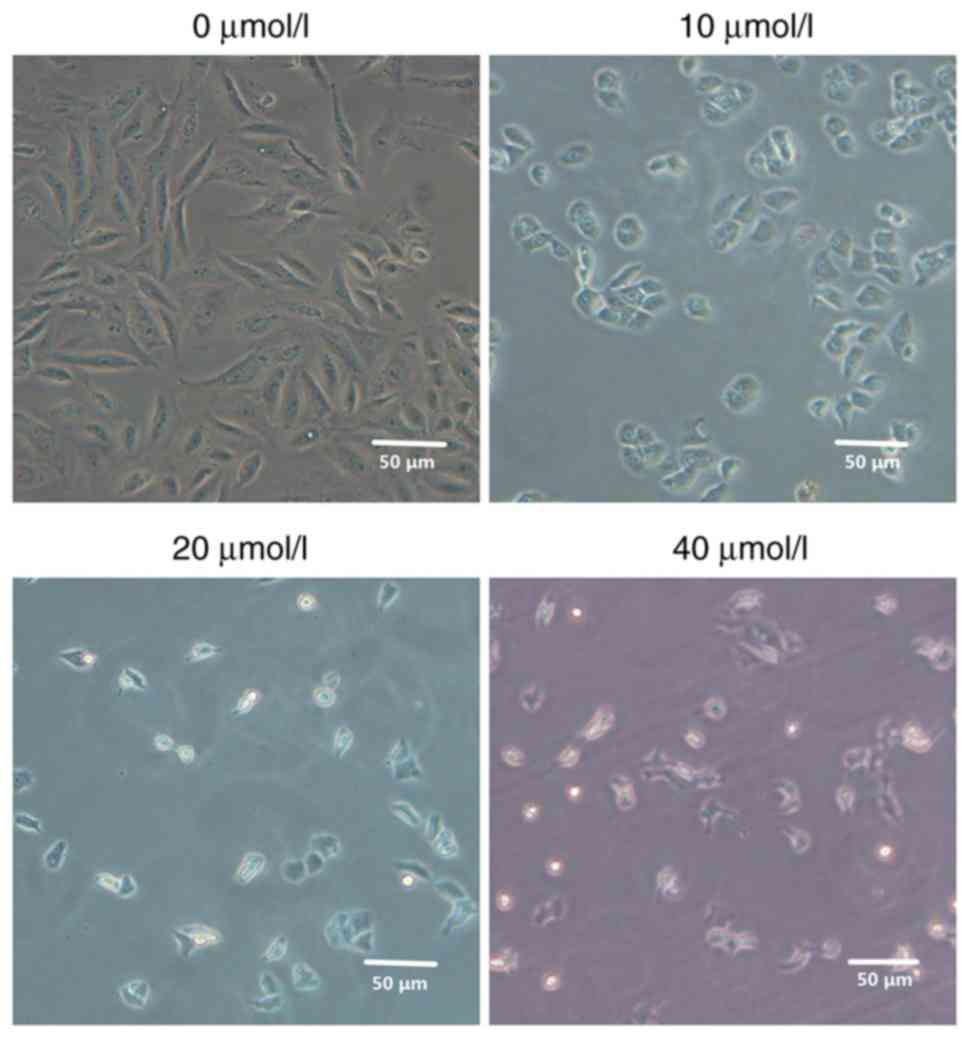
|
1
|
Miwa S, Shirai T, Yamamoto N, Hayashi K,
Takeuchi A, Igarashi K and Tsuchiya H: Current and emerging targets
in immunotherapy for osteosarcoma. J Oncol. 2019:70350452019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhao N, Wang C, Kamar S,
Zhou Y, He Z, Yang J, Sun B, Shi X, et al: Progress in the
chemotherapeutic treatment of osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett.
16:6228–6237. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Teter Z, Śliwczyński A, Brzozowska M,
Świerkowski M, Jacyna A, Pinkas J, Sierocka A, Marczak M,
Dańska-Bidzińska A, Bidziński M and Wierzba W: The assessment of
overall survival (OS) after adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with
malignant endometrial cancer in Poland. Ginekol Pol. 88:296–301.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Ren M, Zhao X, Wang A and Wang J:
Emerging roles of circular RNAs in osteosarcoma. Med Sci Monit.
24:7043–7050. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zou X, Zhou L, Zhu W, Mao Y and Chen L:
Effectiveness of 2-methoxyestradiol in alleviating angiogenesis
induced by intracranial venous hypertension. J Neurosurg.
125:746–753. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang MZ, Liu YF, Ding N, Zhao PX, Zhang
X, Liu MY, Adzavon YM, Huang JN, Long X, Wang XJ, et al:
2-Methoxyestradiol improves the apoptosis level in keloid
fibroblasts through caspase-dependent mechanisms in vitro. Am J
Transl Res. 10:4017–4029. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dikshit A, Hales K and Hales DB: Whole
flaxseed diet alters estrogen metabolism to promote
2-methoxtestradiol-induced apoptosis in hen ovarian cancer. J Nutr
Biochem. 42:117–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song LM, Wang GD, Wang HP and Xing NZ:
Effect of 2-methoxyestradiol combined with quercetin on prostate
cancer in vitro. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:95–99. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi X, Wang Z, Xu F, Lu X, Yao H, Wu D,
Sun S, Nie R, Gao S, Li P, et al: Design, synthesis and
antiproliferative effect of 17β-amide derivatives of
2-methoxyestradiol and their studies on pharmacokinetics. Steroids.
128:6–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang SH, Cho HT, Devi S, Zhang Z, Escuin
D, Liang Z, Mao H, Brat DJ, Olson JJ, Simons JW, et al: Antitumor
effect of 2-methoxyestradiol in a rat orthotopic brain tumor model.
Cancer Res. 66:11991–11997. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nolte EM, Joubert AM, Lakier R, van
Rensburg A and Mercier AE: Exposure of breast and lung cancer cells
to a novel estrone analog prior to radiation enhances
Bcl-2-mediated cell death. Int J Mol Sci. 19:28872018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Smolle MA, Leithner A, Posch F, Szkandera
J, Liegl-Atzwanger B and Pichler M: MicroRNAs in different
histologies of soft tissue sarcoma: A comprehensive review. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:19602017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhao ZW, Yang LL, Ji JS, Zheng LY, Fang SJ
and Wang JL: Effects and mechanism ofitraconazole on prostate
cancer PC-3 cell apoptosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:3160–3163.
2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun J, Zhang X, Sun Y, Tang ZS and Guo DY:
Effects of hylomecon vernalis ethanol extracts on cell cycle and
apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 15:3485–3492. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee J, Jung MK, Park HJ, Kim KE and Cho D:
Erdr1 suppresses murine melanoma growth via regulation of
apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 17:1072016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
van Vuuren RJ, Botes M, Jurgens T, Joubert
AM and van den Bout I: Novel sulphamoylated 2-methoxy estradiol
derivatives inhibit breast cancer migration by disrupting
microtubule turnover and organization. Cancer Cell Int. 19:12019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maran A, Zhang M, Kennedy AM, Sibonga JD,
Rickard DJ, Spelsberg TC and Turner RT: 2-methoxyestradiol induces
interferon gene expression and apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells.
Bone. 30:393–398. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo X, Chen C, Liu X, Hou P, Guo X, Ding
F, Wang Z, Hu Y, Li Z and Zhang Z: High oral bioavailability of
2-methoxyestradiol in PEG-PLGA micelles-microspheres for cancer
therapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 117:116–122. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu J, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu M and
Liu Y: Effects of Spica prunellae on caspase-3-associated
proliferation and apoptosis in human lung cancer cells in vitro. J
Cancer Res Ther. 14:760–763. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nan Y, Wang S and Jia W: Caspase
independent cleavages of TDP-43 generates 35 kD fragment that cause
apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
497:51–57. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grunewald S, Fitzl G and Springsguth C:
Induction of ultra-morphological features of apoptosis in mature
and immature sperm. Asian J Androl. 19:533–537. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S and Almasan A:
Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic
stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 1219:1–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Treffkorn S and Mayer G: Conserved versus
derived patterns of controlled cell death during the embryonic
development of two species of Onychophora (velvet worms). Dev Dyn.
246:403–416. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rogers C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Mayes L,
Alnemri D, Cingolani G and Alnemri ES: Cleavage of DFNA5 by
caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary
necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat Commun. 8:141282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cianciulli A, Porro C, Calvello R, Trotta
T and Panaro MA: Resistance to apoptosis in Leishmania
infantum-infected human macrophages: A critical role for
anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and cellular IAP1/2. Clin Exp Med.
18:251–261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Masuda H, Hirose J, Omata Y, Tokuyama N,
Yasui T, Kadono Y, Miyazaki T and Tanaka S: Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2
family member Mcl-1 regulates cell viability and bone-resorbing
activity of osteoclasts. Bone. 58:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Villanova L, Careccia S, De Maria R and
Fiori ME: Micro-economics of apoptosis in cancer: NcRNAs modulation
of BCL-2 family members. Int J Mol Sci. 19:9582018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Alzate JM, Montoya-Florez LM, Pérez JE,
Rocha NS and Pedraza-Ordonez FJ: The role of the multi-drug
resistance 1, p53, b cell lymphoma 2, and BCL 2-associated X genes
in the biologic behavior and chemotherapeutic resistance of canine
transmissible venereal tumors. Vet Clin Pathol. 48:730–739. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ebrahim AS, Sabbagh H, Liddane A, Raufi A,
Kandouz M and Al-Katib A: Hematologic malignancies: Newer
strategies to counter the BCL-2 protein. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
142:2013–2022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qiu XG, Chen YD, Yuan J, Zhang N, Lei T,
Liu J and Yang M: Functional BCL-2 rs2279115 promoter noncoding
variant contributes to glioma predisposition, especially in males.
DNA Cell Biol. 38:85–90. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghasemi A, Khanzadeh T, di Heydarabad M,
Khorrami A, Jahanban Esfahlan A, Ghavipanjeh S, Gholipour Belverdi
M, Darvishani Fikouhi S, Darbin A, Najafpour M and Azimi A:
Evaluation of BAX and BCL-2 gene expression and apoptosis induction
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line CCRFCEM after High- dose
prednisolone treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 19:2319–2323.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bui NL, Pandey V, Zhu T, Ma L, Basapp a
and Lobie PE: Bad phosphorylation as a target of inhibition in
oncology. Cancer Lett. 415:177–186. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Zhao D, Zhuang J, Zhang F and Xu C:
Caspase-8 and caspase-9 functioned differently at different stages
of the cyclic stretch-induced apoptosis in human periodontal
ligament cells. PLoS One. 11:e01682682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Watts FM Jr, Pouland T, Bunce RA, Berlin
KD, Benbrook DM, Mashayekhi M, Bhandari D and Zhou D: Activity of
oxygen-versus sulfur-containing analogs of the Flex-Het anticancer
agent SHetA2. Eur J Med Chem. 158:720–732. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yao L, Zou X, Jin C, Fan J, Guo Z, Lin Q,
Li J and Fu D: The roles of ID-1 in human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and the therapeutic effects of 2-methoxyestradiol.
Carcinogenesis. 39:728–737. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Minorics R and Zupko I: Steroidal
anticancer agents: An overview of estradiol-related compounds.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 18:652–666. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lundström-Stadelmann B, Rufener R, Ritler
D, Zurbriggen R and Hemphill A: The importance of being
parasiticidal an update on drug development for the treatment of
alveolar echinococcosis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 15:e000402019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shen Z, Wu Y, Chen X, Chang X, Zhou Q,
Zhou J, Ying H, Zheng J, Duan T and Wang K: Decreased maternal
serum 2-methoxyestradiol levels are associated with the development
of preeclampsia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:2189–2199. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Caporarello N, Lupo G, Olivieri M,
Cristaldi M, Cambria MT, Salmeri M and Anfuso CD: Classical VEGF,
Notch and ang signalling in cancer angiogenesis, alternative
approaches and future directions (Review). Mol Med Rep.
16:4393–4402. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Przychodzen P, Wyszkowska R,
Gorzynik-Debicka M, Kostrzewa T, Kuban-Jankowska A and
Gorska-Ponikowska M: Anticancer potential of oleuropein, the
polyphenol of olive oil, with 2-methoxyestradiol, separately or in
combination, in human osteosarcoma cells. Anticancer Res.
39:1243–1251. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|