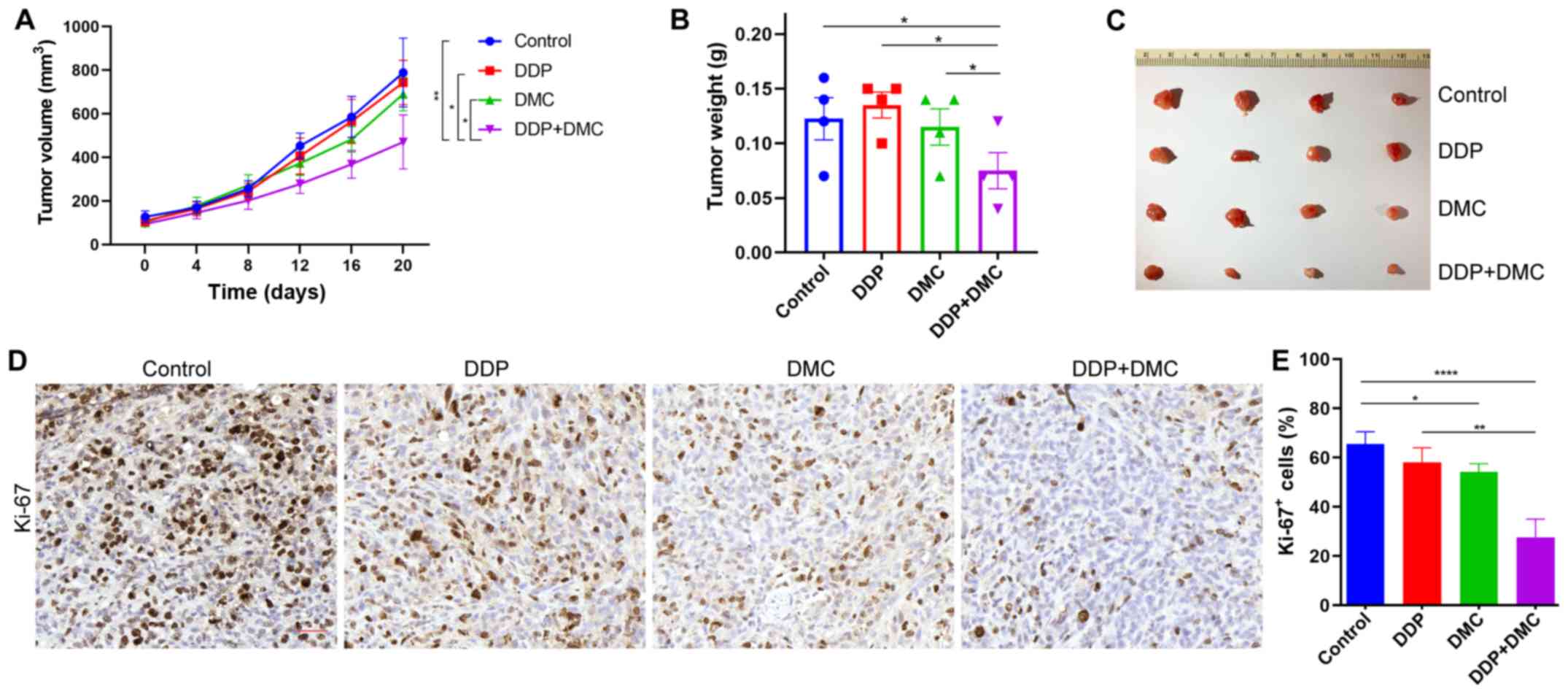
|
1
|
Nasim F, Sabath BF and Eapen GA: Lung
cancer. Med Clin North Am. 103:463–473. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Gadgeel S,
Ahn JS, Kim DW, Ou SI, Pérol M, Dziadziuszko R, Rosell R, et al:
Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 377:829–838. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rinaldi M, Cauchi C and Gridelli C: First
line chemotherapy in advanced or metastatic NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 17
(Suppl 5):v64S–v67S. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ke B, Wei T, Huang Y, Gong Y, Wu G, Liu J,
Chen X and Shi L: Interleukin-7 resensitizes non-small-cell lung
cancer to cisplatin via inhibition of ABCG2. Mediators Inflamm.
2019:72414182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels
J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms
of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 31:1869–1883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amable L: Cisplatin resistance and
opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol Res. 106:27–36.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Janyou A, Changtam C, Suksamrarn A,
Tocharus C and Tocharus J: Suppression effects of
O-demethyldemethoxycurcumin on thapsigargin triggered on
endoplasmic reticulum stress in SK-N-SH cells. Neurotoxicology.
50:92–100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simental-Mendia LE, Pirro M, Gotto AM Jr,
Banach M, Atkin SL, Majeed M and Sahebkar A: Lipid-modifying
activity of curcuminoids: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 59:1178–1187.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benediktsdottir BE, Baldursson O,
Gudjonsson T, Tonnesen HH and Masson M: Curcumin,
bisdemethoxycurcumin and dimethoxycurcumin complexed with
cyclodextrins have structure specific effect on the paracellular
integrity of lung epithelia in vitro. Biochem Biophys Rep.
4:405–410. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan F, Dong H, Gong J, Wang D, Hu M,
Huang W, Fang K, Qin X, Qiu X, Yang X and Lu F: A systematic review
and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the effects of
turmeric and curcuminoids on blood lipids in adults with metabolic
diseases. Adv Nutr. 10:791–802. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Imran M, Ullah A, Saeed F, Nadeem M,
Arshad MU and Suleria HAR: Cucurmin, anticancer, & antitumor
perspectives: A comprehensive review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.
58:1271–1293. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Al Ayoub Y, Gopalan RC, Najafzadeh M,
Mohammad MA, Anderson D, Paradkar A and Assi KH: Development and
evaluation of nanoemulsion and microsuspension formulations of
curcuminoids for lung delivery with a novel approach to
understanding the aerosol performance of nanoparticles. Int J
Pharm. 557:254–263. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Adiwidjaja J, McLachlan AJ and Boddy AV:
Curcumin as a clinically-promising anti-cancer agent:
Pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Expert Opin Drug Metab
Toxicol. 13:953–972. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shanmugam MK, Rane G, Kanchi MM, Arfuso F,
Chinnathambi A, Zayed ME, Alharbi SA, Tan BK, Kumar AP and Sethi G:
The multifaceted role of curcumin in cancer prevention and
treatment. Molecules. 20:2728–2769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hassanalilou T, Ghavamzadeh S and Khalili
L: Curcumin and gastric cancer: A review on mechanisms of action. J
Gastrointest Cancer. 50:185–192. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mendonca LM, Machado Cda S, Teixeira CC,
Freitas LA, Bianchi ML and Antunes LM: Comparative study of
curcumin and curcumin formulated in a solid dispersion: Evaluation
of their antigenotoxic effects. Genet Mol Biol. 38:490–498. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Quitschke WW: Differential solubility of
curcuminoids in serum and albumin solutions: Implications for
analytical and therapeutic applications. BMC Biotechnol. 8:842008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen G, Chen Y, Yang N, Zhu X, Sun L and
Li G: Interaction between curcumin and mimetic biomembrane. Sci
China Life Sci. 55:527–532. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hatamipour M, Ramezani M, Tabassi SAS,
Johnston TP and Sahebkar A: Demethoxycurcumin: A naturally
occurring curcumin analogue for treating non-cancerous diseases. J
Cell Physiol. 234:19320–19330. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee JW, Hong HM, Kwon DD, Pae HO and Jeong
HJ: Dimethoxycurcumin, a structural analogue of curcumin, induces
apoptosis in human renal carcinoma caki cells through the
production of reactive oxygen species, the release of cytochrome C,
and the activation of caspase-3. Korean J Urol. 51:870–878. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ni X, Zhang A, Zhao Z, Shen Y and Wang S:
Demethoxycurcumin inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
invasion in prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 28:85–90.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ko YC, Lien JC, Liu HC, Hsu SC, Lin HY,
Chueh FS, Ji BC, Yang MD, Hsu WH and Chung JG:
Demethoxycurcumin-induced DNA damage decreases DNA
Repair-associated protein expression levels in NCI-H460 human lung
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 35:2691–2698. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ko YC, Lien JC, Liu HC, Hsu SC, Ji BC,
Yang MD, Hsu WH and Chung JG: Demethoxycurcumin induces the
apoptosis of human lung cancer NCI-H460 cells through the
mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Oncol Rep. 33:2429–2437. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang HB and Chen BH: Inhibition of lung
cancer cells A549 and H460 by curcuminoid extracts and
nanoemulsions prepared from Curcuma longa linnaeus. Int J
Nanomedicine. 10:5059–5080. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McNeil EM and Melton DW: DNA repair
endonuclease ERCC1-XPF as a novel therapeutic target to overcome
chemoresistance in cancer therapy. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:9990–10004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother WJ, Leverson JD
and Souers AJ: From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced
selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:273–284.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rheaume E, Cohen LY, Uhlmann F, Lazure C,
Alam A, Hurwitz J, Sékaly RP and Denis F: The large subunit of
replication factor C is a substrate for caspase-3 in vitro and is
cleaved by a caspase-3-like protease during Fas-mediated apoptosis.
EMBO J. 16:6346–6354. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rotolo F, Dunant A, Le Chevalier T, Pignon
JP and Arriagada R; IALT Collaborative Group, : Adjuvant
cisplatin-based chemotherapy in nonsmall-cell lung cancer: New
insights into the effect on failure type via a multistate approach.
Ann Oncol. 25:2162–2166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ricci S, Antonuzzo A, Galli L, Tibaldi C,
Bertuccelli M, Lopes Pegna A, Petruzzelli S, Bonifazi V, Orlandini
C and Franco Conte P: A randomized study comparing two different
schedules of administration of cisplatin in combination with
gemcitabine in advanced nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer.
89:1714–1719. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moldvay J, Rokszin G, Abonyi-Toth Z,
Katona L and Kovacs G: Analysis of drug therapy of lung cancer in
Hungary. Magy Onkol. 57:33–38. 2013.(In Hungarian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bayat Mokhtari R, Homayouni TS, Baluch N,
Morgatskaya E, Kumar S, Das B and Yeger H: Combination therapy in
combating cancer. Oncotarget. 8:38022–38043. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hung CM, Su YH, Lin HY, Lin JN, Liu LC, Ho
CT and Way TD: Demethoxycurcumin modulates prostate cancer cell
proliferation via AMPK-induced down-regulation of HSP70 and EGFR. J
Agric Food Chem. 60:8427–8434. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sheu MJ, Lin HY, Yang YH, Chou CJ, Chien
YC, Wu TS and Wu CH: Demethoxycurcumin, a major active curcuminoid
from Curcuma longa, suppresses balloon injury induced
vascular smooth muscle cell migration and neointima formation: An
in vitro and in vivo study. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:1586–1597. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Teng YN, Hsieh YW, Hung CC and Lin HY:
Demethoxycurcumin modulates human P-glycoprotein function via
uncompetitive inhibition of ATPase hydrolysis activity. J Agric
Food Chem. 63:847–855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ruiz de Porras V, Bystrup S,
Martinez-Cardus A, Pluvinet R, Sumoy L, Howells L, James MI, Iwuji
C, Manzano JL, Layos L, et al: Curcumin mediates
oxaliplatin-acquired resistance reversion in colorectal cancer cell
lines through modulation of CXC-Chemokine/NF-KB signalling pathway.
Sci Rep. 6:246752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao S, Pi C, Ye Y, Zhao L and Wei Y:
Recent advances of analogues of curcumin for treatment of cancer.
Eur J Med Chem. 180:524–535. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Changtam C, Hongmanee P and Suksamrarn A:
Isoxazole analogs of curcuminoids with highly potent
multidrug-resistant antimycobacterial activity. Eur J Med Chem.
45:4446–4457. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen YY, Lin YJ, Huang WT, Hung CC, Lin
HY, Tu YC, Liu DM, Lan SJ and Sheu MJ: Demethoxycurcumin-Loaded
chitosan nanoparticle downregulates DNA repair pathway to improve
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Molecules. 23:32172018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhu H, Luo H, Zhang W, Shen Z, Hu X and
Zhu X: Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance in cervical
cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:1885–1895. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vikhanskaya F, Marchini S, Marabese M,
Galliera E and Broggini M: P73a overexpression is associated with
resistance to treatment with DNA-damaging agents in a human ovarian
cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 61:935–938. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsai MS, Weng SH, Kuo YH, Chiu YF and Lin
YW: Synergistic effect of curcumin and cisplatin via
down-regulation of thymidine phosphorylase and excision repair
cross-complementary 1 (ERCC1). Mol Pharmacol. 80:136–146. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin CY, Hung CC, Wang CCN, Lin HY, Huang
SH and Sheu MJ: Demethoxycurcumin sensitizes the response of
non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin through downregulation of
TP and ERCC1-related pathways. Phytomedicine. 53:28–36. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|