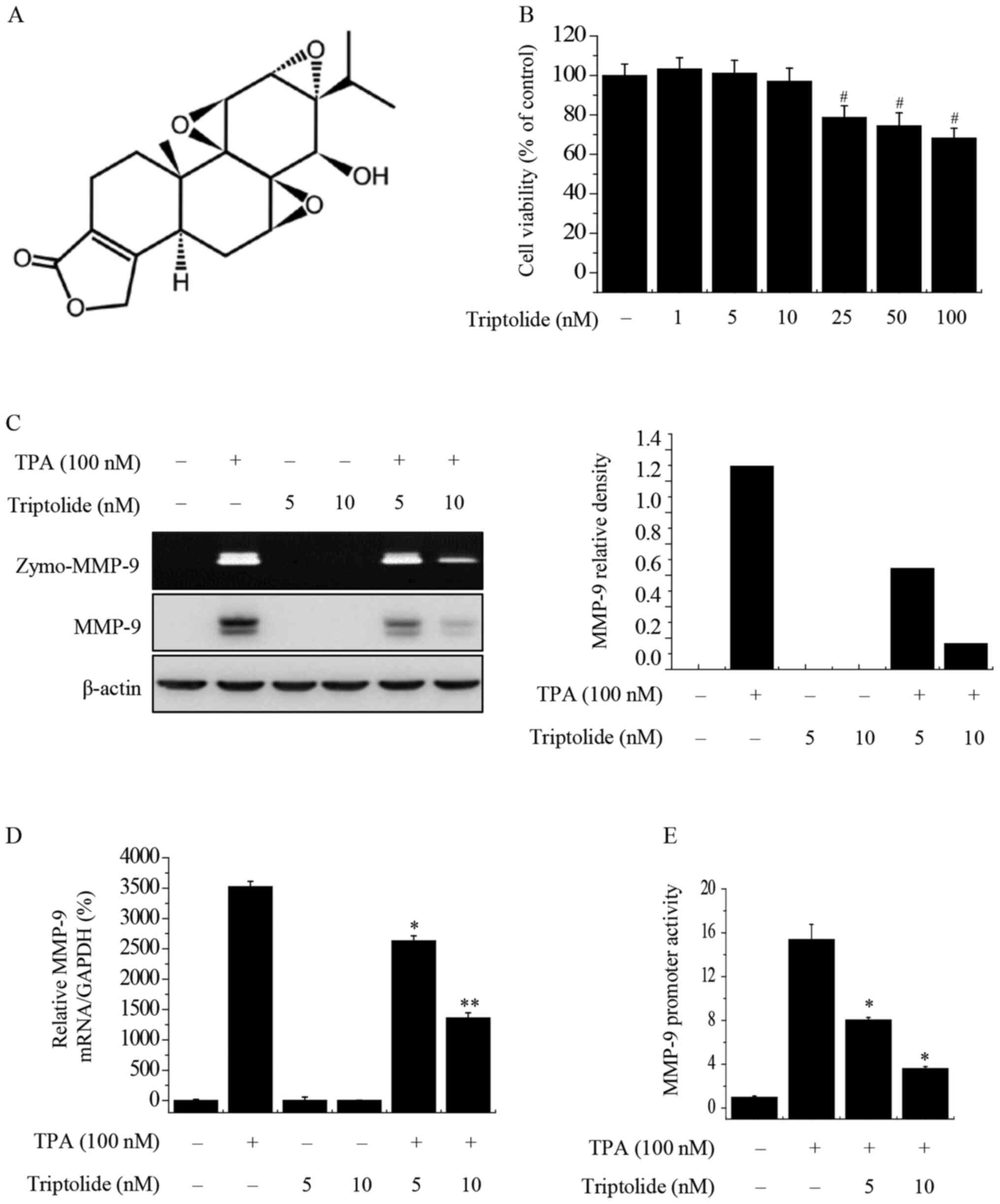
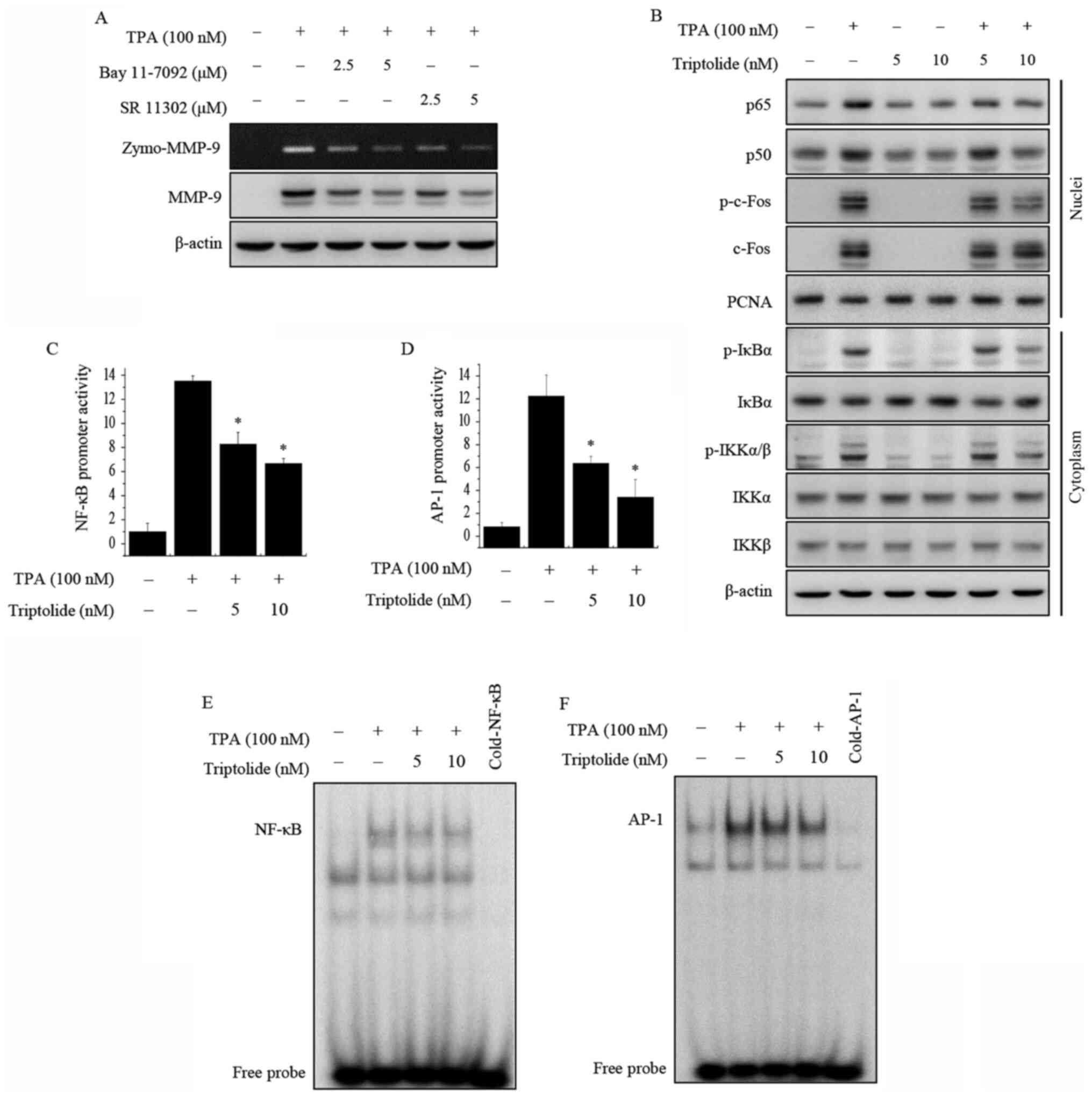
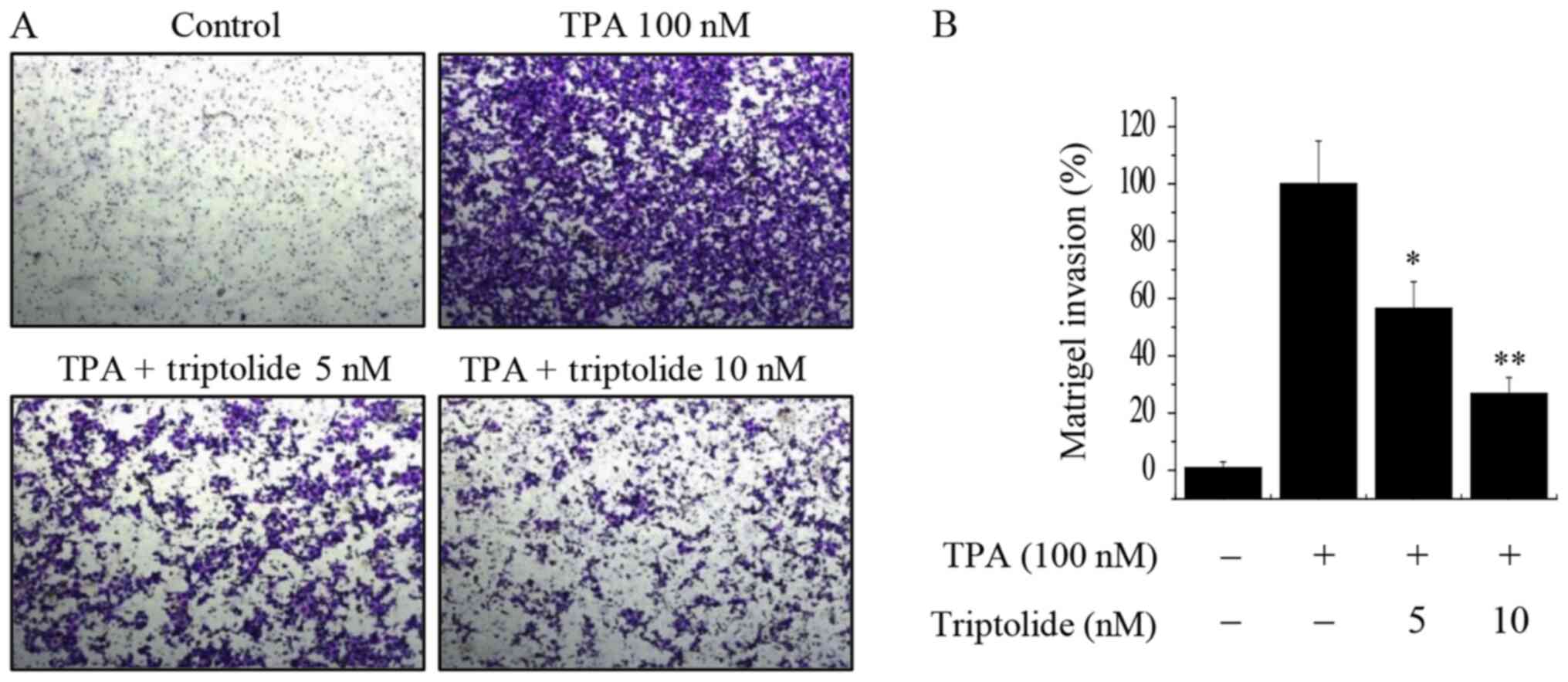
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tian D, Li Y, Li X and Tian Z: Aloperine
inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion and induces
apoptosis by blocking the Ras signaling pathway in human breast
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 18:3699–3710. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Di Leo A, Curigliano G, Diéras V, Malorni
L, Sotiriou C, Swanton C, Thompson A, Tutt A and Piccart M: New
approaches for improving outcomes in breast cancer in Europe.
Breast. 24:321–330. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
García Rodríguez J, García Colmenero C,
Clèries Soler R and Oleaga Sánchez I: Five years survival of women
diagnosed with breast cancer during the period 1997-1999 in
Toledo-Centro and Mancha Area, Spain. Rev Esp Salud Publica.
84:843–850. 2010.(In Spanish).
|
|
5
|
Rose DP, Connolly JM and Coleman M: Effect
of omega-3 fatty acids on the progression of metastases after the
surgical excision of human breast cancer cell solid tumors growing
in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 2:1751–1756. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakajima M, Welch DR, Belloni PN and
Nicolson GL: Degradation of basement membrane type IV collagen and
lung subendothelial matrix by rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell
clones of differing metastatic potentials. Cancer Res.
47:4869–4876. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hwang JK, Yu HN, Noh EM, Kim JM, Hong OY,
Youn HJ, Jung SH, Kwon KB, Kim JS and Lee YR: DHA blocks
TPA-induced cell invasion by inhibiting MMP-9 expression via
suppression of the PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway in MCF-7 cells. Oncol Lett.
13:243–249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mehner C, Hockla A, Miller E, Ran S,
Radisky DC and Radisky ES: Tumor cell-produced matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) drives malignant progression and
metastasis of basal-like triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget.
5:2736–2749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noh EM, Lee YR, Hong OY, Jung SH, Youn HJ
and Kim JS: Aurora kinases are essential for PKC-induced invasion
and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 34:803–810. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rao JS, Steck PA, Mohanam S,
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Liotta LA and Sawaya R: Elevated levels of
M(r) 92,000 type IV collagenase in human brain tumors. Cancer Res.
53 (Suppl):2208–2211. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sato H and Seiki M: Regulatory mechanism
of 92 kDa type IV collagenase gene expression which is associated
with invasiveness of tumor cells. Oncogene. 8:395–405.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin CW, Hou WC, Shen SC, Juan SH, Ko CH,
Wang LM and Chen YC: Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via
suppressing PKC delta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9
activation in breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1807–1815.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weng CJ, Chau CF, Hsieh YS, Yang SF and
Yen GC: Lucidenic acid inhibits PMA-induced invasion of human
hepatoma cells through inactivating MAPK/ERK signal transduction
pathway and reducing binding activities of NF-kappaB and AP-1.
Carcinogenesis. 29:147–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cho HJ, Kang JH, Kwak JY, Lee TS, Lee IS,
Park NG, Nakajima H, Magae J and Chang YC: Ascofuranone suppresses
PMA-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene activation through the
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK- and Ap1-dependent mechanisms. Carcinogenesis.
28:1104–1110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kajanne R, Miettinen P, Mehlem A, Leivonen
SK, Birrer M, Foschi M, Kähäri VM and Leppä S: EGF-R regulates MMP
function in fibroblasts through MAPK and AP-1 pathways. J Cell
Physiol. 212:489–497. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Srivastava AK, Qin X and Wedhas N: Amush
m, Linkhart TA, Chadwick RB and Kumar A: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha augments matrix metalloproteinase-9 production in
skeletal muscle cells through the activation of transforming growth
factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-dependent signaling pathway.
J Biol Chem. 282:35113–35124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee SO, Jeong YJ, Kim M, Kim CH and Lee
IS: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by capillarisin
via the inhibition of NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 366:1019–1024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY and Baldwin
AS Jr: Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65
Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase
and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol
Chem. 276:18934–18940. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cohen M, Meisser A, Haenggeli L and
Bischof P: Involvement of MAPK pathway in TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9
expression in human trophoblastic cells. Mol Hum Reprod.
12:225–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng X, Shi W, Zhao C, Zhang D, Liang P,
Wang G and Lu L: Triptolide sensitizes human breast cancer cells to
tumor necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis by inhibiting activation
of the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:3257–3264. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xi C, Peng S, Wu Z, Zhou Q and Zhou J:
Toxicity of triptolide and the molecular mechanisms involved.
Biomed Pharmacother. 90:531–541. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Liu R, Yang Y, Huang Y, Li X, Liu R
and Shen X: Triptolide-induced in vitro and in vivo cytotoxicity in
human breast cancer stem cells and primary breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 31:2181–2186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang S, Gu C, Zhang G, Kang J, Wen H, Lu Q
and Huang J: Inhibitive effect of triptolide on invasiveness of
human fibrosarcoma cells by downregulating matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 4:482–485.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Phillips PA, Dudeja V, McCarroll JA,
Borja-Cacho D, Dawra RK, Grizzle WE, Vickers SM and Saluja AK:
Triptolide induces pancreatic cancer cell death via inhibition of
heat shock protein 70. Cancer Res. 67:9407–9416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fan D, Guo Q, Shen J, Zheng K, Lu C, Zhang
G, Lu A and He X: The effect of triptolide in rheumatoid arthritis:
from basic research towards clinical translation. Int J Mol Sci.
19:3762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu W, Ou Y, Li Y, Xiao R, Shu M, Zhou Y,
Xie J, He S, Qiu P and Yan G: A small-molecule triptolide
suppresses angiogenesis and invasion of human anaplastic thyroid
carcinoma cells via down-regulation of the nuclear factor-kappa B
pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 75:812–819. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chan EW, Cheng SC, Sin FW and Xie Y:
Triptolide induced cytotoxic effects on human promyelocytic
leukemia, T cell lymphoma and human hepatocellular carcinoma cell
lines. Toxicol Lett. 122:81–87. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang S, Chen J, Guo Z, Xu XM, Wang L, Pei
XF, Yang J, Underhill CB and Zhang L: Triptolide inhibits the
growth and metastasis of solid tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:65–72.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu L, Kanwar J, Schmitt S, Cui QC, Zhang
C, Zhao C and Dou QP: Inhibition of tumor cellular proteasome
activity by triptolide extracted from the Chinese medicinal plant
‘thunder god vine’. Anticancer Res. 31:1–10. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li H, Pan GF, Jiang ZZ, Yang J, Sun LX and
Zhang LY: Triptolide inhibits human breast cancer MCF-7 cell growth
via downregulation of the ERα-mediated signaling pathway. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 36:606–613. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shao H, Ma J, Guo T and Hu R: Triptolide
induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells via a mechanism associated
with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 8:505–508.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Z, Sun C, Zhang L, Chi X, Ji J, Gao
X, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Liu L, Cao X, et al: Triptolide interferes with
XRCC1/PARP1-mediated DNA repair and confers sensitization of
triple-negative breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:1541–1546. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng Y, Li F, He P, Yang Y, Yang J, Zhang
Y, Liu J, Tong Y, Li Q, Mei X, et al: Triptolide sensitizes breast
cancer cells to Doxorubicin through the DNA damage response
inhibition. Mol Carcinog. 57:807–814. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang XH, Wong BC, Lin MC, Zhu GH, Kung
HF, Jiang SH, Yang D and Lam SK: Functional p53 is required for
triptolide-induced apoptosis and AP-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB
activation in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 20:8009–8018. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tan BJ and Chiu GNC: Role of oxidative
stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and ERK activation in
triptolide-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 42:1605–1612. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gao H, Zhang Y, Dong L, Qu XY, Tao LN,
Zhang YM, Zhai JH and Song YQ: Triptolide induces autophagy and
apoptosis through ERK activation in human breast cancer MCF-7
cells. Exp Ther Med. 15:3413–3419. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sarkar S and Paul S: Triptolide mediated
amelioration of breast cancer via modulation of molecular pathways.
Pharmacogn J. 9:838–845. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mackay AR, Ballin M, Pelina MD, Farina AR,
Nason AM, Hartzler JL and Thorgeirsson UP: Effect of phorbol ester
and cytokines on matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase expression in tumor and normal cell lines.
Invasion Metastasis. 12:168–184. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L,
Mazza B, Kidd VJ, Mak TW and Ingram AJ: ERK activation mediates
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of
p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee
YC, Cho G, Kim SH, Kim JG and Kim CH: Novel and therapeutic effect
of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma
cells: Complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by
dual mechanism. FASEB J. 18:1670–1681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jao HY, Yu FS, Yu CS, Chang SJ, Liu KC,
Liao CL, Ji BC, Bau DT and Chung JG: Suppression of the migration
and invasion is mediated by triptolide in B16F10 mouse melanoma
cells through the NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Environ Toxicol.
31:1974–1984. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Song X, Zhang Y and Dai E: Therapeutic
targets of thunder god vine (Tripterygium wilfordii hook) in
rheumatoid arthritis (Review). Mol Med Rep. 21:2303–2310.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin CW, Shen SC, Hou WC, Yang LY and Chen
YC: Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits breast cancer invasion via
suppressing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1195–1206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|