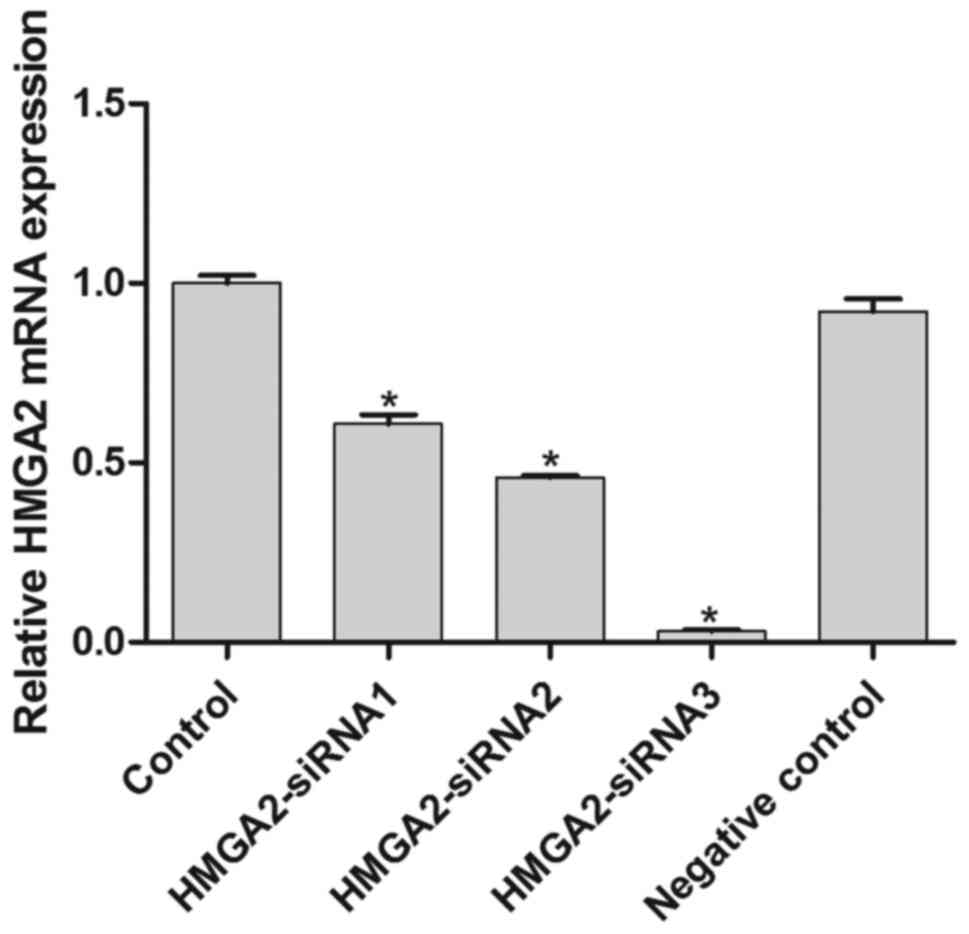
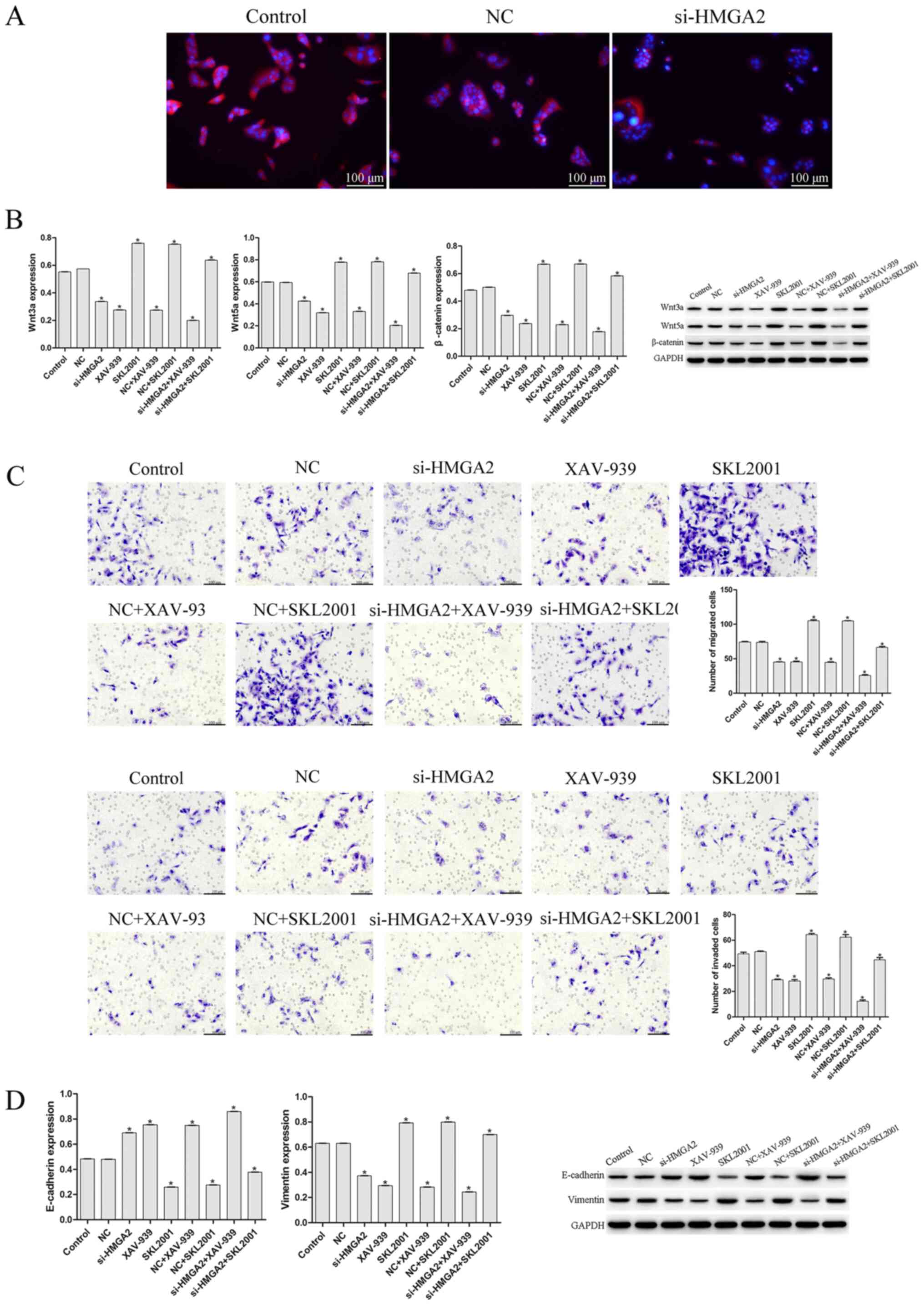
|
1
|
Noriyuki T: Thymic epithelial tumors.
Haigan. 47:181–185. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ji W, Feng QF, Zhou ZM, Wang M, Chen DF,
Zhang HX, Xiao ZF, Wang LH and Yin WB: Treatment and prognosis
analysis of 73 cases of thymic carcinoma. Chin J Radia Oncol.
15:97–100. 2006.
|
|
3
|
Kondo K and Monden Y: Therapy for thymic
epithelial tumors: A clinical study of 1,320 patients from Japan.
Ann Thorac Surg. 76:878–884; discussion 884–885. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lamarca A, Moreno V and Feliu J: Thymoma
and thymic carcinoma in the target therapies era. Cancer Treat Rev.
39:413–420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ozturk N, Singh I, Mehta A, Braun T and
Barreto G: HMGA proteins as modulators of chromatin structure
during transcriptional activation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2:52014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Narita M, Narita M, Krizhanovsky V, Nuñez
S, Chicas A, Hearn SA, Myers MP and Lowe SW: A novel role for
high-mobility group a proteins in cellular senescence and
heterochromatin formation. Cell. 126:503–514. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cleynen I and Van de Ven WJ: The HMGA
proteins: A myriad of functions (Review). Int J Oncol. 32:289–305.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Di Cello F, Hillion J, Hristov A, Wood LJ,
Mukherjee M, Schuldenfrei A, Kowalski J, Bhattacharya R, Ashfaq R
and Resar LM: HMGA2 participates in transformation in human lung
cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 6:743–750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malek A, Bakhidze E, Noske A, Sers C,
Aigner A, Schäfer R and Tchernitsa O: HMGA2 gene is a promising
target for ovarian cancer silencing therapy. Int J Cancer.
123:348–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang ML, Chen CC and Chang LC: Gene
expressions of HMGI-C and HMGI(Y) are associated with stage and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis.
24:1281–1286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hristov AC, Cope L, Reyes MD, Singh M,
Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Maitra A and Resar LM: HMGA2 protein
expression correlates with lymph node metastasis and increased
tumor grade in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol.
22:43–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartuma H, Panagopoulos I, Collin A,
Trombetta D, Domanski HA, Mandahl N and Mertens F: Expression
levels of HMGA2 in adipocytic tumors correlate with morphologic and
cytogenetic subgroups. Mol Cancer. 8:362009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng P, Zheng CN, Ben W, Gao HJ, Niu WB,
He ZB, Gao C, Zou ZJ, Ma C, Niu J, et al: Norcantharidin inhibit
colon cancer cell EMT process through blocking αvβ6-ERK-ETS1 signal
pathway. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg. 10:757–762. 2014.(In
Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Lin Q, Zhou CR, Bai MJ, Zhu D, Chen JW,
Wang HF, Li MA, Wu C, Li ZR and Huang MS: Exosome-mediated miRNA
delivery promotes liver cancer EMT and metastasis. Am J Transl Res.
12:1080–1095. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zha L, Zhang J, Tang WX, Zhang N, He M,
Gao Y and Wang ZW: HMGA2 elicits EMT by activating the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 58:724–733.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eugenio Z, Gabri VDP, Gray PC and Marianna
KJ: Epithelial plasticity in cancer: unmasking a microRNA network
for TGF-β- and Notch-, and Wnt-mediated EMT. J Oncol.
2015:1989672015. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Ma L, Zhang YL, Jiang T, Bi GB and
Sao C: Expression and clinical significance of β-catenin and axin
in ovarian epithelial cell carcinoma. J Modern Integ Med.
26:2871–2873+2957. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang XW, Cui WW, Wang BF, Song YL, Liang
YJ and Dong Y: Abnormal activation of wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Tongji Med Univ. 46:295–298.
2017.
|
|
22
|
Zha L, Zhang J, Tang W, Zhang N, He M, Guo
Y and Wang Z: HMGA2 elicits EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 58:724–733. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pan CB, Zhao XP and Zhang H: High
expression of HMGA2 promotes metastasis of tongue carcinoma through
EMT. The 13th National Conference on Oral and Maxillofacial
Surgery.
|
|
24
|
Li W, Wang J, Zhang D, Zhang X, Xu J and
Zhao L: MicroRNA-98 targets HMGA2 to inhibit the development of
retinoblastoma through mediating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer
Biomark. 25:79–88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tan S, Zhang QG, Zhang L, Liu N and Cheng
Y: Expression and clinical significance of β-catenin and c-myc in
invasive thymoma. J Chin Med Univ. 34:464–465. 2005.
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TDL: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rogalla P, Drechsler K, Kazmierczak B,
Rippe V, Bonk U and Bullerdiek J: Expression of HMGI-C, a member of
the high mobility group protein family, in a subset of breast
cancers: Relationship to histologic grade. Mol Carcinog.
19:153–156. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Berner JM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Kools PF, Forus
A, Schoenmakers EF, Van de Ven WJ, Fodstad O and Myklebost O:
HMGIC, the gene for an architectural transcription factor, is
amplified and rearranged in a subset of human sarcomas. Oncogene.
14:2935–2941. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abe N, Watanabe T, Suzuki Y, Matsumoto N,
Masaki T, Mori T, Sugiyama M, Chiappetta G, Fusco A and Atomi Y: An
increased high-mobility group A2 expression level is associated
with malignant phenotype in pancreatic exocrine tissue. Br J
Cancer. 89:2104–2109. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meyer B, Loeschke S, Schultze A, Weigel T,
Sandkamp M, Goldmann T, Vollmer E and Bullerdiek J: HMGA2
overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
46:503–511. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arsianti A, Fadilah F, Bahtiar A and
Tanimoto H: Phytochemical analysis and in vitro cytotoxicity of
seaweed sargassum sp. Against colon HCT-116 and Lung-A549 cancer
cells. Proceedings of The 18th World Congress of Basic and Clinical
Pharmacology (WCP2018). pp. WCP2018Kyoto: 2018
|
|
32
|
Gökmen-Polar Y, Sanders KL, Goswami CP,
Cano OD, Zaheer NA, Jain RK, Kesler KA, Nelson RP Jr, Vance GH,
Smith D, et al: Establishment and characterization of a novel cell
line derived from human thymoma AB tumor. Lab Invest. 92:1564–1573.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee HS, Jang HJ, Lo EM, Truong CY, Groth
SS, Friedberg JS, Sugarbaker DJ and Burt BM: Povidone-iodine
results in rapid killing of thymic epithelial tumour cells through
cellular fixation†. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 28:353–359.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Theys J, Jutten B, Habets R, Paesmans K,
Groot AJ, Lambin P, Wouters BG, Lammering G and Vooijs M:
E-Cadherin loss associated with EMT promotes radioresistance in
human tumor cells. Radiother Oncol. 99:392–397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fransvea E, Angelotti U, Antonaci S and
Giannelli G: Blocking transforming growth factor-beta up-regulates
E-cadherin and reduces migration and invasion of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 47:1557–1566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bussemakers MJG, van Moorselaar RJ,
Giroldi LA, Ichikawa T, Isaacs JT, Takeichi M, Debruyne FM and
Schalken JA: Decreased expression of E-cadherin in the progression
of rat prostatic cancer. Cancer Res. 52:2916–2922. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fearon ER: Cancer: Context is key for
E-cadherin in invasion and metastasis. Curr Biol. 29:R1140–R1142.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun S, Sun W, Xia L, Liu L, Du R, He L, Li
R, Wang H and Huang C: The T-box transcription factor Brachyury
promotes renal interstitial fibrosis by repressing E-cadherin
expression. Cell Commun Signal. 12:762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Z, Jin H, Yang S, Zhang ZY, Wen B and
Zhou SB: SDC1 knockdown induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells via the
ERK/Snail pathway. J Inter Med Res.
8:3000605209478832020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Telford BJ, Chen A, Beetham H, Frick J,
Brew TP, Gould CM, Single A, Godwin T, Simpson KJ and Guilford P:
Synthetic lethal screens identify vulnerabilities in GPCR signaling
and cytoskeletal organization in E-Cadherin-Deficient cell. Mol
Cancer Ther. 14:1213–1223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang D, Nai MY, Chen JZ and Wei LX:
Effect of silencing HMGA2 on signal transduction pathway of
Wnt/β-catenin in gastric cancer cells. World Chin J Dig.
21:1062–1069. 2013.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qin BB, Li YQ, Li XL, Lu LS, Zhang XD and
Zhang MZ: Expression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway key molecules in NK/T
cell lymphoma and its clinical significance. J Jilin Univ.
41:230–234. 2015.
|
|
45
|
Ebert MP, Fei G, Kahmann S, Müller O, Yu
J, Sung JJ and Malfertheiner P: Increased beta-catenin mRNA levels
and mutational alterations of the APC and beta-catenin gene are
present in intestinal-type gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis.
23:87–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shi JF and Yin F: Expression of β-catenin
and hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 α in HCC and its effect on
prognosis. Chin J Oncol. 36:587–591. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|