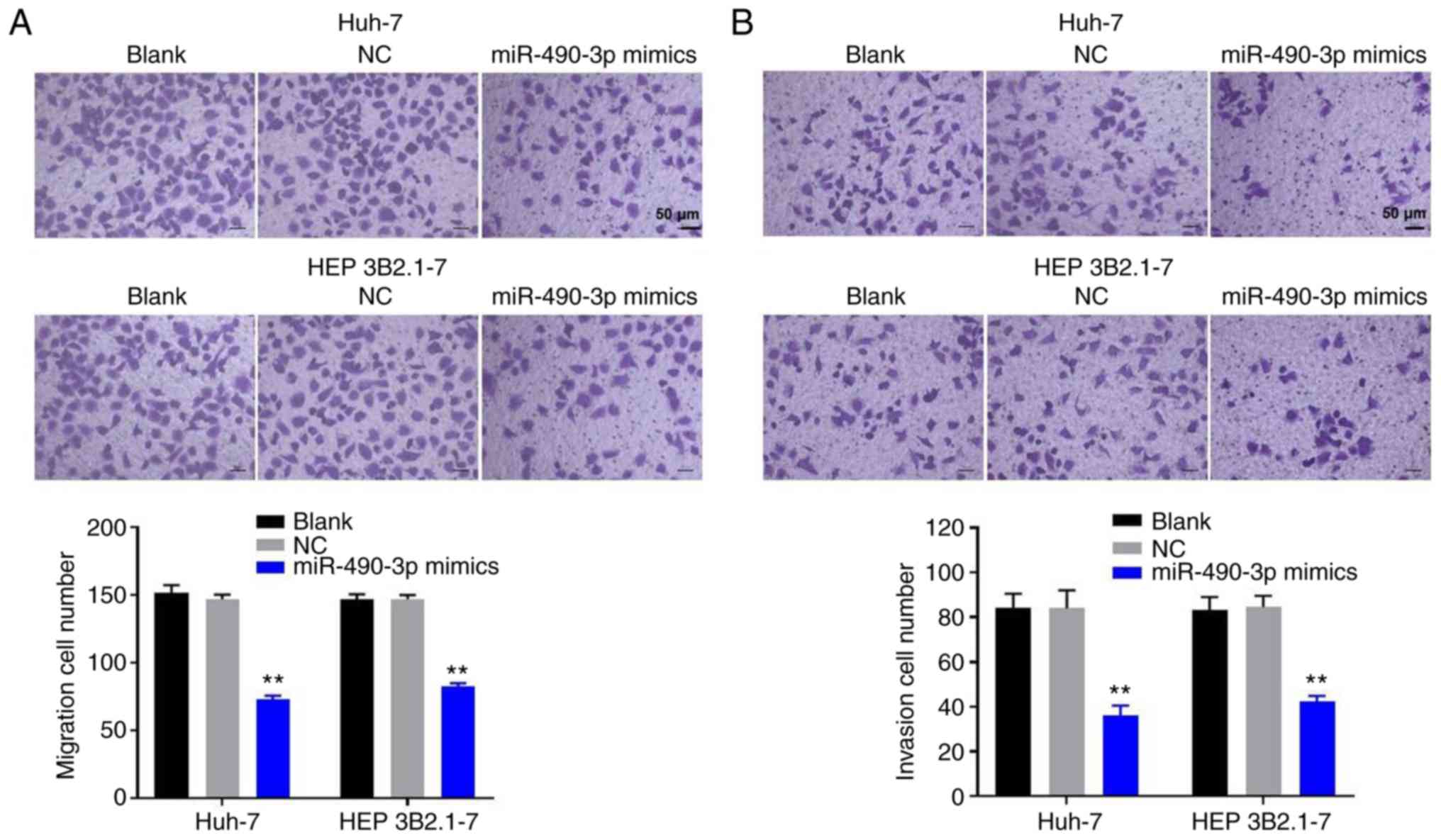
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wallace MC, Preen D, Jeffrey GP and Adams
LA: The evolving epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: A global
perspective. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:765–779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Blanc JF, Frulio N, Chiche L, Bioulac-Sage
P and Balabaud C: Hepatocellular adenoma management: Advances but
still a long way to go. Hepat Oncol. 2:171–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Omyła-Staszewska J and Deptała A:
Effective therapeutic management of hepatocellular carcinoma-on the
basis of a clinical case. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 16:60–63.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li L, Yuan L, Luo J, Gao J, Guo J and Xie
X: miR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer
through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin Exp Med.
13:109–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Wang G and Zheng H: Role
of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 14:e186722014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Romano G, Nuovo G,
Suh SS, Ngankeu A, Taccioli C, Pichiorri F, Alder H, Secchiero P,
et al: miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance
tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell.
16:498–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrier M,
Mesman E, Mangiola A, Anile C, Maira G, Mercatelli N, Ciafrè SA, et
al: Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and
miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 26:3699–3708.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng J, Sadot E, Vigidal JA, Klimstra DS,
Balachandran VP, Kingham TP, Allen PJ, D'Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP,
Jarnagin WR and Ventura A: Characterization of hepatocellular
adenoma and carcinoma using microRNA profiling and targeted gene
sequencing. PLoS One. 13:e02007762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gougelet A, Sartor C, Bachelot L, Godard
C, Marchiol C, Renault G, Tores F, Nitschke P, Cavard C, Terris B,
et al: Antitumour activity of an inhibitor of miR-34a in liver
cancer with β-catenin-mutations. Gut. 65:1024–1034. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio
A, Battiston C, Terris B, Mazzaferro V, Lowe SW, Croce CM and
Dejean A: miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:264–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tian J, Xu YY, Li L and Hao Q: miR-490-3p
sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by directly targeting
ABCC2. Am J Transl Res. 9:1127–1138. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang NN, Ge SL, Zhang RQ, Huang YL, Liu SD
and Wu KM: miR-490-3p inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting HMGA2. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:8298–8305. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qu M, Li L and Zheng WC: Reduced
miR-490-3p expression is associated with poor prognosis of
Helicobacter pylori induced gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:3384–3388. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu X, He B, Xu T, Pan Y, Hu X, Chen X and
Wang S: miR-490-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting
oncogene VDAC1 expression in colorectal cancer. J Cancer.
9:1218–1230. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamashiro S, Gokhin DS, Kimura S, Nowak RB
and Fowler VM: Tropomodulins: Pointed-end capping proteins that
regulate actin filament architecture in diverse cell types.
Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 69:337–370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fischer RS, Fritz-Six KL and Fowler VM:
Pointed-end capping by tropomodulin3 negatively regulates
endothelial cell motility. J Cell Biol. 161:371–380. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jo YJ, Jang WI, Kim NH and Namgoong S:
Tropomodulin-3 is essential in asymmetric division during mouse
oocyte maturation. Sci Rep. 6:292042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin C, Chen Z, Shi W and Lian Q:
Tropomodulin 3 promotes liver cancer progression by activating the
MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 41:3060–3068.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng H, Yang Y, Hong YG, Wang MC, Yuan
SX, Wang ZG, Bi FR, Hao LQ, Yan HL and Zhou WP: Tropomodulin 3
modulates EGFR-PI3K-AKT signaling to drive hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis. Mol Carcinog. 58:1897–1907. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhan XH, Jiao JW, Zhang HF, Xu XE, He JZ,
Li RL, Zou HY, Wu ZY, Wang SH, Wu JY, et al: LOXL2 upregulates
phosphorylation of ezrin to promote cytoskeletal reorganization and
tumor cell invasion. Cancer Res. 79:4951–4964. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paul D, Chanukuppa V, Reddy PJ, Taunk K,
Adhav R, Srivastava S, Santra MK and Rapole S: Global proteomic
profiling identifies etoposide chemoresistance markers in non-small
cell lung carcinoma. J Proteomics. 138:95–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|