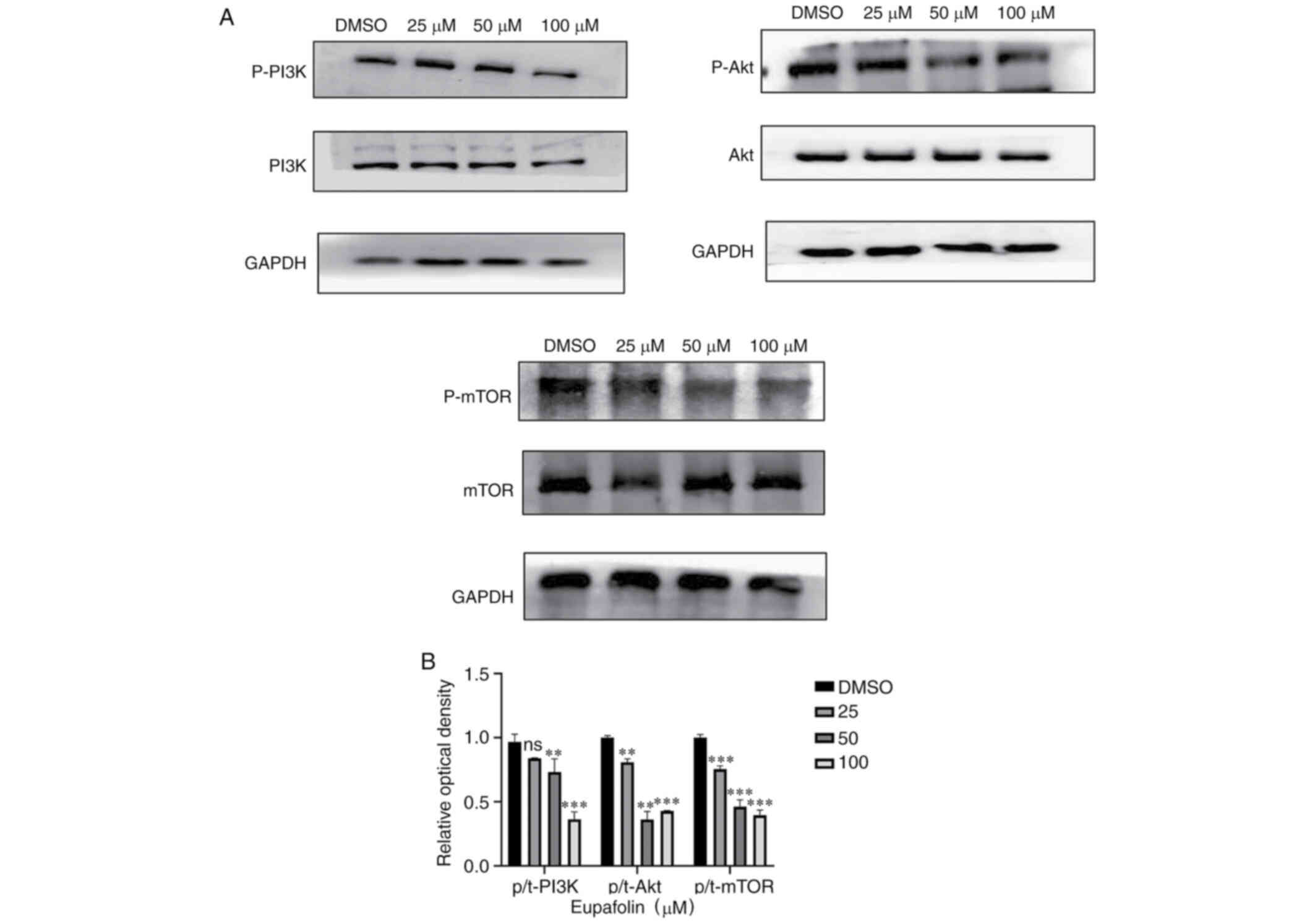
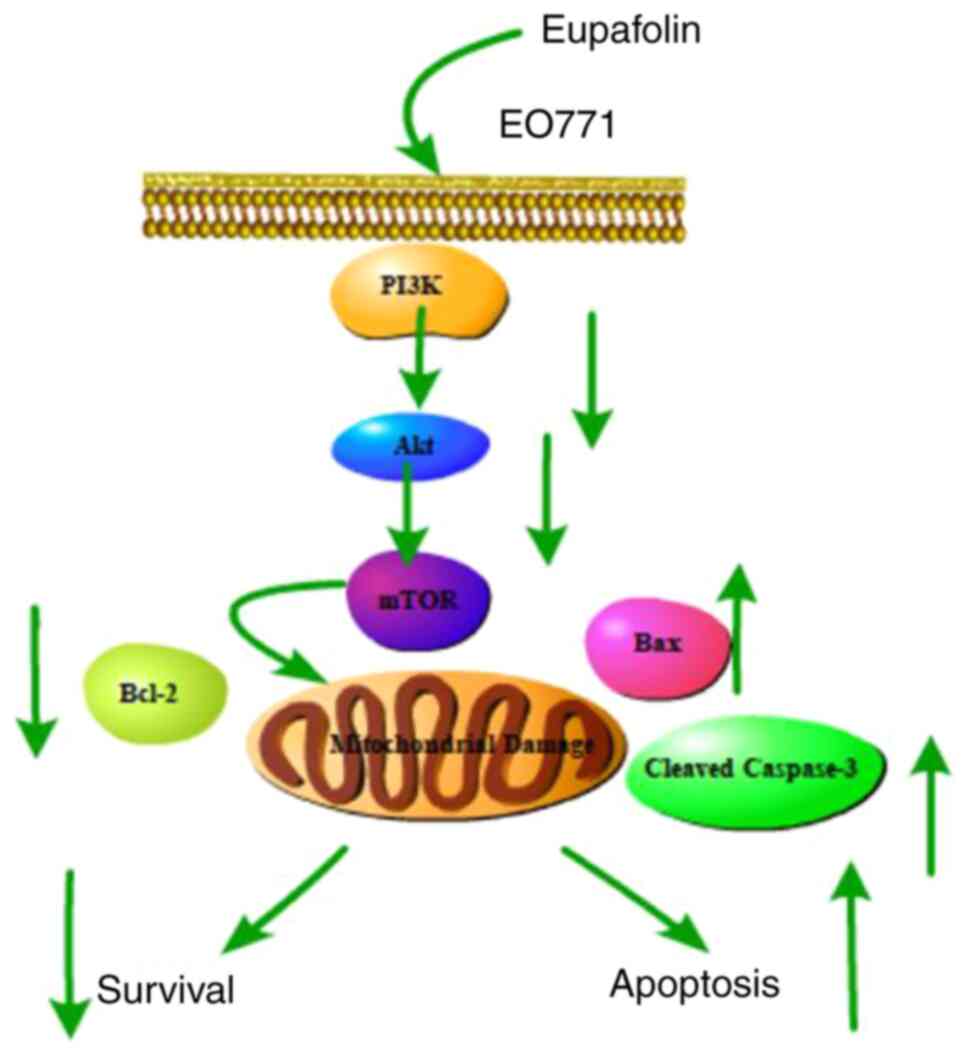
|
1
|
Watkins EJ: Overview of breast cancer.
JAAPA. 32:13–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao W, Ge S and Sun J: Ailanthone exerts
anticancer effect by up-regulating miR-148a expression in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and inhibiting proliferation,
migration and invasion. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:1062–1069. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chung KS, Choi JH, Back NI, Choi MS, Kang
EK, Chung HG, Jeong TS and Lee KT: Eupafolin, a flavonoid isolated
from Artemisia princeps, induced apoptosis in human cervical
adenocarcinoma HeLa cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1318–1328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang H, Wu D, Xu D, Yu H, Zhao Z, Ma D
and Jin J: Eupafolin exhibits potent anti-angiogenic and antitumor
activity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 13:701–711.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan X, Tao J, Cai Z, Fredimoses M, Wu J,
Jiang Z, Zhang K and Li S: Eupafolin suppresses esophagus cancer
growth by targeting T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase. Front
Pharmacol. 10:12482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu K, Park C, Chen H, Hwang J,
Thimmegowda NR, Bae EY, Lee KW, Kim HG, Liu H, Soung NK, et al:
Eupafolin suppresses prostate cancer by targeting
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated Akt signaling. Mol Carcinog.
54:751–760. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Am JU, Gong WJ, Su Y and Mou ZB:
Imperatorin shows selective antitumor effects in SGC-7901 human
gastric adenocarcinoma cells by inducing apoptosis, cell cycle
arrest and targeting PI3K/Akt/m-TOR signalling pathway. J BUON.
22:1471–1476. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Zhang R and Ni H: Eriodictyol
exerts potent anticancer activity against A549 human lung cancer
cell line by inducing mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, G2/M cell
cycle arrest and inhibition of m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway.
Arch Med Sci. 16:446–452. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao JG, Zhang L, Xiang XJ, Yu F, Ye WL,
Wu DP, Wang JF and Xiong JP: Amarogentin secoiridoid inhibits in
vivo cancer cell growth in xenograft mice model and induces
apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells (SNU-16) through G2/M cell
cycle arrest and PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J BUON. 21:609–617.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thorat MA and Balasubramanian R: Breast
cancer prevention in high-risk women. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet
Gynaecol. 65:18–31. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang XQ, Yao C, Bian WH, Chen X, Xue JX,
Zhu ZY, Ying Y, Xu YL and Wang C: Effects of Astragaloside IV on
treatment of breast cancer cells execute possibly through
regulation of Nrf2 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Food Sci
Nutr. 7:3403–3413. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai ZR, Ho YL, Huang SC, Huang TH, Lai SC,
Tsai JC, Wang CY, Huang GJ and Chang YS: Antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative activities of Kalanchoe
gracilis (L.) DC Stem. Am J Chin Med. 39:1275–1290. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han MA, Min KJ, Woo SM, Seo BR and Kwon
TK: Eupafolin enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through cathepsin
S-induced down-regulation of Mcl-1 expression and AMPK-mediated Bim
up-regulation in renal carcinoma Caki cells. Oncotarget.
7:65707–65720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Hu Z, Wang Z, Cui Y and Cui X:
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is an important facilitator of tumor
proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis and glycolysis in
osteosarcoma. Am J Transl Res. 11:6341–6355. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aksenenko MB, Palkina NV, Sergeeva ON, Yu
Sergeeva E, Kiriehenko AK and Ruksha TG: miR-155 overexpression is
followed by downregulation of its target gene, NFE2L2, and altered
pattern of VEGFA expression in the liver of melanoma B16-bearing
mice at the premetastatic stage. Int J Exp Pathol. 100:311–319.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Dawar S and Kumar S:
Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ.
22:526–539. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeng C, Ke Z, Song Y, Yao Y, Hu X, Zhang
M, Li H and Yin J: Annexin A3 is associated with a poor prognosis
in breast cancer and participates in the modulation of apoptosis in
vitro by affecting the Bcl-2/Bax balance. Exp Mol Pathol. 95:23–31.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao Z, Zhang G, Xie C and Zhou Y: miR-34b
regulates cervical cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Artif
Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:2042–2047. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu R, Chen Y, Shou T, Hu J, Chen J and
Qing C: TRIM67 promotes NFκB pathway and cell apoptosis in
GA-13315-treated lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 20:2936–2944.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu G, Zheng H, Xu J, Guo Y, Zheng G, Ma C,
Hao S, Liu X, Chen H, Wei S, et al: miR-429 suppresses cell growth
and induces apoptosis of human thyroid cancer cell by targeting
ZEB1. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:548–554. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou J, Xia L and Zhang Y: Naringin
inhibits thyroid cancer cell proliferation and induces cell
apoptosis through repressing PI3K/AKT pathway. Pathol Res Pract.
215:1527072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qiu J, Zhang T, Zhu X, Yang C, Wang Y,
Zhou N, Ju B, Zhou T, Deng G and Qiu C: Hyperoside induces breast
cancer cells apoptosis via ROS-Mediated NF-κB signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:1312019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Noori S and Hassan ZM: Tehranolide
inhibits proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by
inducing G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
52:1987–1999. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suryavanshi S, Choudhari A, Raina P and
Kaul-Ghanekar R: A polyherbal formulation, HC9 regulated cell
growth and expression of cell cycle and chromatin modulatory
proteins in breast cancer cell lines. J Ethnopharmacol.
242:1120222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ahn H, Im E, Lee DY, Lee HJ, Jung JH and
Kim SH: Antitumor Effect of pyrogallol via miR-134 mediated S phase
arrest and inhibition of PI3K/AKT/Skp2/cMyc signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 20:39852019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hunter T and Pines J: Cyclins and cancer.
II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 79:573–582.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park W, Park S, Song G and Lim W:
Inhibitory effects of osthole on human breast cancer cell
progression via induction of cell cycle arrest, mitochondrial
dysfunction, and ER stress. Nutrients. 11:27772019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gao X, Wang Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Yan M, Sun H,
Chen S and Pan X: Huganpian, a traditional Chinese medicine,
inhibits liver cancer growth in vitro and in vivo by inducing
autophagy and cell cycle arrest. Biomed Pharmacother.
120:1094692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Sun L, Zhang S, Zhang S and Li W:
GINS2 facilitates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
non-small-cell lung cancer through modulating PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK
signaling. J Cell Physiol. 235:7747–7756. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo L and Yang T: Oxymatrine inhibits the
proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells via the PI3K
pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 11:10499–10508. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Murugan AK: Special issue: PI3K/Akt
signaling in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 59:1–2. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Qu Z, Yao H, Sun L, Harata-Lee Y,
Cui J, Aung TN, Liu X, You R, Wang W, et al: An effective drug
sensitizing agent increases gefitinib treatment by down regulating
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and up regulating autophagy in non-small cell
lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1091692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi N, Yu H and Chen T: Inhibition of
esophageal cancer growth through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 12:7637–7647. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|