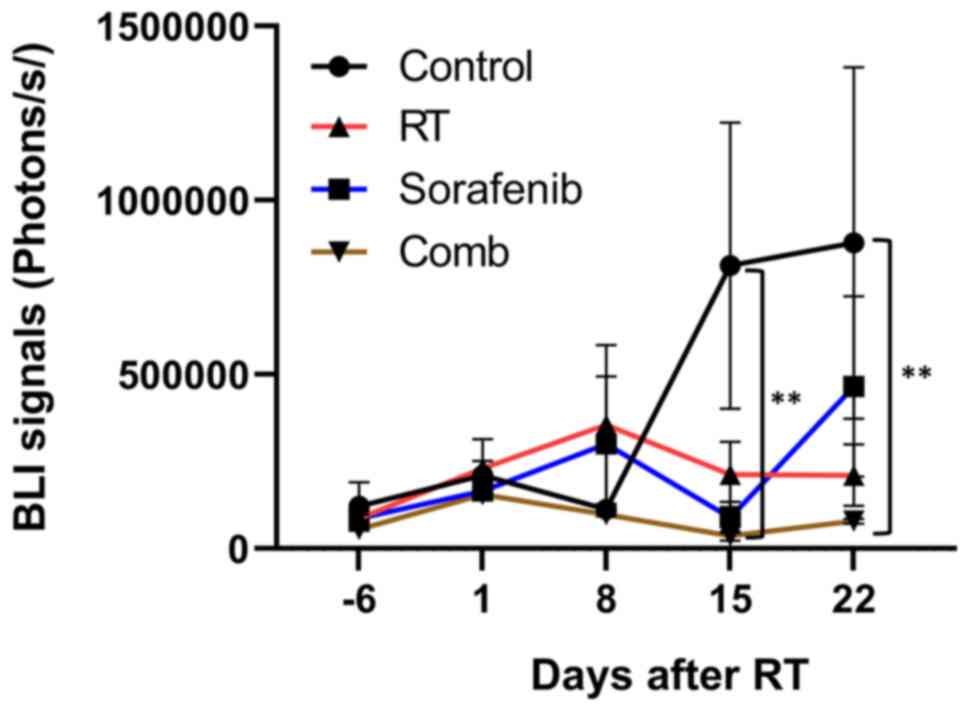
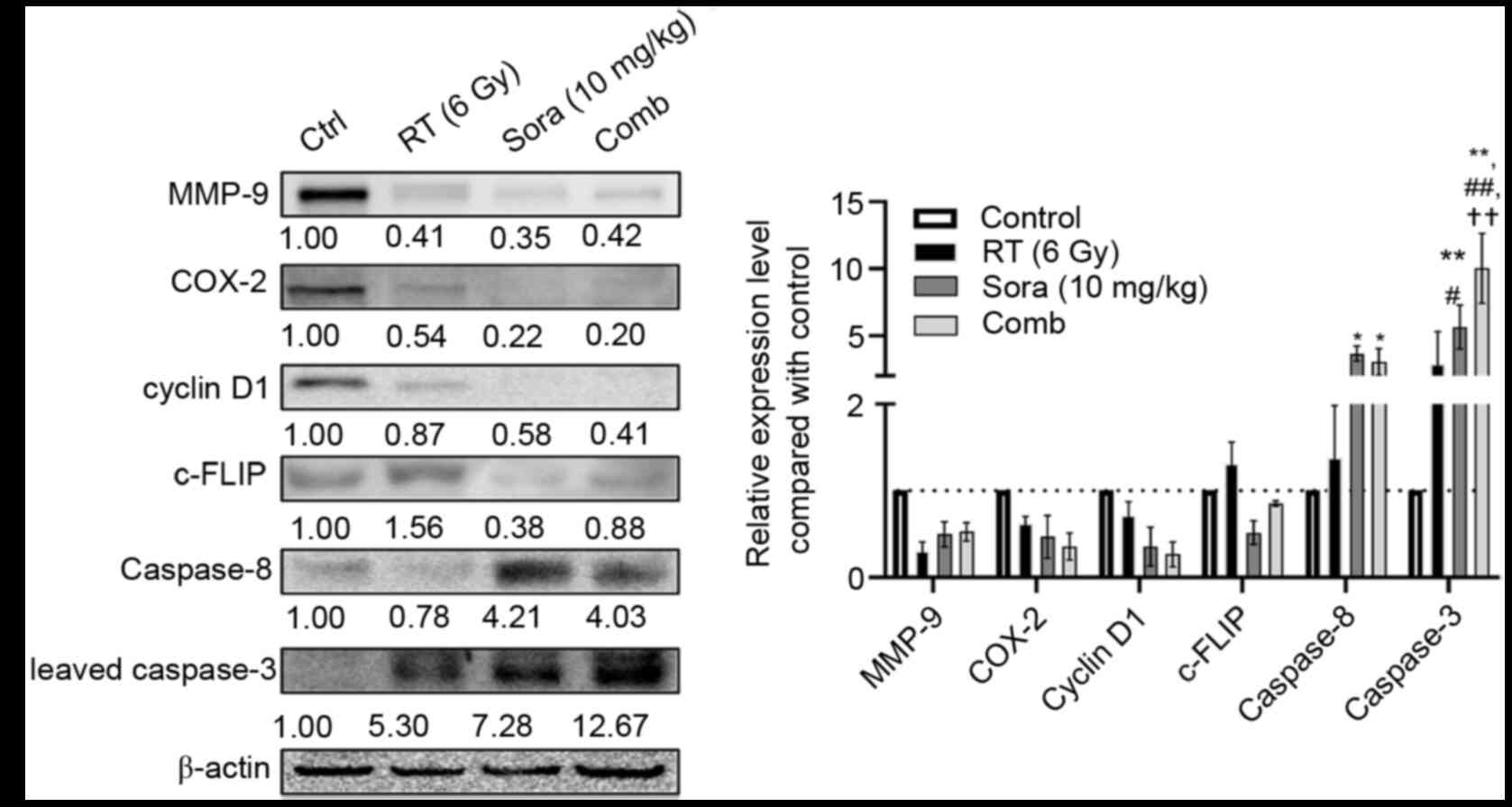
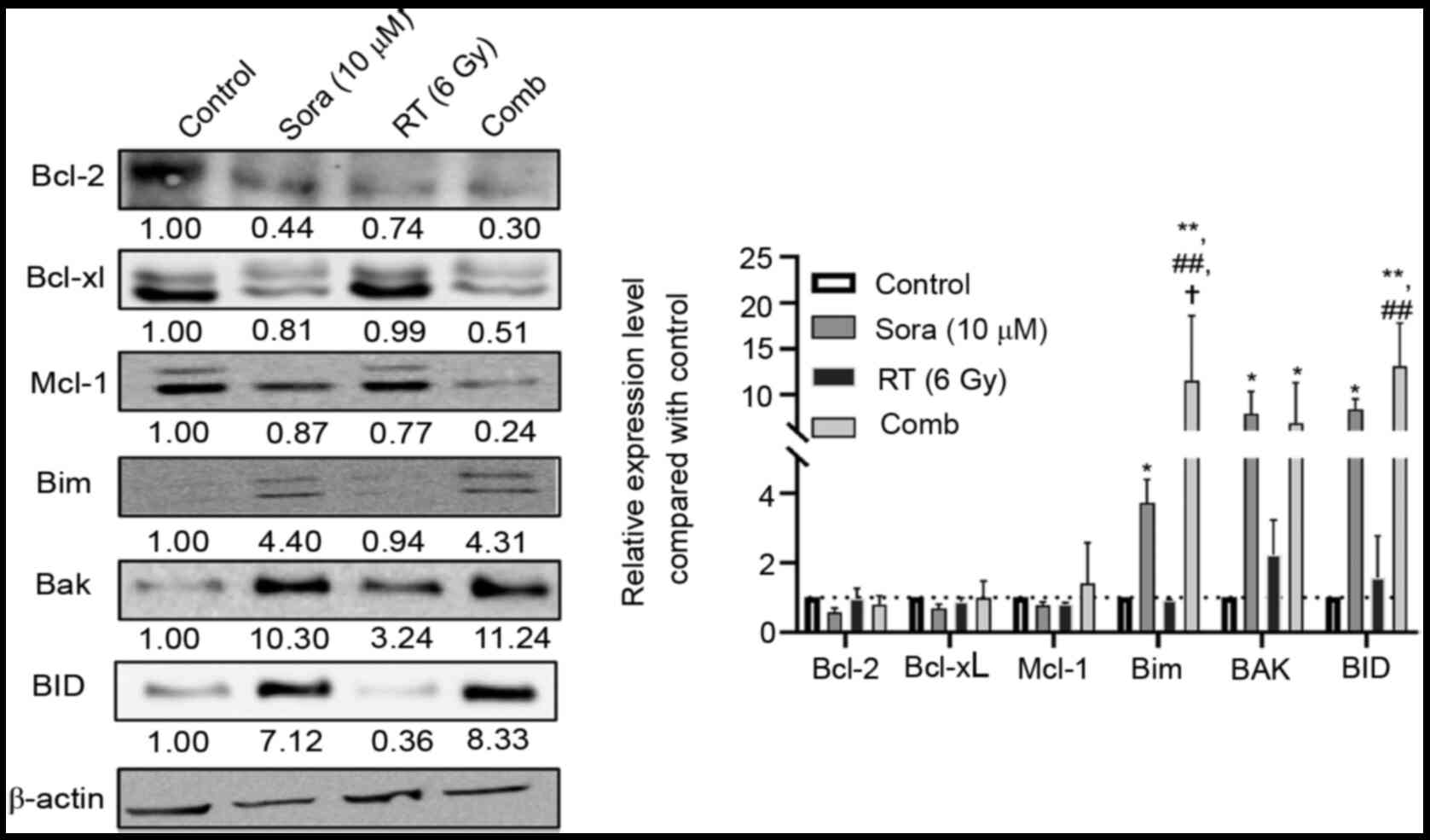
|
1
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and London WT:
Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: An emphasis on
demographic and regional variability. Clin Liver Dis. 19:223–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Golabi P, Fazel S, Otgonsuren M, Sayiner
M, Locklear CT and Younossi ZM: Mortality assessment of patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma according to underlying disease and
treatment modalities. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e5904. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen L, Sun J and Yang X: Radiofrequency
ablation-combined multimodel therapies for hepatocellular
carcinoma: Current status. Cancer Lett. 370:78–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chao Y, Chung YH, Han G, Yoon JH, Yang J,
Wang J, Shao GL, Kim BI and Lee TY: The combination of
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is well
tolerated and effective in Asian patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma: Final results of the START trial. Int J Cancer.
136:1458–1467. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsieh CH, Jeng KS, Lin CC, Chen CK, Liu
CY, Lin CP, Tai HC, Wang CH, Shueng PW and Chen YJ: Combination of
sorafenib and intensity modulated radiotherapy for unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Drug Investig. 29:65–71. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cha J, Seong J, Lee IJ, Kim JW and Han KH:
Feasibility of Sorafenib combined with local radiotherapy in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Yonsei Med J. 54:1178–1185.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen SW, Lin LC, Kuo YC, Liang JA, Kuo CC
and Chiou JF: Phase 2 study of combined sorafenib and radiation
therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 88:1041–1047. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brade AM, Ng S, Brierley J, Kim J,
Dinniwell R, Ringash J, Wong RR, Cho C, Knox J and Dawson LA: Phase
1 trial of sorafenib and stereotactic body radiation therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 94:580–587.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stryker JA: Science to practice: Why is
the liver a radiosensitive organ? Radiology. 242:1–2. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kalogeridi MA, Zygogianni A, Kyrgias G,
Kouvaris J, Chatziioannou S, Kelekis N and Kouloulias V: Role of
radiotherapy in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
systematic review. World J Hepatol. 7:101–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ricke J, Bulla K, Kolligs F,
Peck-Radosavljevic M, Reimer P, Sangro B, Schott E, Schütte K,
Verslype C, Walecki J, et al: Safety and toxicity of
radioembolization plus Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: Analysis of the European multicentre trial SORAMIC.
Liver Int. 35:620–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riaz A, Gabr A, Abouchaleh N, Ali R, Al
Asadi A, Mora R, Kulik L, Desai K, Thornburg B, Mouli S, et al:
Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Statistical
confirmation of improved survival in responders by landmark
analyses. Hepatology. 67:873–883. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guha C and Kavanagh BD: Hepatic radiation
toxicity: Avoidance and amelioration. Semin Radiat Oncol.
21:256–263. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seidensticker R, Seidensticker M, Damm R,
Mohnike K, Schütte K, Malfertheiner P, Van Buskirk M, Pech M,
Amthauer H and Ricke J: Hepatic toxicity after radioembolization of
the liver using (90)Y-microspheres: Sequential lobar versus whole
liver approach. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 35:1109–1118. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mahvash A, Murthy R, Odisio BC, Raghav KP,
Girard L, Cheung S, Nguyen V, Ensor J, Gadani S, Elsayes KM, et al:
Yttrium-90 resin microspheres as an adjunct to sorafenib in
patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell
Carcinoma. 3:1–7. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ricke J, Klumpen HJ, Amthauer H,
Bargellini I, Bartenstein P, de Toni EN, Gasbarrini A, Pech M,
Peck-Radosavljevic M, Popovič P, et al: Impact of combined
selective internal radiation therapy and sorafenib on survival in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 71:1164–1174. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu W, Gu K, Yu Z, Yuan D, He M, Ma N, Lai
S, Zhao J, Ren Z, Zhang X, et al: Sorafenib potentiates irradiation
effect in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer
Lett. 329:109–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsu FT, Chang B, Chen JC, Chiang IT, Liu
YC, Kwang WK and Hwang JJ: Synergistic effect of sorafenib and
radiation on human oral carcinoma in vivo. Sci Rep. 5:153912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen JCH, Chuang HY, Hsu FT, Chen YC,
Chien YC and Hwang JJ: Sorafenib pretreatment enhances radiotherapy
through targeting MEK/ERK/NF-κB pathway in human hepatocellular
carcinoma-bearing mouse model. Oncotarget. 7:85450–85463. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang WH, Chiang IT, Liu YC, Hsu FT, Chen
HW, Chen CL, Lee YJ, Lin WJ and Hwang JJ: Simultaneous imaging of
temporal changes of NF-κB activity and viable tumor cells in
Huh7/NF-κB-tk-luc2/rfp tumor-bearing mice. In Vivo. 27:339–350.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zamora-Valdes D, Taner T and Nagorney DM:
Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Control.
24:10732748177292582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eggert T and Greten TF: Current standard
and future perspectives in non-surgical therapy for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Digestion. 96:1–4. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang A, Yang XR, Chung WY, Dennison AR
and Zhou J: Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 5:1462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva
A, Llovet JM and Lynch M: Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a
multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3129–3140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hayabuchi N: Radiocurable tumors and
non-radiocurable tumors. Japan Med Assoc J. 47:79–83. 2004.
|
|
28
|
Piao LS, Hur W, Kim TK, Hong SW, Kim SW,
Choi JE, Sung PS, Song MJ, Lee BC, Hwang D and Yoon SK:
CD133+ liver cancer stem cells modulate radioresistance
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 315:129–137. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li F and Sethi G: Targeting transcription
factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in
cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1805:167–180.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Qiao Q, Sun C, Han C, Han N, Zhang M and
Li G: Endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway PERK-eIF2α confers
radioresistance in oropharyngeal carcinoma by activating NF-κB.
Cancer Sci. 108:1421–1431. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren K, Li Z, Li Y, Zhang W and Han X:
Sulforaphene enhances radiosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma
through suppression of the NF-κB pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
31:e219172017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ji K, Sun X, Liu Y, Du L, Wang Y, He N,
Wang J, Xu C and Liu Q: Regulation of apoptosis and radiation
sensitization in lung cancer cells via the Sirt1/NF-κB/smac
pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:304–316. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Smartt HJ, Elder DJ, Hicks DJ, Williams NA
and Paraskeva C: Increased NF-kappaB DNA binding but not
transcriptional activity during apoptosis induced by the
COX-2-selective inhibitor NS-398 in colorectal carcinoma cells. Br
J Cancer. 89:1358–1365. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vanden Berghe W, Dijsselbloem N, Vermeulen
L, Ndlovu MN, Boone E and Haegeman G: Attenuation of mitogen- and
stress-activated protein kinase-1-driven nuclear factor-kappaB gene
expression by soy isoflavones does not require estrogenic activity.
Cancer Res. 66:4852–4862. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Close DM, Xu T, Sayler GS and Ripp S: In
vivo bioluminescent imaging (BLI): Noninvasive visualization and
interrogation of biological processes in living animals. Sensors
(Basel). 11:180–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Diagaradjane P, Anand P,
Harikumar KB, Deorukhkar A, Gelovani J, Guha S, Krishnan S and
Aggarwal BB: Curcumin sensitizes human colorectal cancer to
capecitabine by modulation of cyclin D1, COX-2, MMP-9, VEGF and
CXCR4 expression in an orthotopic mouse model. Int J Cancer.
125:2187–2197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bachmeier BE, Killian PH and Melchart D:
The role of curcumin in prevention and management of metastatic
disease. Int J Mol Sci. 19:17162018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lai ZC, Wei X, Shimizu T, Ramos E,
Rohrbaugh M, Nikolaidis N, Ho LL and Li Y: Control of cell
proliferation and apoptosis by mob as tumor suppressor, Mats. Cell.
120:675–685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Safa AR: c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic
regulator. Exp Oncol. 34:176–184. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stagni V, di Bari MG, Cursi S, Condò I,
Cencioni MT, Testi R, Lerenthal Y, Cundari E and Barilà D: ATM
kinase activity modulates Fas sensitivity through the regulation of
FLIP in lymphoid cells. Blood. 111:829–837. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ivanov VN, Zhou H, Partridge MA and Hei
TK: Inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase activity
enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Cancer
Res. 69:3510–3519. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim TE, Hong S, Song K, Park SH and Shin
YK: Sensitization of glycoengineered interferon-β1a-resistant
cancer cells by cFLIP inhibition for enhanced anti-cancer therapy.
Oncotarget. 8:13957–13970. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Poondla N, Chandrasekaran AP, Heese K, Kim
KS and Ramakrishna S: CRISPR-mediated upregulation of DR5 and
downregulation of cFLIP synergistically sensitize HeLa cells to
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 512:60–65.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Maier P, Hartmann L, Wenz F and Herskind
C: Cellular pathways in response to ionizing radiation and their
targetability for tumor radiosensitization. Int J Mol Sci.
17:1022016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
McLaughlin KA, Nemeth Z, Bradley CA,
Humphreys L, Stasik I, Fenning C, Majkut J, Higgins C, Crawford N,
Holohan C, et al: FLIP: A targetable mediator of resistance to
radiation in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
15:2432–2441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ranjan K and Pathak C: FADD regulates
NF-kappaB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cFLIPL to
induce apoptosis. Sci Rep. 6:227872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Catz SD and Johnson JL: Transcriptional
regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor kappa B and its significance
in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 20:7342–7351. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Engels IH, Stepczynska A, Stroh C, Lauber
K, Berg C, Schwenzer R, Wajant H, Jänicke RU, Porter AG, Belka C,
et al: Caspase-8/FLICE functions as an executioner caspase in
anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 19:4563–4573. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Delbridge AR and Strasser A: The BCL-2
protein family, BH3-mimetics and cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ.
22:1071–1080. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tong J, Wang P, Tan S, Chen D,
Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Zou F, Yu J and Zhang L: Mcl-1 degradation is
required for targeted therapeutics to eradicate colon cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 77:2512–2521. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hsu C, Lin LI, Cheng YC, Feng ZR, Shao YY,
Cheng AL and Ou DL: Cyclin E1 Inhibition can overcome sorafenib
resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through Mcl-1
suppression. Clin Cancer Res. 22:2555–2564. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tutusaus A, Stefanovic M, Boix L, Cucarull
B, Zamora A, Blasco L, de Frutos PG, Reig M, Fernandez-Checa JC,
Marí M, et al: Antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins determine
sorafenib/regorafenib resistance and BH3-mimetic efficacy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 9:16701–16717. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hikita H, Takehara T, Shimizu S, Kodama T,
Shigekawa M, Iwase K, Hosui A, Miyagi T, Tatsumi T, Ishida H, et
al: The Bcl-xL inhibitor, ABT-737, efficiently induces apoptosis
and suppresses growth of hepatoma cells in combination with
sorafenib. Hepatology. 52:1310–1321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ivanisenko NV, Buchbinder JH, Espe J,
Richter M, Bollmann M, Hillert LK, Ivanisenko VA and Lavrik IN:
Delineating the role of c-FLIP/NEMO interaction in the CD95 network
via rational design of molecular probes. BMC Genomics. 20 (Suppl
3):S2932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Jiang Z and Clemens PR: Cellular
caspase-8-like inhibitory protein (cFLIP) prevents inhibition of
muscle cell differentiation induced by cancer cells. FASEB J.
20:2570–2572. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Guo ZL, Li JZ, Ma YY, Qian D, Zhong JY,
Jin MM, Huang P, Che LY, Pan B, Wang Y, et al: Shikonin sensitizes
A549 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the JNK, STAT3 and
AKT pathways. BMC Cell Biol. 19:292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim S, Woo SM, Min KJ, Seo SU, Lee TJ,
Kubatka P, Kim DE and Kwon TK: WP1130 enhances TRAIL-induced
apoptosis through USP9X-dependent miR-708-mediated downregulation
of c-FLIP. Cancers (Basel). 11:3442019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Gu FM, Li QL, Gao Q, Jiang JH, Huang XY,
Pan JF, Fan J and Zhou J: Sorafenib inhibits growth and metastasis
of hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking STAT3. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:3922–3932. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tai WT, Cheng AL, Shiau CW, Huang HP,
Huang JW, Chen PJ and Chen KF: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 is a major kinase-independent target of sorafenib
in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 55:1041–1048. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Huang CY, Lin CS, Tai WT, Hsieh CY, Shiau
CW, Cheng AL and Chen KF: Sorafenib enhances radiation-induced
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting STAT3. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 86:456–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen KF, Tai WT, Liu TH, Huang HP, Lin YC,
Shiau CW, Li PK, Chen PJ and Cheng AL: Sorafenib overcomes TRAIL
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the inhibition
of STAT3. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5189–5199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
La Tessa C, Berger T, Kaderka R, Schardt
D, Körner C, Ramm U, Licher J, Matsufuji N, Vallhagen Dahlgren C,
Lomax T, et al: Out-of-field dose studies with an anthropomorphic
phantom: Comparison of X-rays and particle therapy treatments.
Radiother Oncol. 105 1:133–138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Loeffler JS and Durante M: Charged
particle therapy-optimization, challenges and future directions.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:411–424. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-κB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Archiv. 446:475–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Dangerous
liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:11–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|