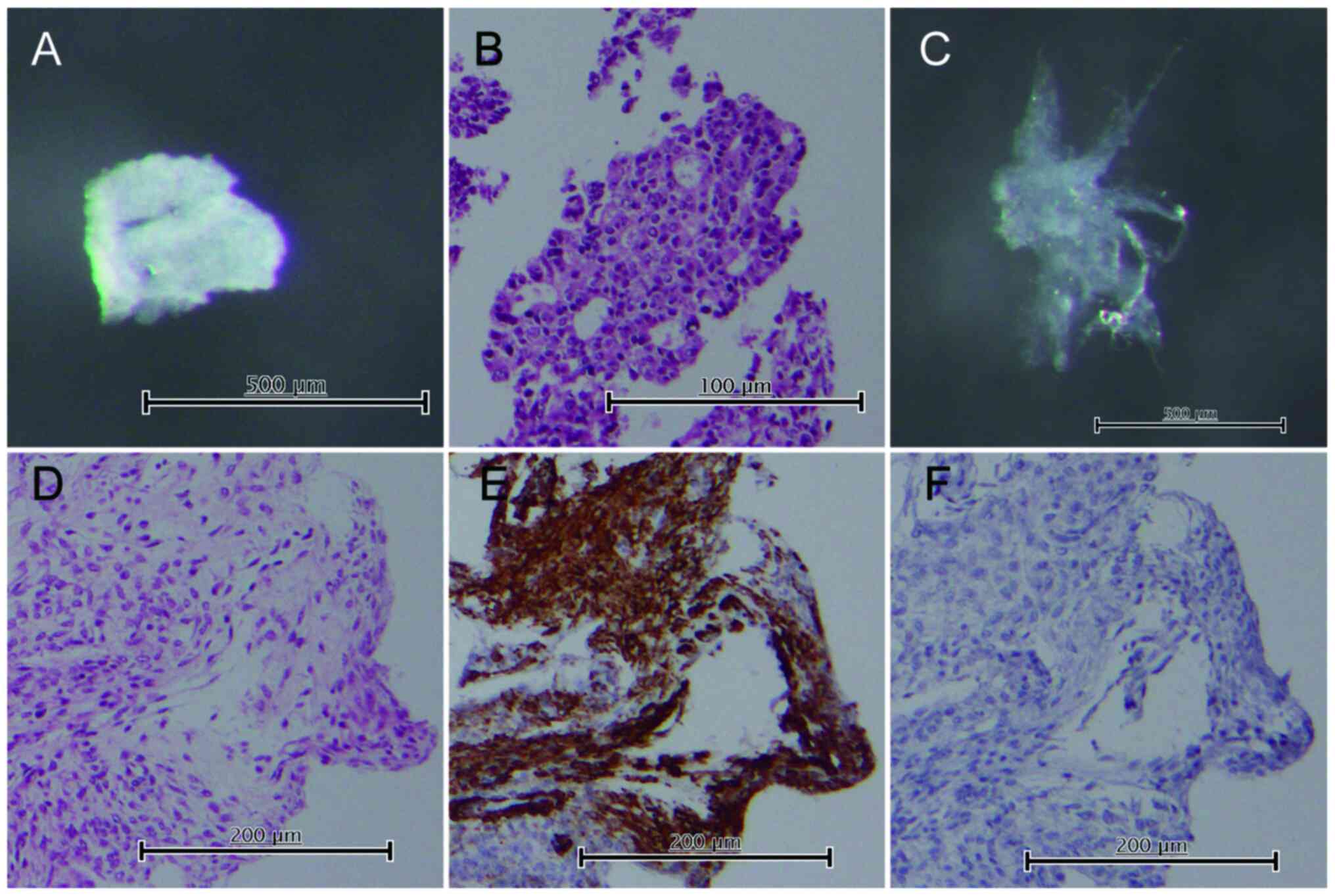
|
1
|
Reid BM, Permuth JB and Sellers TA:
Epidemiology of ovarian cancer: A review. Cancer Biol Med. 14:9–32.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lisio MA, Fu L, Goyeneche A, Gao ZH and
Telleria C: High-grade serous ovarian cancer: Basic sciences,
clinical and therapeutic standpoints. Int J Mol Sci. 20:9522019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Falzone L, Salomone S and Libra M:
Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the
third millennium. Front Pharmacol. 9:13002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chandra A, Pius C, Nabeel M, Nair M,
Vishwanatha JK, Ahmad S and Basha R: Ovarian cancer: Current status
and strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes. Cancer Med.
8:7018–7031. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mathieu KB, Bedi DG, Thrower SL, Qayyum A
and Bast RC Jr: Screening for ovarian cancer: Imaging challenges
and opportunities for improvement. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol.
51:293–303. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mills GB, Bast RC Jr and Srivastava S:
Future for ovarian cancer screening: Novel markers from emerging
technologies of transcriptional profiling and proteomics. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 93:1437–1439. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bandera CA, Ye B and Mok SC: New
technologies for the identification of markers for early detection
of ovarian cancer. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 15:51–55. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang H, Liu T, Zhang Z, Payne SH, Zhang
B, McDermott JE, Zhou JY, Petyuk VA, Chen L, Ray D, et al:
Integrated proteogenomic characterization of human high-grade
serous ovarian cancer. Cell. 166:755–765. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature.
474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Davidson B: Biomarkers of drug resistance
in ovarian cancer-an update. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 19:469–476.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elias KM, Guo J and Bast RC Jr: Early
detection of ovarian cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am.
32:903–914. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Falzone L, Romano GL, Salemi R, Bucolo C,
Tomasello B, Lupo G, Anfuso CD, Spandidos DA, Libra M and Candido
S: Prognostic significance of deregulated microRNAs in uveal
melanomas. Mol Med Rep. 19:2599–2610. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Staicu CE, Predescu DV, Rusu CM, Radu BM,
Cretoiu D, Suciu N, Crețoiu SM and Voinea SC: Role of microRNAs as
clinical cancer biomarkers for ovarian cancer: A short overview.
Cells. 9:1692020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yokoi A, Matsuzaki J, Yamamoto Y, Yoneoka
Y, Takahashi K, Shimizu H, Uehara T, Ishikawa M, Ikeda SI, Sonoda
T, et al: Integrated extracellular microRNA profiling for ovarian
cancer screening. Nat Commun. 9:43192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Falzone L, Lupo G, La Rosa GRM, Crimi S,
Anfuso CD, Salemi R, Rapisarda E, Libra M and Candido S:
Identification of novel MicroRNAs and their diagnostic and
prognostic significance in oral cancer. Cancers (Basel).
11:6102019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P: Cancer associated
fibroblasts: The dark side of the coin. Am J Cancer Res. 1:482–497.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P:
Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: A diabolic liaison
driving cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:195–208.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dasari S, Fang Y and Mitra AK: Cancer
associated fibroblasts: Naughty neighbors that drive ovarian cancer
progression. Cancers (Basel). 10:4062018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sun W and Fu S: Role of cancer-associated
fibroblasts in tumor structure, composition and the
microenvironment in ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 18:2173–2178.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Japanese Society of Obstetrics and
Gynecology, the Japanese Society of Pathology, . The General Rules
for Clinical and Pathological Management of Ovarian Tumors Part 1:
Histological Classification and Color Atlas of Ovarian Tumors.
(2nd). Kanehara. 1–41. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Prat J and FIGO Committee on Gynecologic
Oncology, . Staging classification for cancer of the ovary,
fallopian tube, and peritoneum. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 124:1–5.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sato A, Fujita Y, Otsuka K, Sasaki A,
Suzuki H, Matsumoto T and Sugai T: Differential expression of
microRNAs in colorectal cancer: Different patterns between isolated
cancer gland and stromal cells. Pathol Int. 70:21–30. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Habano W, Sugai T, Nakamura S and Yoshida
T: A novel method for gene analysis of colorectal carcinomas using
a crypt isolation technique. Lab Invest. 74:933–940.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sugai T, Habano W, Nakamura SI, Uesugi N,
Sasou S and Itoh C: A unique method for mutation analysis of tumor
suppressor genes in colorectal carcinomas using a crypt isolation
technique. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 124:382–386. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miles GD, Seiler M, Rodriguez L, Rajagopal
G and Bhanot G: Identifying microRNA/mRNA dysregulations in ovarian
cancer. BMC Res Notes. 5:1642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shiomi E, Sugai T, Ishida K, Osakabe M,
Tsuyukubo T, Kato Y, Takata R and Obara W: Analysis of expression
patterns of microRNAs that are closely associated with renal
carcinogenesis. Front Oncol. 9:4312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kohlhapp FJ, Mitra AK, Lengyel E and Peter
ME: MicroRNAs as mediators and communicators between cancer cells
and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 34:5857–5868. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kossaï M, Leary A, Scoazec JY and Genestie
C: Ovarian cancer: A heterogeneous disease. Pathobiology. 85:41–49.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Comerford SA, Clouthier DE, Hinnant EA and
Hammer RE: Induction of hepatocyte proliferation and death by
modulation of T-Antigen expression. Oncogene. 22:2515–2530. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Li Y, Chen Y, Xie Q, Dong N, Gao Y,
Deng H, Lu C and Wang S: MicroRNA-214-3p inhibits proliferation and
cell cycle progression by targeting MELK in hepatocellular
carcinoma and correlates cancer prognosis. Cancer Cell Int.
17:1022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Phatak P, Byrnes KA, Mansour D, Liu L, Cao
S, Li R, Rao JN, Turner DJ, Wang JY and Donahue JM: Overexpression
of miR-214-3p in esophageal squamous cancer cells enhances
sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting survivin directly and
indirectly through CUG-BP1. Oncogene. 35:2087–2097. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Du T, Qu Y, Li J, Li H, Su L, Zhou Q, Yan
M, Li C, Zhu Z and Liu B: Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase
enhances gastric cancer progression via the FAK/Paxillin pathway.
Mol Cancer. 13:1002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Y, Li Z, Yuan H, Ji W, Wang K, Lu T,
Yu Y, Zeng Q, Li F, Xia W and Lu S: Reciprocal regulatory mechanism
between miR-214-3p and FGFR1 in FGFR1-amplified lung cancer.
Oncogenesis. 8:502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Falzone L, Candido S, Salemi R, Basile MS,
Scalisi A, McCubrey JA, Torino F, Signorelli SS, Montella M and
Libra M: Computational identification of microRNAs associated to
both epithelial to mesenchymal transition and NGAL/MMP-9 pathways
in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 7:72758–72766. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Xu Y, Wang J and Ying H:
Circulating miR-214-3p predicts nasopharyngeal carcinoma recurrence
or metastasis. Clin Chim Acta. 503:54–60. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vishnubalaji R, Hamam R, Yue S, Al-Obeed
O, Kassem M, Liu FF, Aldahmash A and Alajez NM: MicroRNA 320
suppresses colorectal cancer by targeting SOX4, FOXM1, and FOXQ1.
Oncotarget. 7:35789–35802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun JY, Huang Y, Li JP, Zhang X, Wang L,
Meng YL, Yan B, Bian YQ, Zhao J, et al: MicroRNA-320a suppresses
human colon cancer cell proliferation by directly targeting
β-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 420:787–792. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao H, Dong T, Zhou H, Wang L, Huang A,
Feng B, Quan Y, Jin R, Zhang W, Sun J, et al: MiR-320a suppresses
colorectal cancer progression by targeting Rac1. Carcinogenesis.
35:886–895. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang H, Li W, Nan F, Ren F, Wang H, Xu Y
and Zhang F: MicroRNA expression profile of colon cancer stem-like
cells in HT29 adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
404:273–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen L, Yan HX, Yang W, Hu L, Yu LX, Liu
Q, Li L, Huang DD, Ding J, Shen F, et al: The role of microRNA
expression pattern in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J
Hepatol. 50:358–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsieh IS, Chang KC, Tsai YT, Ke JY, Lu PJ,
Lee KH, Yeh SD, Hong TM and Chen YL: MicroRNA-320 suppresses the
stem cell-like characteristics of prostate cancer cells by
downregulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 34:530–538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|