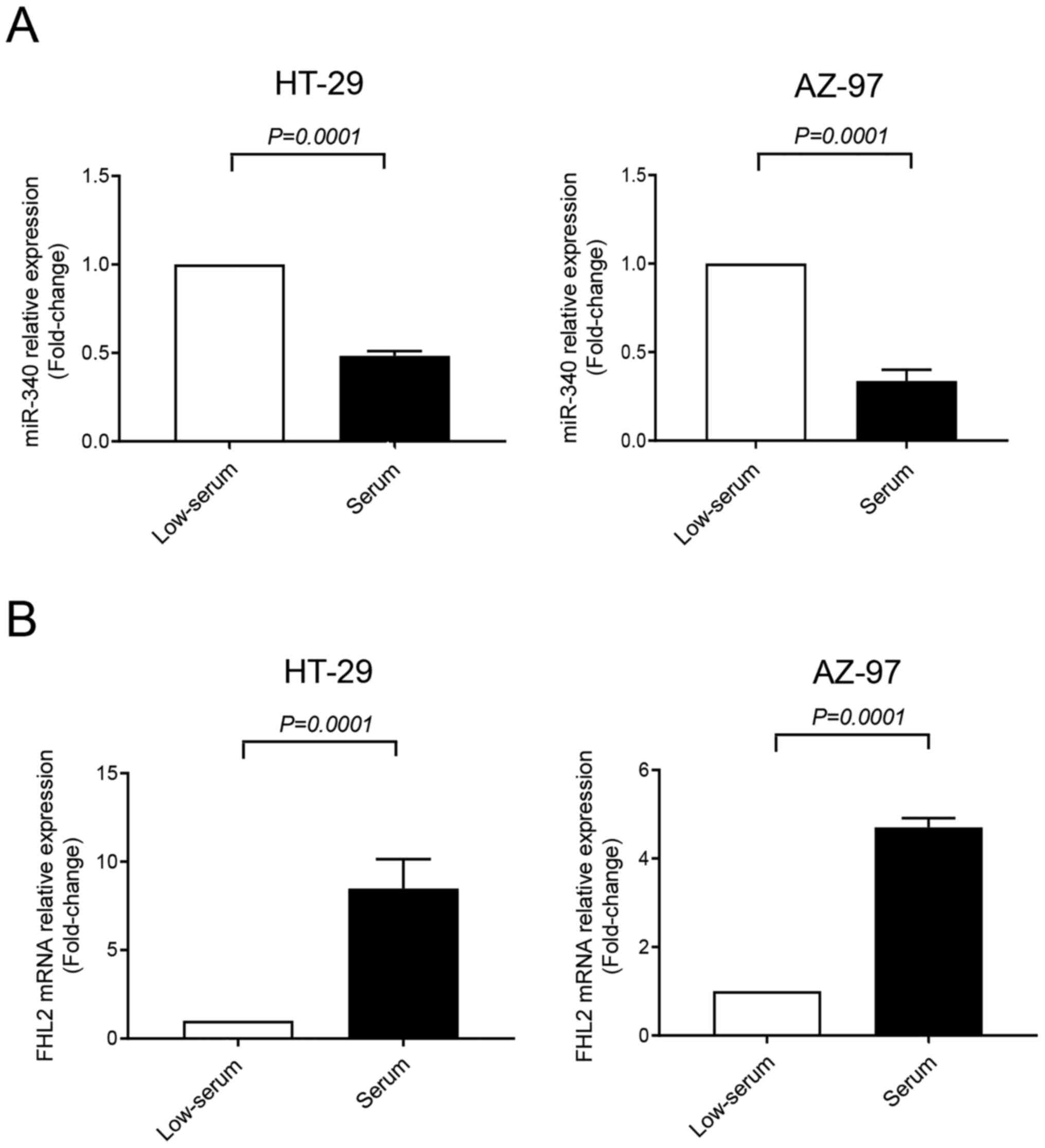
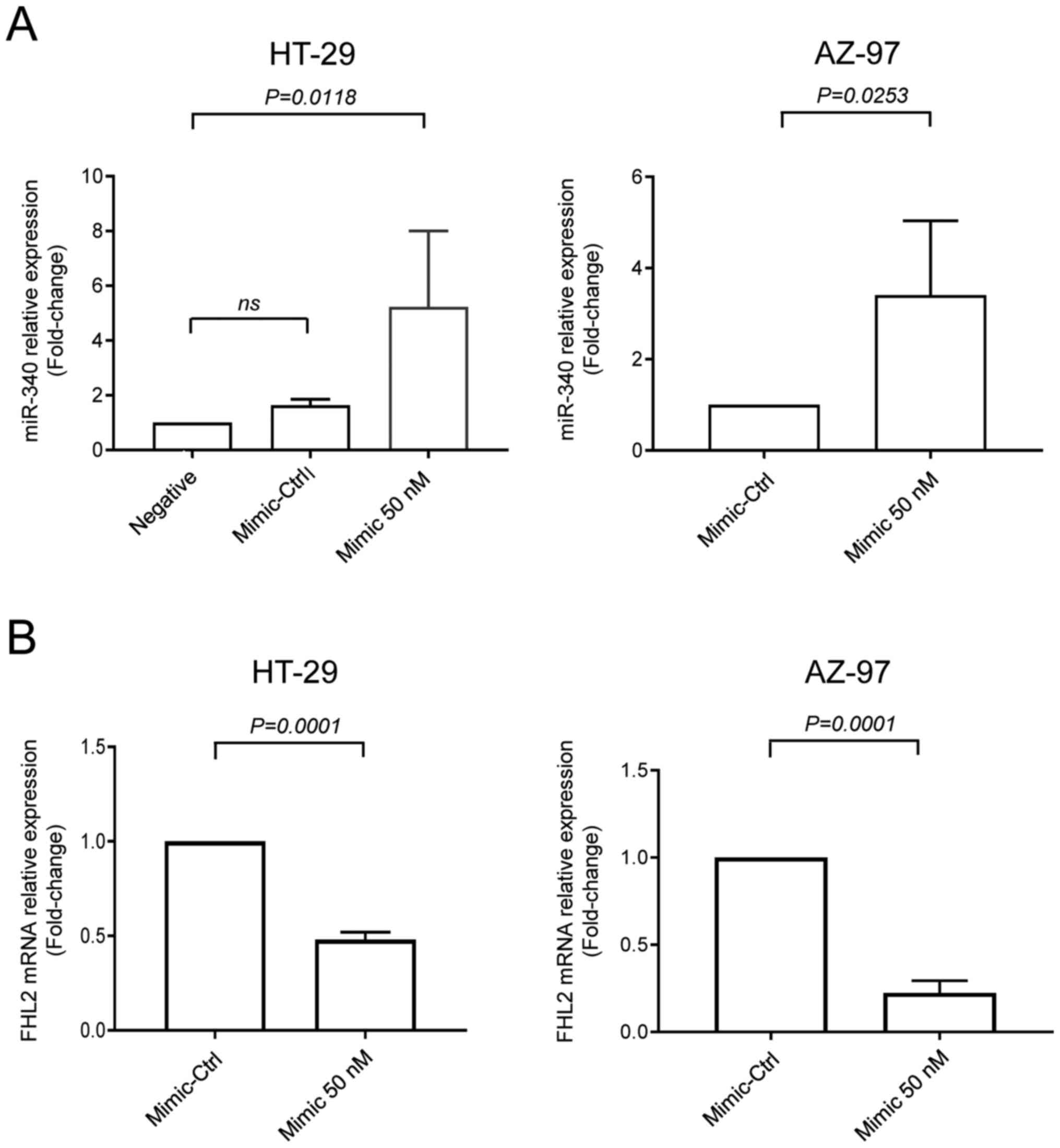
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB,
Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL and Siegel
RL: Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J
Clin. 69:363–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bockelman C, Engelmann BE, Kaprio T,
Hansen TF and Glimelius B: Risk of recurrence in patients with
colon cancer stage II and III: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of recent literature. Acta Oncol. 54:5–16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levin VA, Panchabhai SC, Shen L, Kornblau
SM, Qiu Y and Baggerly KA: Different changes in protein and
phosphoprotein levels result from serum starvation of high-grade
glioma and adenocarcinoma cell lines. J Proteome Res. 9:179–191.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghosh T, Varshney A, Kumar P, Kaur M,
Kumar V, Shekhar R, Devi R, Priyanka P, Khan MM and Saxena S:
MicroRNA-874-mediated inhibition of the major G1/S phase cyclin,
CCNE1, is lost in osteosarcomas. J Biol Chem. 292:21264–21281.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rasool RU, Nayak D, Chakraborty S, Jamwal
VL, Mahajan V, Katoch A, Faheem MM, Iqra Z, Amin H, Gandhi SG and
Goswami A: Differential regulation of NM23-H1 under hypoxic and
serum starvation conditions in metastatic cancer cells and its
implication in EMT. Eur J Cell Biol. 96:164–171. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang Z, Li Q, Luo K, Zhang Q, Geng J,
Zhou X, Xu Y, Qian M, Zhang JA, Ji L and Wu J: miR-340-FHL2 axis
inhibits cell growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 10:3722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang W, Jiang B, Guo Z, Sardet C, Zou B,
Lam CS, Li J, He M, Lan HY, Pang R, et al: Four-and-a-half LIM
protein 2 promotes invasive potential and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in colon cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:1220–1229. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tran MK, Kurakula K, Koenis DS and de
Vries CJ: Protein-protein interactions of the LIM-only protein FHL2
and functional implication of the interactions relevant in
cardiovascular disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:219–228. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kinoshita M, Nakagawa T, Shimizu A and
Katsuoka Y: Differently regulated androgen receptor transcriptional
complex in prostate cancer compared with normal prostate. Int J
Urol. 12:390–397. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hou Y, Wang X, Li L, Fan R, Chen J, Zhu T,
Li W, Jiang Y, Mittal N, Wu W, et al: FHL2 regulates hematopoietic
stem cell functions under stress conditions. Leukemia. 29:615–624.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gabriel B, Fischer DC, Orlowska-Volk M,
zur Hausen A, Schüle R, Müller JM and Hasenburg A: Expression of
the transcriptional coregulator FHL2 in human breast cancer: A
clinicopathologic study. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 13:69–75. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gabriel B, Mildenberger S, Weisser CW,
Metzger E, Gitsch G, Schüle R and Müller JM: Focal adhesion kinase
interacts with the transcriptional coactivator FHL2 and both are
overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res.
24:921–927. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin H, Lee K, Kim YH, Oh HK, Maeng YI, Kim
TH, Suh DS and Bae J: Scaffold protein FHL2 facilitates
MDM2-mediated degradation of IER3 to regulate proliferation of
cervical cancer cells. Oncogene. 35:5106–5118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bates RC and Mercurio AM: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer
progression. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:365–370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beavon IR: The E-cadherin-catenin complex
in tumour metastasis: Structure, function and regulation. Eur J
Cancer. 36:1607–1620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Christofori G and Semb H: The role of the
cell-adhesion molecule E-cadherin as a tumour-suppressor gene.
Trends Biochem Sci. 24:73–76. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, Eberle G,
Voss B, Warda A, Löchner D and Birchmeier W: E-cadherin-mediated
cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells.
J Cell Biol. 113:173–185. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berx G, Cleton-Jansen AM, Nollet F, de
Leeuw WJ, van de Vijver M, Cornelisse C and van Roy F: E-cadherin
is a tumour/invasion suppressor gene mutated in human lobular
breast cancers. EMBO J. 14:6107–6115. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Padmanaban V, Krol I, Suhail Y, Szczerba
BM, Aceto N, Bader JS and Ewald AJ: E-cadherin is required for
metastasis in multiple models of breast cancer. Nature.
573:439–444. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang W, Wang J, Zou B, Sardet C, Li J,
Lam CS, Ng L, Pang R, Hung IF, Tan VP, et al: Four and a half LIM
protein 2 (FHL2) negatively regulates the transcription of
E-cadherin through interaction with Snail1. Eur J Cancer.
47:121–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kreutziger KL and Kreutziger KL:
Comprehensive surgical management of mandibular fractures. South
Med J. 85:506–518. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Roles for
microRNAs in the regulation of cell adhesion molecules. J Cell Sci.
124((Pt 7)): 999–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fridrichova I and Zmetakova I: MicroRNAs
contribute to breast cancer invasiveness. Cells. 8:13612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao P, Ma W, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang S and
Wang Y: Up-regulation of miR-340-5p promotes progression of thyroid
cancer by inhibiting BMP4. J Endocrinol Invest. 41:1165–1172. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shi Z, Li Y, Qian X, Hu Y, Liu J, Zhang S
and Zhang J: miR-340 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer
progression by reversing EZH2 mediated miRNAs dysregulated
expressions. J Cancer. 8:3037–3048. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang D, Qiu S, Ge R, He L, Li M, Li Y and
Peng Y: miR-340 suppresses glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget.
6:9257–9270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen CP, Sun ZL, Lu X, Wu WX, Guo WL, Lu
JJ, Han C, Huang JQ and Fang Y: miR-340 suppresses cell migration
and invasion by targeting MYO10 in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
35:709–716. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsushita Y, Hoff SD, Nudelman ED, Otaka
M, Hakomori S, Ota DM, Cleary KR and Irimura T: Metastatic behavior
and cell surface properties of HT-29 human colon carcinoma variant
cells selected for their differential expression of sialyl-dimeric
Le(x)-antigen. Clin Exp Metastasis. 9:283–299. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bettenworth D, Mucke MM, Schwegmann K,
Faust A, Poremba C, Schäfers M, Domagk D and Lenz P:
Endoscopy-guided orthotopic implantation of colorectal cancer cells
results in metastatic colorectal cancer in mice. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 33:551–562. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zawadzki A, Liu Q, Wang Y, Melander A,
Jeppsson B and Thorlacius H: Verapamil inhibits L-type calcium
channel mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Dis Colon
Rectum. 51:1696–1702. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Y, Guo Z, Zhang D, Zhang W, Yan Q, Shi
X, Zhang M, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Jiang B, et al: A novel colon cancer
gene therapy using rAAVmediated expression of human shRNA-FHL2. Int
J Oncol. 43:1618–1626. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Yang Y, Xia HH, Gu Q, Lin MC,
Jiang B, Peng Y, Li G, An X, Zhang Y, et al: Suppression of FHL2
expression induces cell differentiation and inhibits gastric and
colon carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 132:1066–1076. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Amann T, Egle Y, Bosserhoff AK and
Hellerbrand C: FHL2 suppresses growth and differentiation of the
colon cancer cell line HT-29. Oncol Rep. 23:1669–1674.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Al-Haidari A, Algaber A, Madhi R, Syk I
and Thorlacius H: miR-155-5p controls colon cancer cell migration
via post-transcriptional regulation of Human Antigen R (HuR).
Cancer Lett. 421:145–151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Takeyama H, Yamamoto H, Yamashita S, Wu X,
Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Haraguchi N, Miyake Y, Suzuki R, Murata
K, et al: Decreased miR-340 expression in bone marrow is associated
with liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:976–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Algaber A, Al-Haidari A, Madhi R, Rahman
M, Syk I and Thorlacius H: MicroRNA-340-5p inhibits colon cancer
cell migration via targeting of RhoA. Sci Rep. 10:169342020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang L, Men WL, Yan KM, Tie J, Nie YZ and
Xiao HJ: miR-340-5p is a potential prognostic indicator of
colorectal cancer and modulates ANXA3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:4837–4845. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu ZS, Wu Q, Wang CQ, Wang XN, Huang J,
Zhao JJ, Mao SS, Zhang GH, Xu XC and Zhang N: miR-340 inhibition of
breast cancer cell migration and invasion through targeting of
oncoprotein c-Met. Cancer. 117:2842–2852. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xiao H, Yu L, Li F, Wang H, Li W and He X:
miR-340 suppresses the metastasis by targeting EphA3 in cervical
cancer. Cell Biol Int. 42:1115–1123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fernandez S, Risolino M, Mandia N, Talotta
F, Soini Y, Incoronato M, Condorelli G, Banfi S and Verde P:
miR-340 inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by
targeting multiple negative regulators of p27 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncogene. 34:3240–3250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu M, Wang J, Tang W, Zhan X, Li Y, Peng
Y, Huang X, Bai Y, Zhao J, Li A, et al: FOXK1 interaction with FHL2
promotes proliferation, invasion and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogenesis. 5:e2712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Park SY, Lee SJ, Cho HJ, Kim TW, Kim JT,
Kim JW, Lee CH, Kim BY, Yeom YI, Lim JS, et al: Dehydropeptidase 1
promotes metastasis through regulation of E-cadherin expression in
colon cancer. Oncotarget. 7:9501–9512. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bai S, Zeng R, Zhou Q, Liao W, Zhang Y, Xu
C, Han M, Pei G, Liu L, Liu X, et al: Cdc42-interacting protein-4
promotes TGF-B1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
extracellular matrix deposition in renal proximal tubular
epithelial cells. Int J Biol Sci. 8:859–869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yue B, Qiu S, Zhao S, Liu C, Zhang D, Yu
F, Peng Z and Yan D: LncRNA-ATB mediated E-cadherin repression
promotes the progression of colon cancer and predicts poor
prognosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:595–603. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wendt MK, Taylor MA, Schiemann BJ and
Schiemann WP: Down-regulation of epithelial cadherin is required to
initiate metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer. Mol Biol Cell.
22:2423–2435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fan L, Wang H, Xia X, Rao Y, Ma X, Ma D,
Wu P and Chen G: Loss of E-cadherin promotes prostate cancer
metastasis via upregulation of metastasis-associated gene 1
expression. Oncol Lett. 4:1225–1233. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|