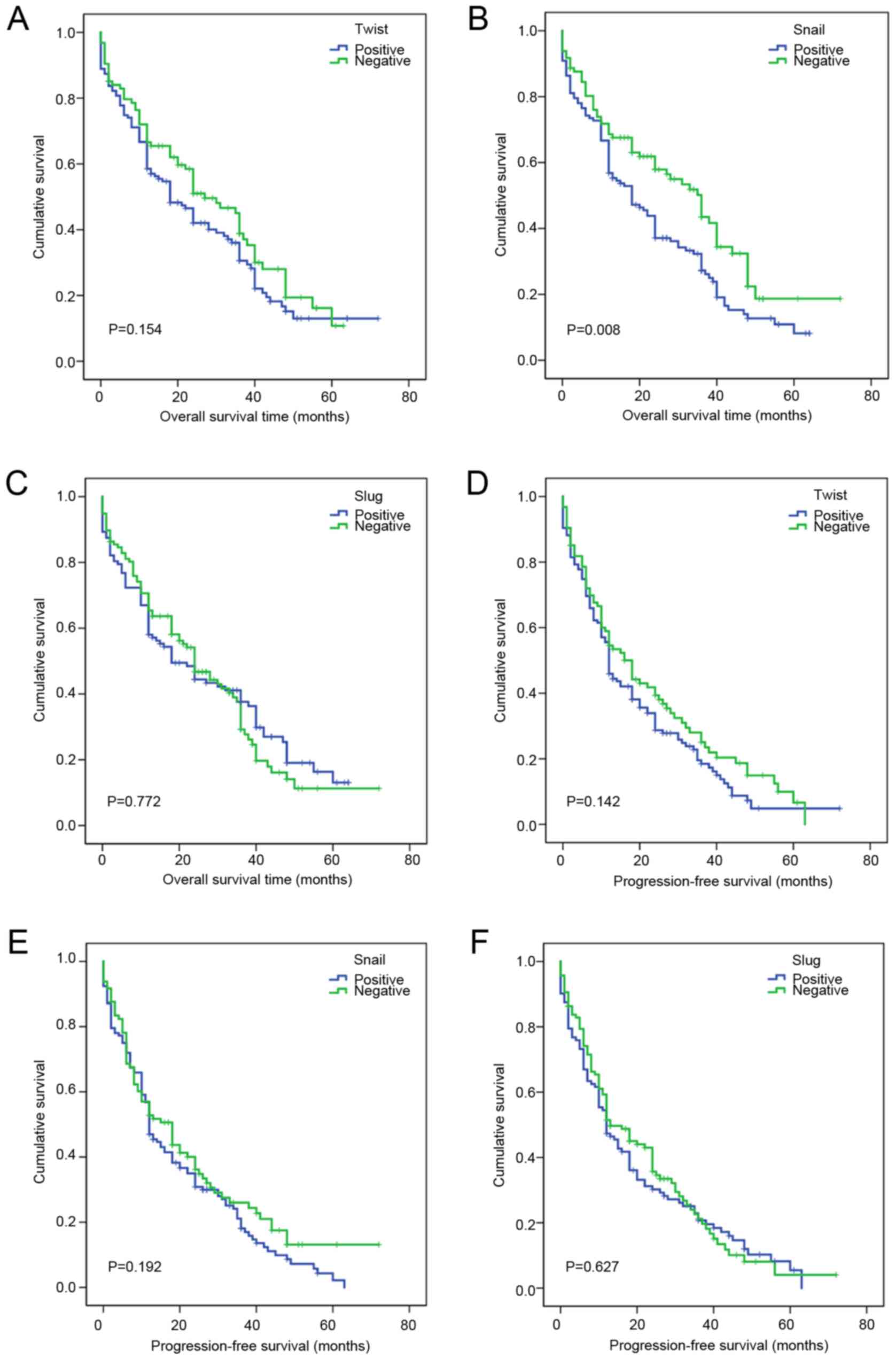
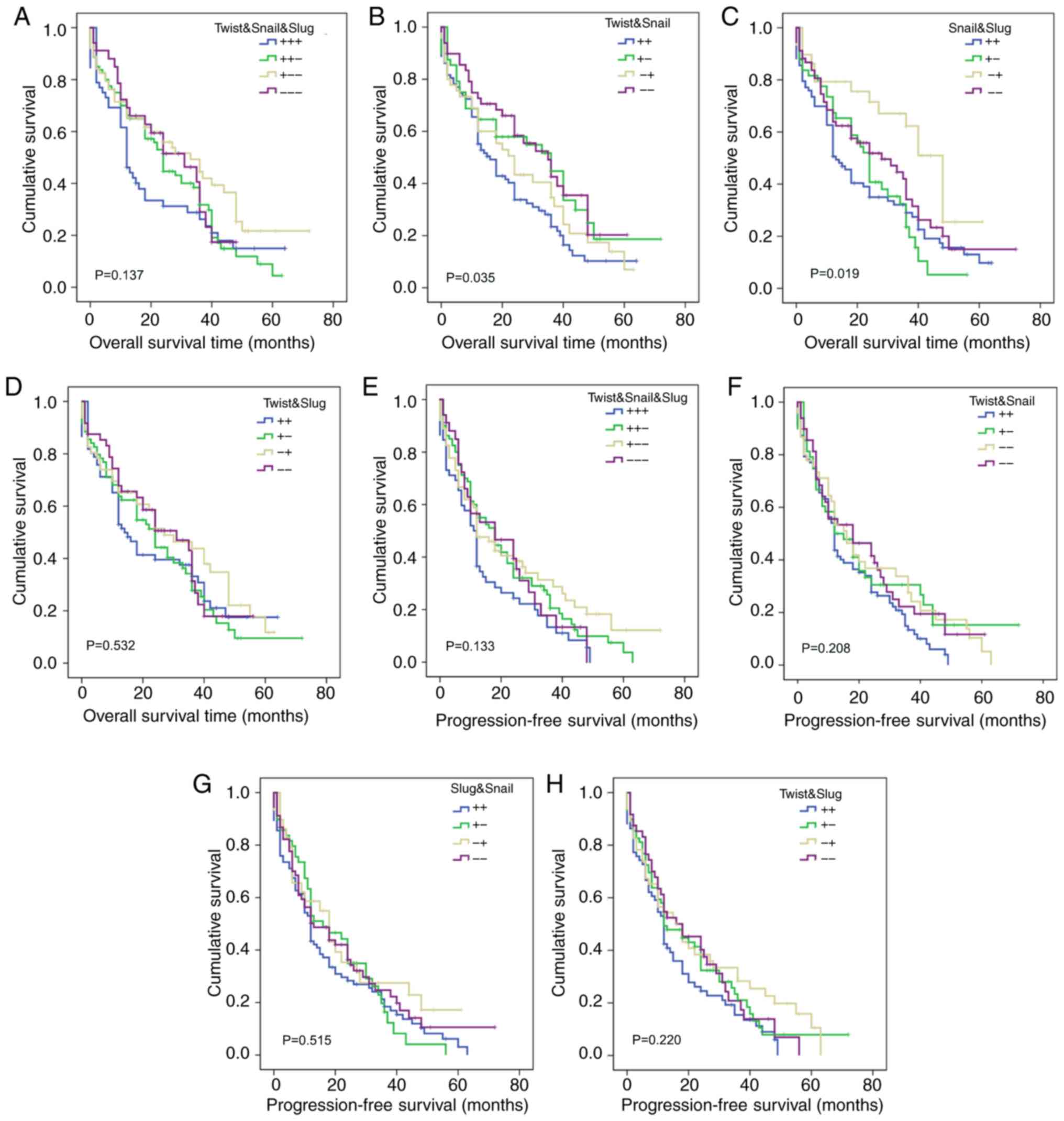
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jema A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen R, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Wang
SM, Sun KX, Gu XY, Wei WW and He J: Analysis of incidence and
mortality of esophageal cancer in China, 2015. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 53:1094–1097. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Napier KJ, Scheerer M and Misra S:
Esophageal cancer: A review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging
workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
6:112–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zheng S, Vuitton L, Sheyhidin I, Vuitton
DA, Zhang Y and Lu X: Northwestern China: A place to learn more on
oesophageal cancer. Part two: Gene alterations and polymorphisms.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1087–1099. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qing L, Liang M, Liu T, Vuitton L, Zheng
S, Gao X, Lu M, Li X, Sheyhidin I and Lu X: M2 isoform of pyruvate
kinase (PKM2) is upregulated in Kazakh's ESCC and promotes
proliferation and migration of ESCC cells. Tumour Biol.
37:2665–2672. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pang L, Li Q, Wei C, Zou H, Li S, Cao W,
He J, Zhou Y, Ju X, Lan J, et al: TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma: In vitro and clinical analyses of cell
lines and nomadic Kazakh patients from northwest Xinjiang, China.
PLoS One. 9:e1123002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de la Iglesia JE, de la Calle MA, pérez
GC, Pérez RR and Delgado AA: Esophageal cancer: Anatomic,
particularities, staging, and, imaging techniques. Radiologia.
58:352–365. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu B, Bo Y, Wang K, Liu Y, Tang X, Zhao
Y, Zhao E and Yuan L: Concurrent neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
could improve survival outcomes for patients with esophageal
cancer: A metaanalysis based on random clinical trials. Oncotarget.
21:20410–20417. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang Y, Wang H, Luo G, Zhang Y, Wang L
and Li K: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of
neoadjuvant therapy combined with surgery for patients with
resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Surg.
38:41–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu Y, Li Z, Mi DM, Cao N, Zu SW, Wen ZZ,
Yu XL and Qu Y: Chemoradiation combined with regional hyperthermia
for advanced oesophageal cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Clin Pharm Ther. 42:155–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Parvani JG and Schiemann WP: Sox4, EMT
programs, and the metastatic progression of breast cancers:
Mastering the masters of EMT. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bruner HC and Derksen WB: Loss of
E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion and the development and
progression of cancer. Cold Spring Herb Perspect Biol.
1:102018.
|
|
13
|
Siar CH and Ng KH: Differential expression
of transcription factors snail, slug, SIP1, and twist in
ameloblastoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 43:45–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qian Q, Young X, Tao H, Qin C and Xu J:
Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and
underlying molecular mechanisms. Cell Res. 22:90–106. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu L, Mu Y, Sa N, Wang H and Xu W: Tumor
necrosis factor α induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
promotes metastasis via NF-κB signaling pathway-mediated twist
expression in hypopharyngeal cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:321–327. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao J, Wang X, Dai T, Wu Y, Zhang M, Cao
R, Zhang R, Wang G, Jiang R, Zhou BP, et al: Twist promotes tumor
metastasis in basal-like breast cancer by transcriptionally
upregulating ROR1. Theranostics. 8:2739–2751. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Shi L, Li J, Wang H and Yang H:
Involvement of twist in NNK exposure-promoted lung cancer cell
migration and invasion. Toxicol In Vitro. 63:1047402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lyu P, Zhang SD, Yuen HF, McCrudden CM,
Wen Q, Chan KW and Kwok HF: Identification of Twist-interacting
genes in prostate cancer. Sci China Life Sci. 60:386–396. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hajra KM, Chen DY and Fearon ER: The slug
zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 62:1613–1618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
de Souza Palma C, Grassi ML, Thomé CH,
Ferreira GA, Albuquerque D, Pinto MT, Melo FU, Kashima S, Covas DT,
Pitteri SJ and Faça VM: Proteomic analysis of epithelial to
mesenchymal transition (EMT) reveals cross-talk between snail and
HDAC1 proteins in breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Proteomics.
15:906–917. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X and Zhou BP:
The role of snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:963–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaufhold S and Bonavida B: Central role of
snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer: A target
for therapeutic intervention. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Phillips S and Kuperwasser C: SLUG:
Critical regulator of epithelial cell identity in breast
development and cancer. Cell Adh Migr. 8:578–587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alves CC, Carneiro F, Hoefler H and Becker
KF: Role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Slug in
primary human cancers. Front Biosci (Landmark ED). 14:3035–3050.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng S, Vuitton L, Sheyhidin I, Vuitton
DA, Zhang Y and Lu X: Northwestern China: A place to learn more on
oesophageal cancer. Part one: Behavioural and environmental risk
factors. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:917–925. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiao W, Jia Z, Liu H, Liu Q, Zhang T, Guo
W, Li P, Deng M and Li S: Prognostic and clinicopathological value
of twist expression in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
12:e01861912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gong T, Xue Z, Tang S, Zheng X, Xu G, Gao
L, Zhao G, Hong L, Tang G, Zhang H, et al: Nuclear expression of
twist promotes lymphatic metastasis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:606–613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho YA, Kim EK, Cho BC, Koh YW and Yoon
SO: Twist and snail/slug expression in oropharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma in correlation with lymph node metastasis. Anticancer
Res. 39:6307–6316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hasan MR, Sharma R, Saraya A,
Chattopadhyay TK, DattaGupta S, Walfish PG, Chauhan SC and Ralhan
R: Slug is a predictor of poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma patients. PLoS One. 8:e828462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cui N, Yang WT and Zheng PS: Slug inhibits
the proliferation and tumor formation of human cervical cancer
cells by up-regulating the p21/p27 proteins and down-regulating the
activity of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via the
trans-suppression akt1/p-akt1 expression. Oncotarget.
7:26152–26167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun X and Liu Y: Activation of the
wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway may contribute to cervical cancer
pathogenesis via upregulation of twist. Oncol Lett. 14:4841–4844.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Salehi S, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A,
Davoudian S, Shenas SM, Shajari N, Majidi J and Baradaran B: An
analysis of suppressing migratory effect on human urinary bladder
cancer cell line by silencing of snail-1. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:545–550. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shenas SM, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Salehi
S, Kaffash B, Talebi B, Babaloo Z, Shanehbandi D and Baradaran B:
SiRNA-Mediated silencing of snail-1 induces apoptosis and alters
micro RNA expression in human urinary bladder cancer cell line.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 45:969–974. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang HY, Tseng YK, Chen YC, Shu CW, Lin
MI, Liou HH, Fu TY, Lin YC, Ger LP, Yeh MH and Liu PF: High snail
expression predicts a poor prognosis in breast invasive ductal
carcinoma patients with HER2/EGFR-positive subtypes. Surg Oncol.
27:314–320. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Smit MA, Geiger TR, Song JY, Gitelman I
and Peeper DS: A twist-snail axis critical for TrkB-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like transformation, anoikis
resistance, and metastasis. Mol Cell Biol. 29:3722–3737. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dave N, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Gutarra S,
Frias A, Beltran M, Peiró S and de Herreros AG: Functional
cooperation between snail1 and twist in the regulation of ZEB1
expression during epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol
Chem. 286:12024–12032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oh KY, Yoon HJ, Lee JI, Ahn SH and Hong
SD: Twist and snail expression in tumor and stromal cells of
epithelial odontogenic tumors. J Oral Pathol Med. 46:127–133. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mahmood MQ, Walters EH, Shukla SD, Weston
S, Muller HK, Ward C and Sohal SS: β-Catenin, twist and snail:
Transcriptional regulation of EMT in smokers and COPD, and relation
to airflow obstruction. Sci Rep. 7:108322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Casas E, Kim J, Bendesky A, Ohno-Machado
L, Wolfe CJ and Yang J: Snail2 is an essential mediator of
twist1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and metastasis.
Cancer Res. 71:245–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|