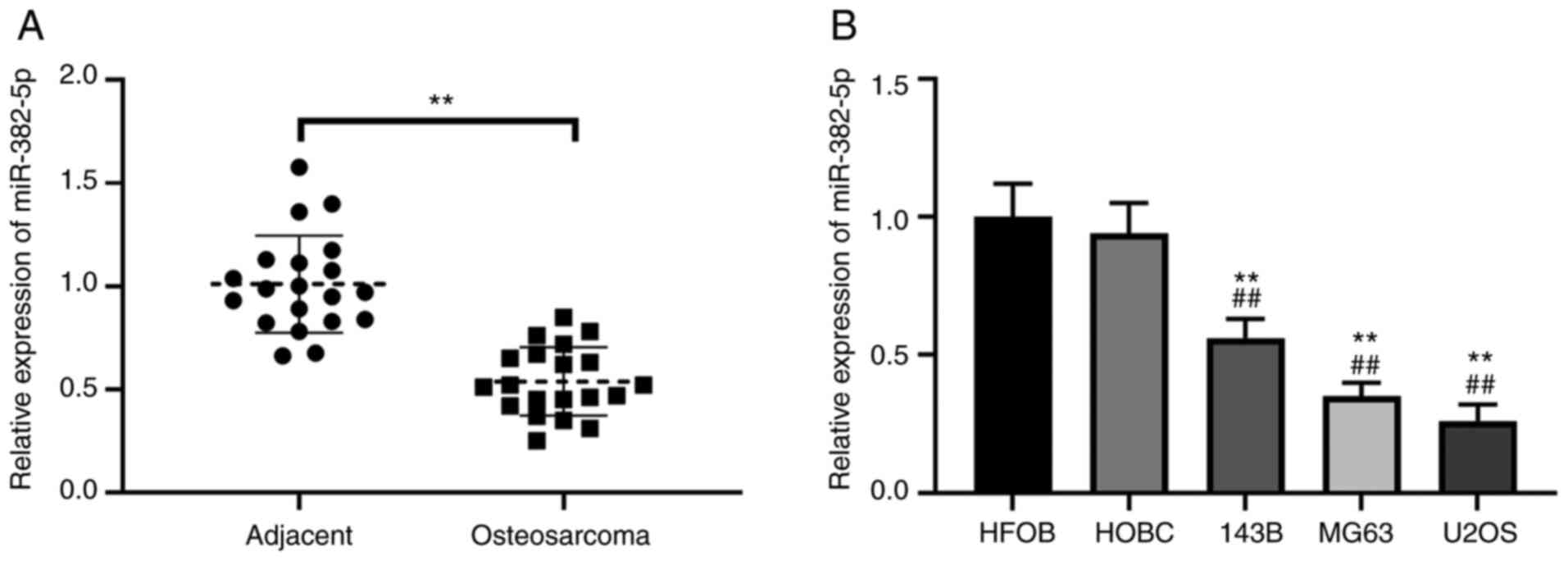
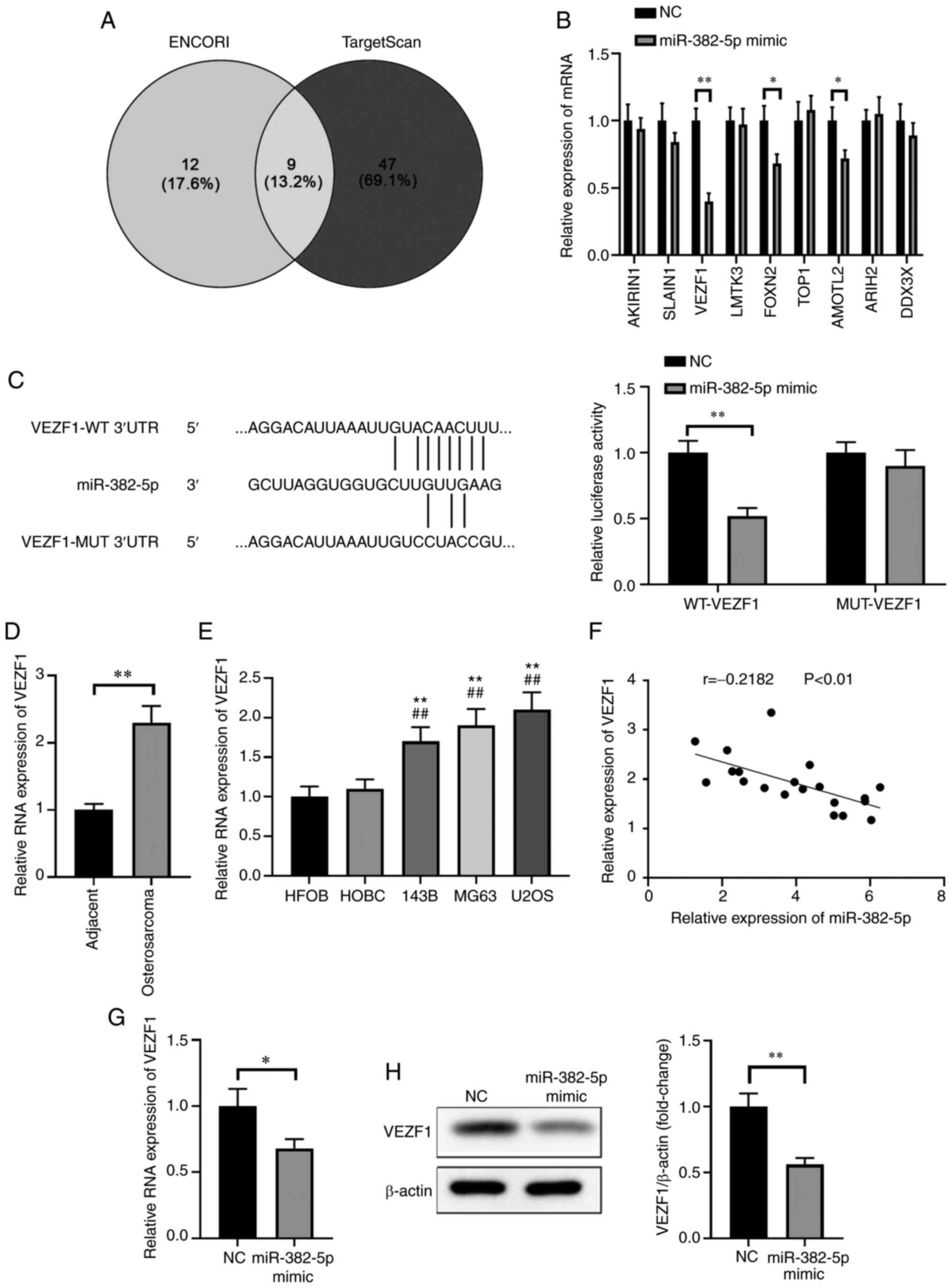
|
1
|
Broadhead ML, Clark JC, Myers DE, Dass CR
and Choong PF: The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: A
review. Sarcoma. 2011:9592482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ and Thomas
DM: Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer.
14:722–735. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu CC, Beird HC, Andrew Livingston J,
Advani S, Mitra A, Cao S, Reuben A, Ingram D, Wang WL, Ju Z, et al:
Immuno-genomic landscape of osteosarcoma. Nat Commun. 11:10082020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rytting M, Pearson P, Raymond AK, Ayala A,
Murray J, Yasko AW, Johnson M and Jaffe N: Osteosarcoma in
preadolescent patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 39–50. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Petrilli AS, de Camargo B, Filho VO,
Bruniera P, Brunetto AL, Jesus-Garcia R, Camargo OP, Pena W,
Péricles P, Davi A, et al: Results of the Brazilian osteosarcoma
treatment group studies III and IV: Prognostic factors and impact
on survival. J Clin Oncol. 24:1161–1168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hosseinahli N, Aghapour M, Duijf PHG and
Baradaran B: Treating cancer with microRNA replacement therapy: A
literature review. J Cell Physiol. 233:5574–5588. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aredia F and Scovassi AI: A new function
for miRNAs as regulators of autophagy. Future Med Chem. 9:25–36.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song B, Wang Y, Xi Y, Kudo K, Bruheim S,
Botchkina GI, Gavin E, Wan Y, Formentini A, Kornmann M, et al:
Mechanism of chemoresistance mediated by miR-140 in human
osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:4065–4074. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Naeli P, Yousefi F, Ghasemi Y,
Savardashtaki A and Mirzaei H: The role of MicroRNAs in lung
cancer: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Curr Mol Med.
20:90–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Bottcher R, Croce CM,
Jenster G, Visakorpi T and Calin GA: Long noncoding RNA in
prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer. Eur Urol. 65:1140–1151. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng Z, Ding M, Ni J, Song D, Huang J and
Wang J: miR-142 acts as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma cell
lines by targeting Rac1. Oncol Rep. 33:1291–1299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu Q, Chu X and Wang P: MicroRNA-195-5p
suppresses osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by
suppressing naked cuticle homolog 1. Cell Biol Int. 41:287–295.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Ma Z, Kan P and Zhang B: The
diagnostic value of serum miRNA-221-3p, miRNA-382-5p, and
miRNA-4271 in ischemia stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.
26:1055–1060. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Yang X, Zhang J,
Yi M and Zhang C: The MicroRNA-382-5p/MXD1 axis relates to breast
cancer progression and promotes cell malignant phenotypes. J Surg
Res. 246:442–449. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tan H, He Q, Gong G, Wang Y, Li J, Wang J,
Zhu D and Wu X: miR-382 inhibits migration and invasion by
targeting ROR1 through regulating EMT in ovarian cancer. Int J
Oncol. 48:181–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shan N, Shen L, Wang J, He D and Duan C:
miR-153 inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell
lung cancer by targeting ADAM19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
456:385–391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu Z, He B, He J and Mao X: Upregulation
of miR-153 promotes cell proliferation via downregulation of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human prostate cancer. Prostate.
73:596–604. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Vlachos IS, Karagkouni
D, Georgakilas G, Kanellos I, Vergoulis T, Zagganas K, Tsanakas P,
Floros E, Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-LncBase v2:
Indexing microRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44(D1): D231–D238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee JH, Kim C, Baek SH, Ko JH, Lee SC,
Yang WM, Um JY, Sethi G and Ahn KS: Capsazepine inhibits JAK/STAT3
signaling, tumor growth, and cell survival in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:17700–17711. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA
binding sites. PLoS One. 13:e02062392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rennie W, Kanoria S, Liu C, Mallick B,
Long D, Wolenc A, Carmack CS, Lu J and Ding Y: STarMirDB: A
database of microRNA binding sites. RNA Biol. 13:554–560. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu HF, Wang YH, Liu D, Sun XQ and Wang
FR: Vanadium rutin complex sensitizes breast cancer cells via
modulation of p53/Bax/Bcl2/VEGF correlated with apoptotic events.
Acta Pol Pharm Drug Res. 77:89–98. 2020.
|
|
26
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nugent M: MicroRNA function and
dysregulation in bone tumors: The evidence to date. Cancer Manag
Res. 6:15–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li S, Fu H, Wang Y, Tie Y, Xing R, Zhu J,
Sun Z, Wei L and Zheng X: MicroRNA-101 regulates expression of the
v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (FOS) oncogene
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:1194–1202. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vishnol A and Rani S: miRNA biogenesis and
regulation of disease: An overview. Methods Mol Biol. 1509:1–10.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reddy KB: MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 15:382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ho JY, Hsu RJ, Liu JM, Chen SC, Liao GS,
Gao HW and Yu CP: MicroRNA-382-5p aggravates breast cancer
progression by regulating the RERG/Ras/ERK signaling axis.
Oncotarget. 8:22443–22459. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Chen C, Yan X and Wang P: The role
of miR-382-5p in glioma cell proliferation, migration and invasion.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:4993–5002. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu M, Jin H, Xu CX, Sun B, Song ZG, Bi WZ
and Wang Y: miR-382 inhibits osteosarcoma metastasis and relapse by
targeting Y box-binding protein 1. Mol Ther. 23:89–98. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Wang P, Su X and Zhao B:
Circ_0001658 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells via regulating miR-382-5p/YB-1 axis. Cell
Biochem Funct. 38:77–86. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiao Y, Li C, Wang H and Liu Y: LINC00265
targets miR-382-5p to regulate SAT1, VAV3 and angiogenesis in
osteosarcoma. Aging (Albany NY). 12:20212–20225. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kobayashi E, Hornicek FJ and Duan Z:
MicroRNA involvement in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma. 2012:3597392012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nugent M: microRNA and bone cancer. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 889:201–230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu L and Qu X: Cancer biomarker detection:
Recent achievements and challegenges. Chem Soc Rev. 44:2963–2997.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang XX, Ye FG, Zhang J, Li JJ, Chen QX,
Lin PY and Song CG: Serum miR-4530 sensitizes breast cancer to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy by suppressing RUNX2. Cancer Manag Res.
10:4393–4400. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sampson VB, Yoo S, Kumar A, Vetter NS and
Kolb EA: MicroRNAs and potential targets in osteosarcoma: Review.
Front Pediatr. 3:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
AlAbdi L, He M, Yang Q, Norvil AB and
Gowher H: The transcription factor Vezf1 represses the expression
of the antiangiogenic factor Cited2 in endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 293:11109–11118. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He M, Yang Q, Norvil AB, Sherris D and
Gowher H: Characterization of small molecules inhibiting the
pro-angiogenic activity of the zinc finger transcription factor
Vezf1. Molecules. 23:16152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gerald D, Adini I, Shechter S, Prendergast
GC, Klagsbrun M, Stuhlmann H, Rigby AC, Nagy JA and Benjamin LE:
RhoB controls coordination of adult angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis following injury by regulating VEZF1-mediated
transcription. Nat Commun. 4:28242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yin R, Guo L, Gu J, Li C and Zhang W: Over
expressing miR-19b-1 suppress breast cancer growth by inhibiting
tumor microenvironment induced angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 97:43–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ahmed M, Lai TH, Zada S, Hwang JS, Pham
TM, Yun M and Kim DR: Functional linkage of RKIP to the epithelial
to mesenchymal transition and autophagy during the development of
prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 10:2732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|