4
signaling promotes japanese encephalitis virus-mediated
inflammation in astrocytes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 7:2712017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fu X, Feng J, Zeng D, Ding Y, Yu C and
Yang B: PAK4 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells
via PI3K/Akt- and MEK/ERK-dependent pathways. Biosci Rep.
34:e000942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fang ZP, Jiang BG, Gu XF, Zhao B, Ge RL
and Zhang FB: P21-activated kinase 5 plays essential roles in the
proliferation and tumorigenicity of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:82–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han ZX, Wang XX, Zhang SN, Wu JX, Qian HY,
Wen YY, Tian H, Pei DS and Zheng JN: Downregulation of PAK5
inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion potentially through the
PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway. Brain Tumor Pathol. 31:234–241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun X and Liu Y: Activation of the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway may contribute to cervical cancer
pathogenesis via upregulation of twist. Oncol Lett. 14:4841–4844.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang YH, Chu TY and Ding DC:
WNT/β-Catenin signaling pathway regulates non-tumorigenesis of
human embryonic stem cells co-cultured with human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 7:419132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mao XW, Xiao JQ, Li ZY, Zheng YC and Zhang
N: Effects of microRNA-135a on the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by
targeting GSK3β through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp
Mol Med. 50:e4292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Taelman VF, Dobrowolski R, Plouhinec JL,
Fuentealba LC, Vorwald PP, Gumper I, Sabatini DD and De Robertis
EM: Wnt signaling requires sequestration of glycogen synthase
kinase 3 inside multivesicular endosomes. Cell. 143:1136–1148.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|