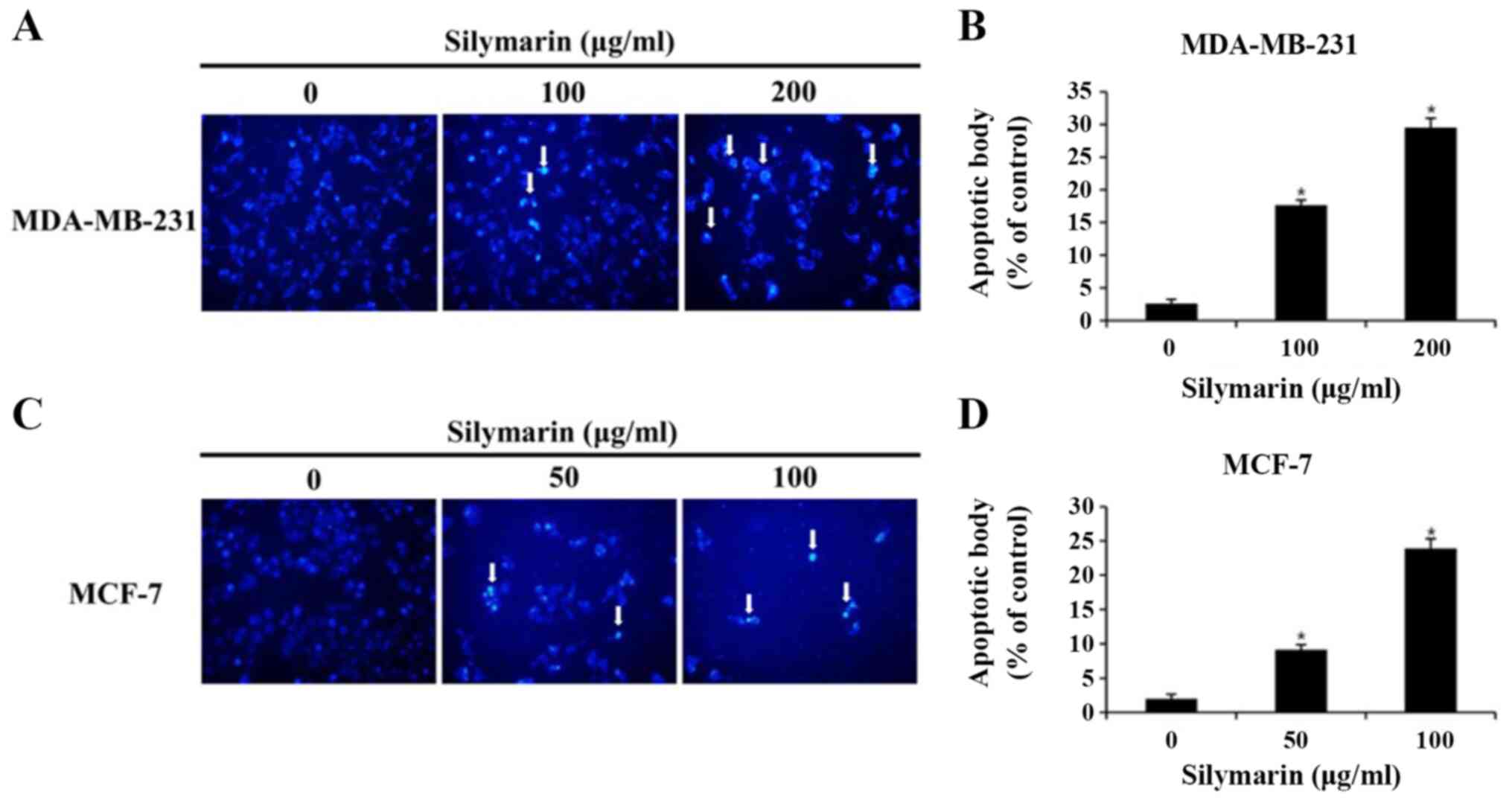
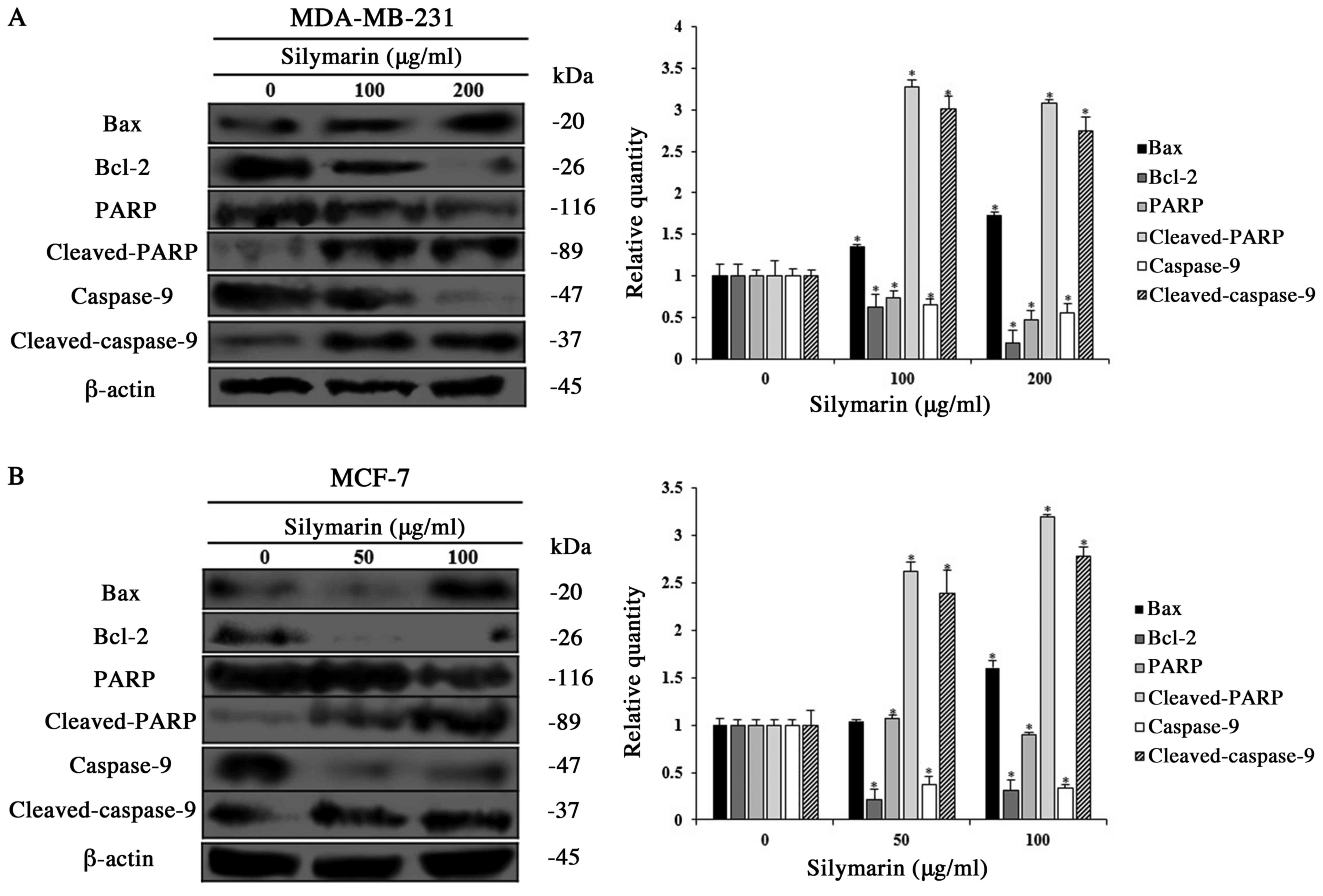
|
1
|
Liu MM, Huang Y and Wang J: Developing
phytoestrogens for breast cancer prevention. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 12:1306–1313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Z, Qin B, Qi X, Mao J and Wu D:
Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells via
ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and downregulation of SIRT1.
Arch Pharm Res. 39:1441–1453. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nizamutdinova IT, Lee GW, Son KH, Jeon SJ,
Kang SS, Kim YS, Lee JH, Seo HG, Chang KC and Kim HJ: Tanshinone I
effectively induces apoptosis in estrogen receptor-positive (MCF-7)
and estrogen receptor-negative (MDA-MB-231) breast cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 33:485–491. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Panche AN, Diwan AD and Chandra SR:
Flavonoids: An overview. J Nutr Sci. 5:e472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Comelli MC, Mengs U, Schneider C and
Prosdocimi M: Toward the definition of the mechanism of action of
silymarin: Activities related to cellular protection from toxic
damage induced by chemotherapy. Integr Cancer Ther. 6:120–129.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen IS, Chen YC, Chou CH, Chuang RF,
Sheen LY and Chiu CH: Hepatoprotection of silymarin against
thioacetamide-induced chronic liver fibrosis. J Sci Food Agric.
92:1441–1447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sherif IO and Al-Gayyar MM: Antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects of silymarin on
hepatic dysfunction induced by sodium nitrite. Eur Cytokine Netw.
24:114–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Lakkany NM, Hammam OA, El-Maadawy WH,
Badawy AA, Ain-Shoka AA, Ebeid FA and EI-Lakkany NM:
Anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic effects of the hepatoprotective
silymarin and the schistosomicide praziquantel against Schistosoma
mansoni-induced liver fibrosis. Parasit Vectors. 5:92012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu T, Liu W, Guo W and Zhu X: Silymarin
suppressed lung cancer growth in mice via inhibiting
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 81:460–467.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deep G, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Kroll DJ and
Agarwal R: Silymarin and silibinin cause G1 and G2-M cell cycle
arrest via distinct circuitries in human prostate cancer PC3 cells:
A comparison of flavanone silibinin with flavanolignan mixture
silymarin. Oncogene. 25:1053–1069. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han SI, Kim YS and Kim TH: Role of
apoptotic and necrotic cell death under physiologic conditions. BMB
Rep. 41:1–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J,
Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Donovan M and Cotter TG: Control of
mitochondrial integrity by Bcl-2 family members and
caspase-independent cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:133–147.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang Y, Zhu X, Chen Y, Wang X and Chen R:
p38 and JNK MAPK, but not ERK1/2 MAPK, play important role in
colchicine-induced cortical neurons apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol.
576:26–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Joneson T, White MA, Wigler MH and
Bar-Sagi D: Stimulation of membrane ruffling and MAP kinase
activation by distinct effectors of RAS. Science. 271:810–812.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Doll R: The lessons of life: Keynote
address to the nutrition and cancer conference. Cancer Res. 52
(Suppl 7):2024s–2029s. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Porter PL: Global trends in breast cancer
incidence and mortality. Salud Publica Mex. 51 (Suppl 2):s141–s146.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan L, Ma Y, Liu Y, Zheng D and Huang G:
Silymarin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ovarian cancer
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 743:79–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kalla PK, Chitti S, Aghamirzaei ST,
Senthilkumar R and Arjunan S: Anti-cancer activity of silymarin on
MCF-7 and NCIH-23 cell lines. Adv Biol Res (Faisalabad). 8:57–61.
2014.
|
|
22
|
Vaid M, Singh T, Prasad R and Katiyar SK:
Silymarin inhibits melanoma cell growth both in vitro and in vivo
by targeting cell cycle regulators, angiogenic biomarkers and
induction of apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 54:1328–1339. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katiyar SK, Roy AM and Baliga MS:
Silymarin induces apoptosis primarily through a p53-dependent
pathway involving Bcl-2/Bax, cytochrome c release, and caspase
activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:207–216. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li LH, Wu LJ, Tashiro SI, Onodera S,
Uchiumi F and Ikejima T: The roles of Akt and MAPK family members
in silymarin's protection against UV-induced A375-S2 cell
apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 6:190–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Q, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Li
LH and Ikejima T: Silymarin augments human cervical cancer HeLa
cell apoptosis via P38/JNK MAPK pathways in serum-free medium. J
Asian Nat Prod Res. 7:701–709. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pereira L, Igea A, Canovas B, Dolado I and
Nebreda AR: Inhibition of p38 MAPK sensitizes tumour cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis mediated by reactive oxygen species and
JNK. EMBO Mol Med. 5:1759–1774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cui L, Bu W, Song J, Feng L, Xu T, Liu D,
Ding W, Wang J, Li C, Ma B, et al: Apoptosis induction by
alantolactone in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through reactive
oxygen species-mediated mitochondrion-dependent pathway. Arch Pharm
Res. 41:299–313. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin KL, Su JC, Chien CM, Tseng CH, Chen
YL, Chang LS and Lin SR: Naphtho[1,2-b]furan-4,5-dione induces
apoptosis and S-phase arrest of MDA-MB-231 cells through JNK and
ERK signaling activation. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:61–70. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu P, Zhang C, Gao CY, Ma T, Zhang H, Zhou
MM, Yang YW, Yang L and Kong LY: Anti-proliferation of
triple-negative breast cancer cells with physagulide P: ROS/JNK
signaling pathway induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death.
Oncotarget. 8:64032–64049. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Palit S, Kar S, Sharma G and Das PK:
Hesperetin induces apoptosis in breast carcinoma by triggering
accumulation of ROS and activation of ASK1/JNK pathway. J Cell
Physiol. 230:1729–1739. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rabi T and Banerjee S: Novel synthetic
triterpenoid methyl 25-hydroxy-3-oxoolean-12-en-28-oate induces
apoptosis through JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in human breast
adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells. Mol Carcinog. 47:415–423. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Singh RP, Tyagi AK, Zhao J and Agarwal R:
Silymarin inhibits growth and causes regression of established skin
tumors in SENCAR mice via modulation of mitogen-activated protein
kinases and induction of apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 23:499–510.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim LH, Khadka S, Shin JA, Jung JY, Ryu
MH, Yu HJ, Lee HN, Jang B, Yang IH, Won DH, et al: Nitidine
chloride acts as an apoptosis inducer in human oral cancer cells
and a nude mouse xenograft model via inhibition of STAT3.
Oncotarget. 8:91306–91315. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shivakumar P, Rani MU, Reddy AG and
Anjaneyulu Y: A study on the toxic effects of Doxorubicin on the
histology of certain organs. Toxicol Int. 19:241–244. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|