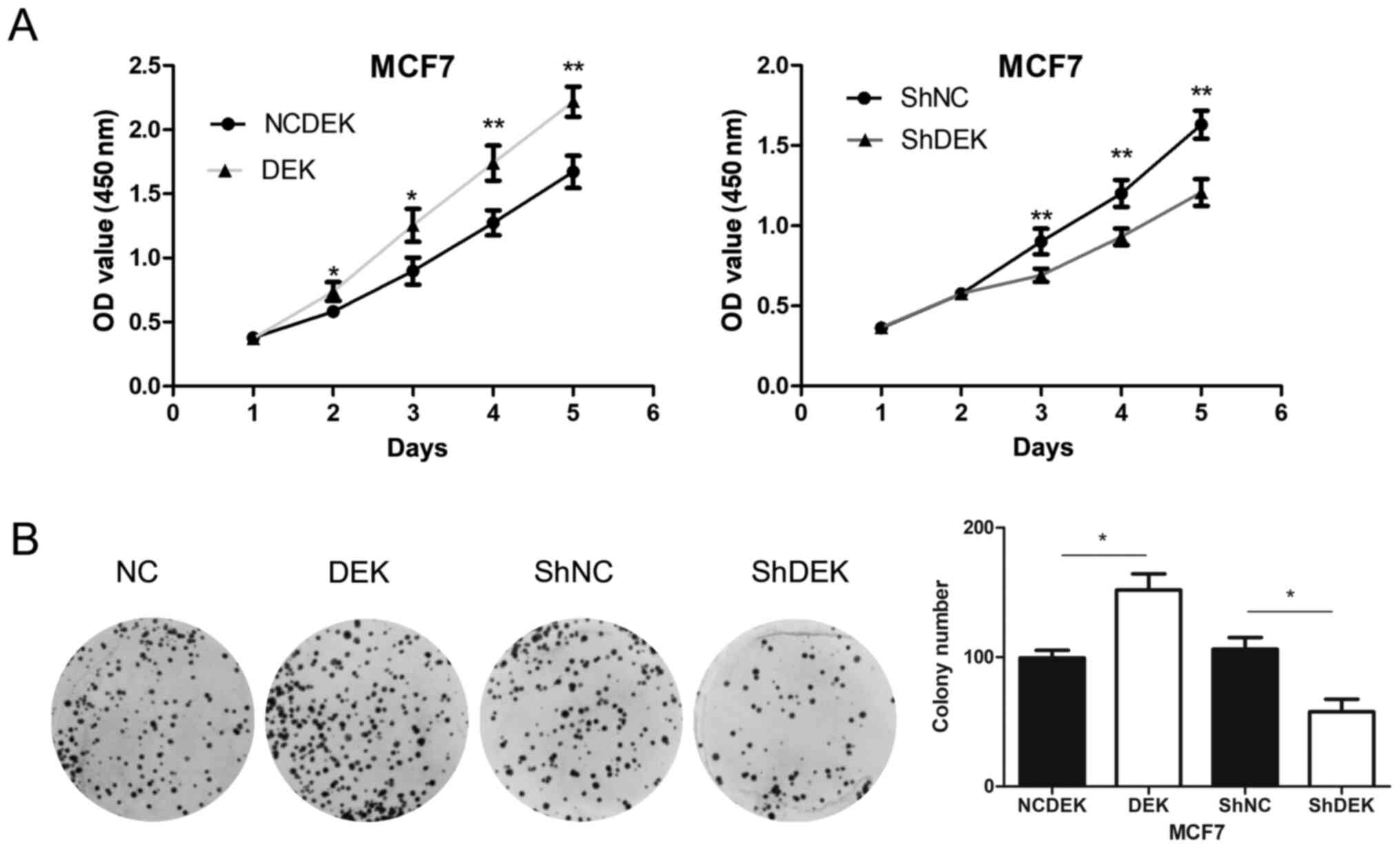
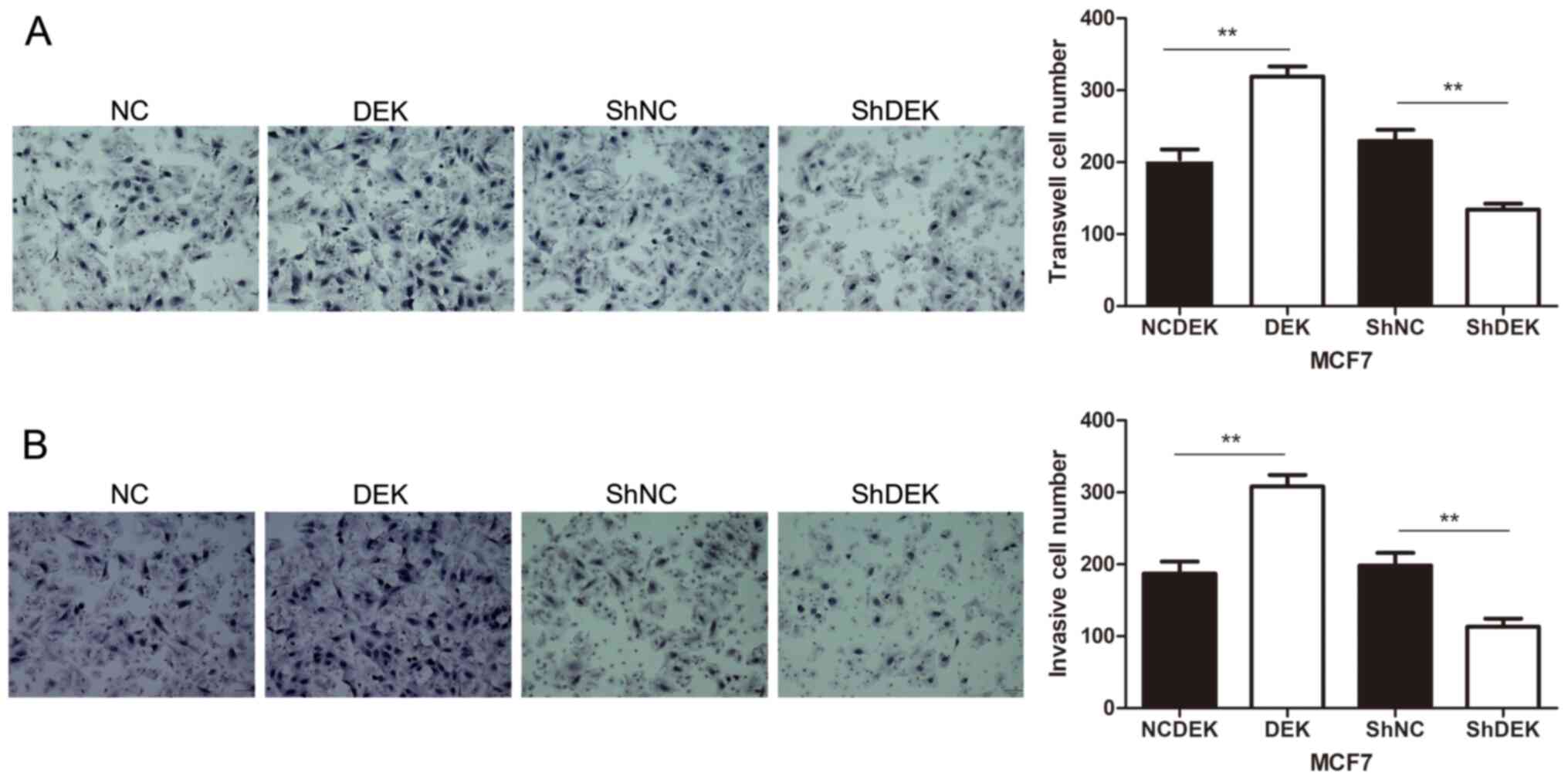
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Morales-Vasquez F and
Hortobagyi GN: Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in
patients with breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 608:1–22. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Redig AJ and McAllister SS: Breast cancer
as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J Intern Med.
274:113–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kappes F, Scholten I, Richter N, Gruss C
and Waldmann T: Functional domains of the ubiquitous chromatin
protein DEK. Mol Cell Biol. 24:6000–6010. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu GK, Grosveld G and Markovitz DM: DEK,
an autoantigen involved in a chromosomal translocation in acute
myelogenous leukemia, binds to the HIV-2 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:1811–1815. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boer J, Mahmoud H, Raimondi S, Grosveld G
and Krance R: Loss of the DEK-CAN fusion transcript in a child with
t(6;9) acute myeloid leukemia following chemotherapy and allogeneic
bone marrow transplantation. Leukemia. 11:299–300. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McGarvey T, Rosonina E, McCracken S, Li Q,
Arnaout R, Mientjes E, Nickerson JA, Awrey D, Greenblatt J,
Grosveld G and Blencowe BJ: The acute myeloid leukemia-associated
protein, DEK, forms a splicing-dependent interaction with
exon-product complexes. J Cell Biol. 150:309–320. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kappes F, Burger K, Baack M, Fackelmayer
FO and Gruss C: Subcellular localization of the human
proto-oncogene protein DEK. J Biol Chem. 276:26317–26323. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Waldmann T, Eckerich C, Baack M and Gruss
C: The ubiquitous chromatin protein DEK alters the structure of DNA
by introducing positive supercoils. J Biol Chem. 277:24988–24994.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SY, Jung W, Lee J, Kim A, Kim HK and
Kim BH: High expression of DEK is associated with poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 34:1279–1288.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Capitano ML, Mor-Vaknin N, Saha AK, Cooper
S, Legendre M, Guo H, Contreras-Galindo R, Kappes F, Sartor MA, Lee
CT, et al: Secreted nuclear protein DEK regulates hematopoiesis
through CXCR2 signaling. J Clin Invest. 129:2555–2570. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith EA, Kumar B, Komurov K, Smith SM,
Brown NV, Zhao S, Kumar P, Teknos TN and Wells SI: DEK associates
with tumor stage and outcome in HPV16 positive oropharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:23414–23426. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Riveiro-Falkenbach E, Ruano Y,
Garcia-Martin RM, Lora D, Cifdaloz M, Acquadro F, Ballestín C,
Ortiz-Romero PL, Soengas MS and Rodríguez-Peralto JL: DEK oncogene
is overexpressed during melanoma progression. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 30:194–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hacker KE, Bolland DE, Tan L, Saha AK,
Niknafs YS, Markovitz DM and McLean K: The DEK oncoprotein
functions in ovarian cancer growth and survival. Neoplasia.
20:1209–1218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao T, Qiu B, Zhou S, Ding G, Cao L and
Wu Z: Expression of DEK in pancreatic cancer and its correlation
with clinicopathological features and prognosis. J Cancer.
10:911–917. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Serrano-Lopez J, Nattamai K, Pease NA,
Shephard MS, Wellendorf AM, Sertorio M, Smith EA, Geiger H, Wells
SI, Cancelas JA and Privette Vinnedge LM: Loss of DEK induces
radioresistance of murine restricted hematopoietic progenitors. Exp
Hematol. 59:40–50.e3. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou QC, Deng XF, Yang J, Jiang H, Qiao
MX, Liu HH, Qian Z, Hou LL and Hu HG: Oncogene DEK is highly
expressed in lung cancerous tissues and positively regulates cell
proliferation as well as invasion. Oncol Lett. 15:8573–8581.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ou Y, Xia R, Kong F, Zhang X, Yu S, Jiang
L, Zheng L and Lin L: Overexpression of DEK is an indicator of poor
prognosis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett.
11:1823–1828. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matrka MC, Watanabe M, Muraleedharan R,
Lambert PF, Lane AN, Romick-Rosendale LE and Wells SI:
Overexpression of the human DEK oncogene reprograms cellular
metabolism and promotes glycolysis. PLoS One. 12:e01779522017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qiao MX, Li C, Zhang AQ, Hou LL, Yang J
and Hu HG: Regulation of DEK expression by AP-2α and methylation
level of DEK promoter in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
36:2382–2390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu Y, Liang Z, Li C, Yang Z and Chen L:
LCMR1 interacts with DEK to suppress apoptosis in lung cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 16:4159–4164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Sun L, Yang M, Luo W, Gao Y, Liu
Z, Qiu X and Wang E: DEK depletion negatively regulates
Rho/ROCK/MLC pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Histochem
Cytochem. 61:510–521. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu K, Feng T, Liu J, Zhong M and Zhang S:
Silencing of the DEK gene induces apoptosis and senescence in CaSki
cervical carcinoma cells via the up-regulation of NF-κB p65. Biosci
Rep. 32:323–332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cserni G, Chmielik E, Cserni B and Tot T:
The new TNM-based staging of breast cancer. Virchows Arch.
472:697–703. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Lei L, Zheng YW, Zhang L, Li ZH,
Shen HY, Jiang GY, Zhang XP, Wang EH and Xu HT: Odd-skipped related
1 inhibits lung cancer proliferation and invasion by reducing Wnt
signaling through the suppression of SOX9 and β-catenin. Cancer
Sci. 109:1799–1810. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Juríková M, Danihel Ľ, Polák Š and Varga
I: Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the
diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 118:544–552. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Y, Gao M, Lin Z, Chen L, Jin Y, Zhu
G, Wang Y and Jin T: DEK promoted EMT and angiogenesis through
regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:98708–98722. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu S, Wang X, Sun F, Kong J, Li Z and Lin
Z: DEK overexpression is correlated with the clinical features of
breast cancer. Pathol Int. 62:176–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ying G and Wu Y: DEK: A novel early
screening and prognostic marker for breast cancer. Mol Med Rep.
12:7491–7495. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Privette Vinnedge LM, McClaine R, Wagh PK,
Wikenheiser-Brokamp KA, Waltz SE and Wells SI: The human DEK
oncogene stimulates β-catenin signaling, invasion and mammosphere
formation in breast cancer. Oncogene. 30:2741–2752. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Liu J, Wang S, Luo X, Li Y, Lv Z,
Zhu J, Lin J, Ding L and Ye Q: The DEK oncogene activates VEGF
expression and promotes tumor angiogenesis and growth in
HIF-1α-dependent and -independent manners. Oncotarget.
7:23740–23756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feng T, Liu Y, Li C, Li Z and Cai H: DEK
proto-oncogene is highly expressed in astrocytic tumors and
regulates glioblastoma cell proliferation and apoptosis. Tumour
Biol. 39:10104283177162482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu X, Zou L, Yao Q, Zhang Y, Gan L and
Tang L: Silencing DEK downregulates cervical cancer tumorigenesis
and metastasis via the DEK/p-Ser9-GSK-3β/p-Tyr216-GSK-3β/β-catenin
axis. Oncol Rep. 38:1035–1042. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sitwala KV, Adams K and Markovitz DM: YY1
and NF-Y binding sites regulate the transcriptional activity of the
dek and dek-can promoter. Oncogene. 21:8862–8870. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wise-Draper TM, Allen HV, Thobe MN, Jones
EE, Habash KB, Münger K and Wells SI: The human DEK proto-oncogene
is a senescence inhibitor and an upregulated target of high-risk
human papillomavirus E7. J Virol. 79:14309–14317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carro MS, Spiga FM, Quarto M, Di Ninni V,
Volorio S, Alcalay M and Müller H: DEK Expression is controlled by
E2F and deregulated in diverse tumor types. Cell Cycle.
5:1202–1207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|