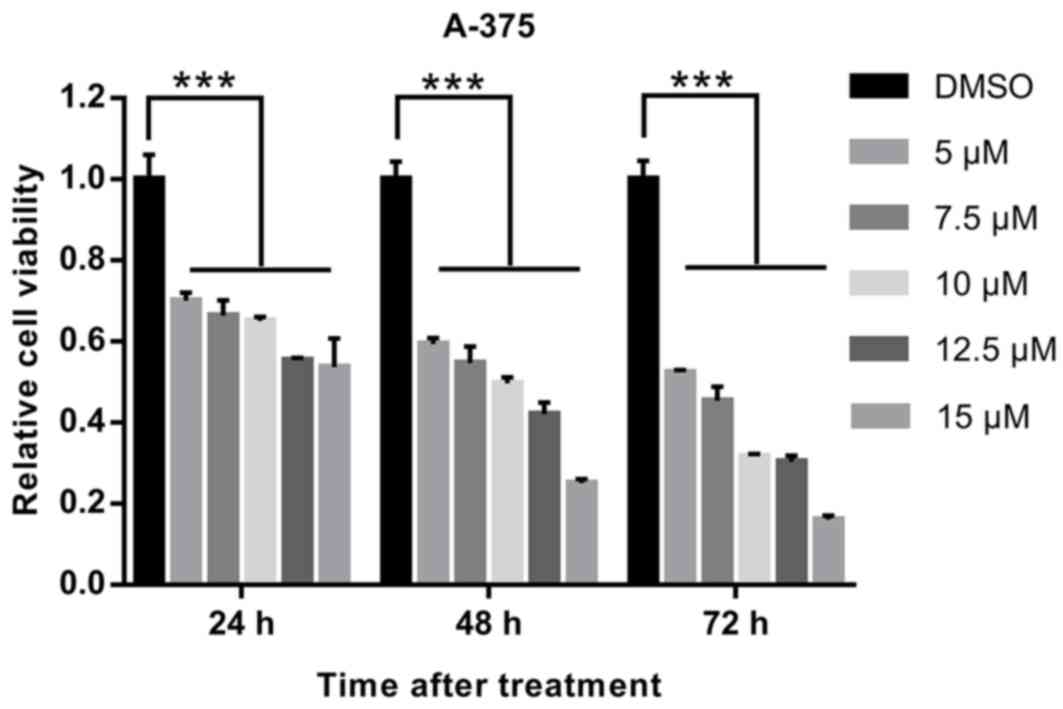
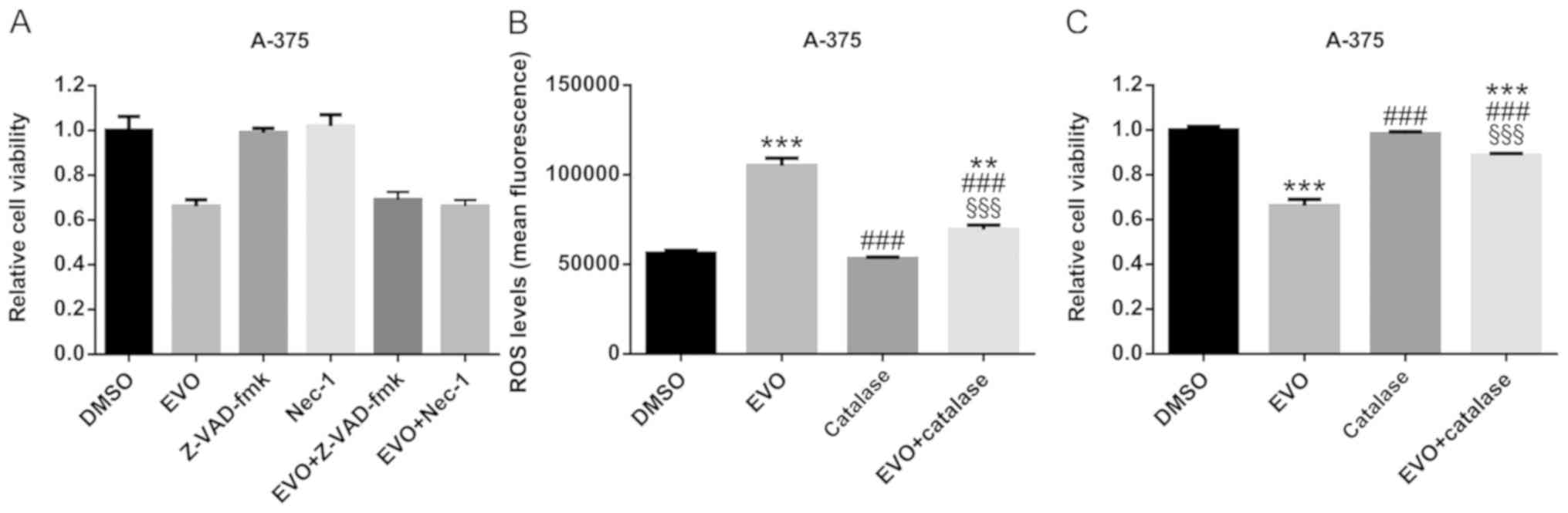
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leonardi GC, Falzone L, Salemi R, Zanghì
A, Spandidos DA, Mccubrey JA, Candido S and Libra M: Cutaneous
melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review). Int J Oncol.
52:1071–1080. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee SH, Son JK, Jeong BS, Jeong TC, Chang
HW, Lee ES and Jahng Y: Progress in the studies on rutaecarpine.
Molecules. 13:272–300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin H, Tsai SC, Chen JJ, Chiao YC, Wang
SW, Wang GJ, Chen CF and Wang PS: Effects of evodiamine on the
secretion of testosterone in rat testicular interstitial cells.
Metabolism. 48:1532–1535. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoshizumi M, Houchi H, Ishimura Y, Hirose
M, Kitagawa T, Tsuchiya K, Minakuchi K and Tamaki T: Effect of
evodiamine on catecholamine secretion from bovine adrenal medulla.
J Med Invest. 44:79–82. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kobayashi Y: The nociceptive and
anti-nociceptive effects of evodiamine from fruits of Evodia
rutaecarpa in mice. Planta Med. 69:425–428. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chiou WF, Sung YJ, Liao JF, Shum AY and
Chen CF: Inhibitory effect of dehydroevodiamine and evodiamine on
nitric oxide production in cultured murine macrophages. J Nat Prod.
60:708–711. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kobayashi Y, Nakano Y, Kizaki M, Hoshikuma
K, Yokoo Y and Kamiya T: Capsaicin-like anti-obese activities of
evodiamine from fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa, a vanilloid
receptor agonist. Planta Med. 67:628–633. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiou WF, Chou CJ, Shum AY and Chen CF:
The vasorelaxant effect of evodiamine in rat isolated mesenteric
arteries: Mode of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 215:277–283. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsai TH, Lee TF, Chen CF and Wang LC:
Thermoregulatory effects of alkaloids isolated from Wu-chu-yu in
afebrile and febrile rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 50:293–298.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
King CL, Kong YC, Wong NS, Yeung HW, Fong
HH and Sankawa U: Uterotonic effect of Evodia rutaecarpa
alkaloids. J Nat Prod. 43:577–582. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee TJ, Kim EJ, Kim S, Jung EM, Park JW,
Jeong SH, Park SE, Yoo YH and Kwon TK: Caspase-dependent and
caspase-independent apoptosis induced by evodiamine in human
leukemic U937 cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2398–2407. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang C, Wang MW, Tashiro SI, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Evodiamine induced human melanoma A375-S2 cell death
partially through interleukin 1 mediated pathway. Biol Pharm Bull.
28:984–989. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao CH, Pan SL, Guh JH, Chang YL, Pai HC,
Lin CH and Teng CM: Antitumor mechanism of evodiamine, a
constituent from Chinese herb Evodiae fructus, in human
multiple-drug resistant breast cancer NCI/ADR-RES cells in vitro
and in vivo. Carcinogenesis. 26:968–975. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kan SF, Yu CH, Pu HF, Hsu JM, Chen MJ and
Wang PS: Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human prostate
cancer cell lines DU145 and PC3. J Cell Biochem. 101:44–56. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fei XF, Wang BX, Li TJ, Tashiro SI, Minami
M, Xing DJ and Ikejima T: Evodiamine, a constituent of Evodiae
fructus, induces anti-proliferating effects in tumor cells. Cancer
Sci. 94:92–98. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ogasawara M, Matsubara T and Suzuki H:
Inhibitory effects of evodiamine on in vitro invasion and
experimental lung metastasis of murine colon cancer cells. Biol
Pharm Bull. 24:917–920. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ogasawara M, Matsunaga T, Takahashi S,
Saiki I and Suzuki H: Anti-invasive and metastatic activities of
evodiamine. Biol Pharm Bull. 25:1491–1493. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dickinson BC and Chang CJ: Chemistry and
biology of reactive oxygen species in signaling or stress
responses. Nat Chem Biol. 7:504–511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong Q, Beel JA and Lillehei KO: A
threshold concept for cancer therapy. Med Hypotheses. 55:29–35.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schafer FQ and Buettner GR: Redox
environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the
glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med.
30:1191–1212. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Obrador E, Liu-Smith F, Dellinger RW,
Salvador R, Meyskens FL and Estrela JM: Oxidative stress and
antioxidants in the pathophysiology of malignant melanoma. Biol
Chem. 400:589–612. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang R, Deng D, Shao N, Xu Y, Xue L, Peng
Y, Liu Y and Zhi F: Evodiamine activates cellular apoptosis through
suppressing PI3K/AKT and activating MAPK in glioma. OncoTargets
Ther. 11:1183–1192. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashino S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Protein tyrosine kinase pathway-derived ROS/NO
productions contribute to G2/M cell cycle arrest in
evodiamine-treated human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. Free Radic
Res. 44:792–802. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linkermann A and Green DR: Necroptosis. N
Engl J Med. 370:455–465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Murphy JM, Czabotar PE, Hildebrand JM,
Lucet IS, Zhang JG, Alvarez-Diaz S, Lewis R, Lalaoui N, Metcalf D,
Webb AI, et al: The pseudokinase MLKL mediates necroptosis via a
molecular switch mechanism. Immunity. 39:443–453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Glorieux C and Calderon PB: Catalase, a
remarkable enzyme: Targeting the oldest antioxidant enzyme to find
a new cancer treatment approach. Biol Chem. 398:1095–1108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang DM, Guh JH, Huang YT, Chueh SC,
Chiang PC and Teng CM: Induction of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in
human prostate cancer pc-3 cells by evodiamine. J Urol.
173:256–261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Taylor WR and Stark GR: Regulation of the
G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene. 20:1803–1815. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Booher RN, Holman PS and Fattaey A: Human
Myt1 is a cell cycle-regulated kinase that inhibits Cdc2 but not
Cdk2 activity. J Biol Chem. 272:22300–22306. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sui H, Zhou LH, Zhang YL, Huang JP, Liu X,
Ji Q, Fu XL, Wen HT, Chen ZS, Deng WL, et al: Evodiamine suppresses
ABCG2 mediated drug resistance by inhibiting p50/p65 NF-kB pathway
in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem. 117:1471–1481. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Cai X, Lu W, Hu C, Xu X, Yu Q and
Cao P: Evodiamine inhibits STAT3 signaling by inducing phosphatase
shatterproof 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
328:243–251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tait SW and Green DR: Mitochondria and
cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:621–632. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Delbridge AR, Grabow S, Strasser A and
Vaux DL: Thirty years of BCL-2: Translating cell death discoveries
into novel cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:99–109. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Riedl SJ and Salvesen GS: The apoptosome:
Signalling platform of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:405–413. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fatokun AA, Dawson VL and Dawson TM:
Parthanatos: Mitochondrial-linked mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities. Br J Pharmacol. 171:2000–2016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams
JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews
DW, et al: Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of
the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ.
25:486–541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I,
Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Andrews D,
Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, et al: Essential versus accessory
aspects of cell death: Recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death
Differ. 22:58–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Prabhakaran K, Li L, Borowitz JL and Isom
GE: Caspase inhibition switches the mode of cell death induced by
cyanide by enhancing reactive oxygen species generation and PARP-1
activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 195:194–202. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Steinhart L, Belz K and Fulda S: Smac
mimetic and demethylating agents synergistically trigger cell death
in acute myeloid leukemia cells and overcome apoptosis resistance
by inducing necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dunai ZA, Imre G, Barna G, Korcsmaros T,
Petak I, Bauer PI and Mihalik R: Staurosporine induces necroptotic
cell death under caspase-compromised conditions in U937 cells. PLoS
One. 7:e419452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|