|
1
|
Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian
SA, Bray F, Coleman J, Gore JL, Sun M, Wood C and Russo P:
Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 75:74–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Capitanio U and Montorsi F: Renal cancer.
Lancet. 387:894–906. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng T, Zhu C, Bassig BA, Liu S, Buka S,
Zhang X, Truong A, Oh J, Fulton J, Dai M, et al: The long-term
rapid increase in incidence of adenocarcinoma of the kidney in the
USA, especially among younger ages. Int J Epidemiol. 48:1886–1896.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Znaor A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Laversanne M,
Jemal A and Bray F: International variations and trends in renal
cell carcinoma incidence and mortality. Eur Urol. 67:519–530. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guida A, Escudier B and Albiges L:
Treating patients with renal cell carcinoma and bone metastases.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 18:1135–1143. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Molina AMD: A multidisciplinary approach
for the management of earlier stage renal cell carcinoma. Urol
Oncol. 36:15–16. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, George DJ,
Pantuck AJ, Patel A, Chang YH, Escudier B, Donskov F, Magheli A, et
al: Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after
nephrectomy. N Engl J Med. 375:2246–2254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bianchi M, Sun M, Jeldres C, Shariat SF,
Trinh QD, Briganti A, Tian Z, Schmitges J, Graefen M, Perrotte P,
et al: Distribution of metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma: A
population-based analysis. Ann Oncoly. 23:973–980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bosse D, Lin X, Simantov R, Lalani AA,
Derweesh I, Chang SL, Choueiri TK and McKay RR: Response of primary
renal cell carcinoma to systemic therapy. Eur Urol. 76:852–860.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joshi SS, Handorf EA, Zibelman M, Plimack
ER, Uzzo RG, Kutikov A, Smaldone MC and Geynisman DM: Treatment
facility volume and survival in patients with metastatic renal cell
carcinoma: A registry-based analysis. Eur Urol. 74:387–393. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhuo H and Zhou L: Gpnmb/osteoactivin: An
indicator and therapeutic target in tumor and nontumorous lesions.
Pharmazie. 71:555–561. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rose AAN, Biondini M, Curiel R and Siegel
PM: Targeting GPNMB with glembatumumab vedotin: Current
developments and future opportunities for the treatment of cancer.
Pharmacol Ther. 179:127–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Truong DD, Kratz A, Park JG, Barrientos
ES, Saini H, Nguyen T, Pockaj B, Mouneimne G, LaBaer J and Nikkhah
M: A Human organotypic microfluidic tumor model permits
investigation of the interplay between patient-derived fibroblasts
and breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 79:3139–3151. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baba M, Furuya M, Motoshima T, Lang M,
Funasaki S, Ma W, Sun HW, Hasumi H, Huang Y, Kato I, et al: TFE3
Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma mouse model reveals novel
therapeutic targets and identifies GPNMB as a diagnostic marker for
human disease. Mol Cancer Res. 17:1613–1626. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sondag GR, Mbimba TS, Moussa FM, Novak K,
Yu B, Jaber FA, Abdelmagid SM, Geldenhuys WJ and Safadi FF:
Osteoactivin inhibition of osteoclastogenesis is mediated through
CD44-ERK signaling. Exp Mol Med. 48:e2572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ono Y, Chiba S, Yano H, Nakayama N, Saio
M, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M, Iwama T and Hara H: Glycoprotein
nonmetastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) promotes the progression
of brain glioblastoma via Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 481:7–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tian F, Liu C, Wu Q, Qu K, Wang R, Wei J,
Meng F, Liu S and Chang H: Upregulation of glycoprotein
nonmetastatic B by colony-stimulating factor-1 and epithelial cell
adhesion molecule in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Res.
20:341–350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tomihari M, Chung JS, Akiyoshi H, Cruz PD
Jr and Ariizumi K: DC-HIL/glycoprotein Nmb promotes growth of
melanoma in mice by inhibiting the activation of tumor-reactive T
cells. Cancer Res. 70:5778–5787. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin R, Jin YY, Tang YL, Yang HJ, Zhou XQ
and Lei Z: GPNMB silencing suppresses the proliferation and
metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 39:3034–3040. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fiorentini C, Bodei S, Bedussi F, Fragni
M, Bonini SA, Simeone C, Zani D, Berruti A, Missale C, Memo M, et
al: GPNMB/OA protein increases the invasiveness of human metastatic
prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC3 through MMP-2 and MMP-9
activity. Exp Cell Res. 323:100–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nannuru KC, Futakuchi M, Varney ML,
Vincent TM, Marcusson EG and Singh RK: Matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-13 regulates mammary tumor-induced osteolysis by activating
MMP9 and transforming growth factor-β Signaling at the tumor-bone
interface. Cancer Res. 70:3494–3504. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
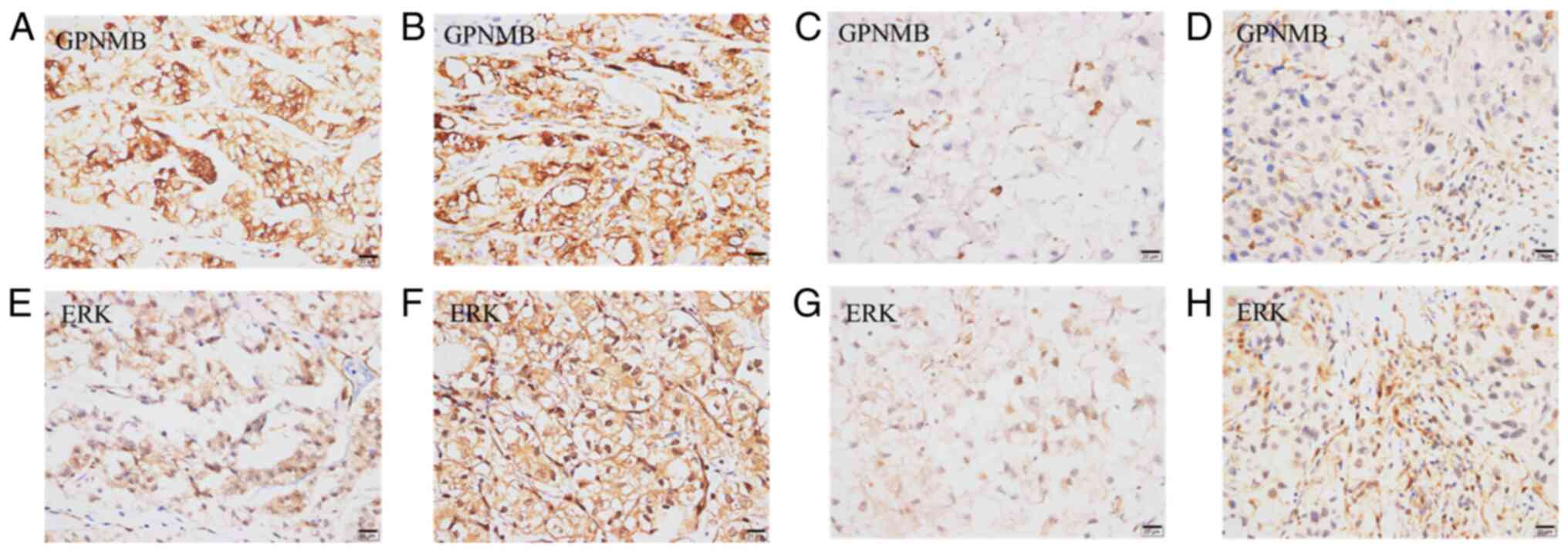
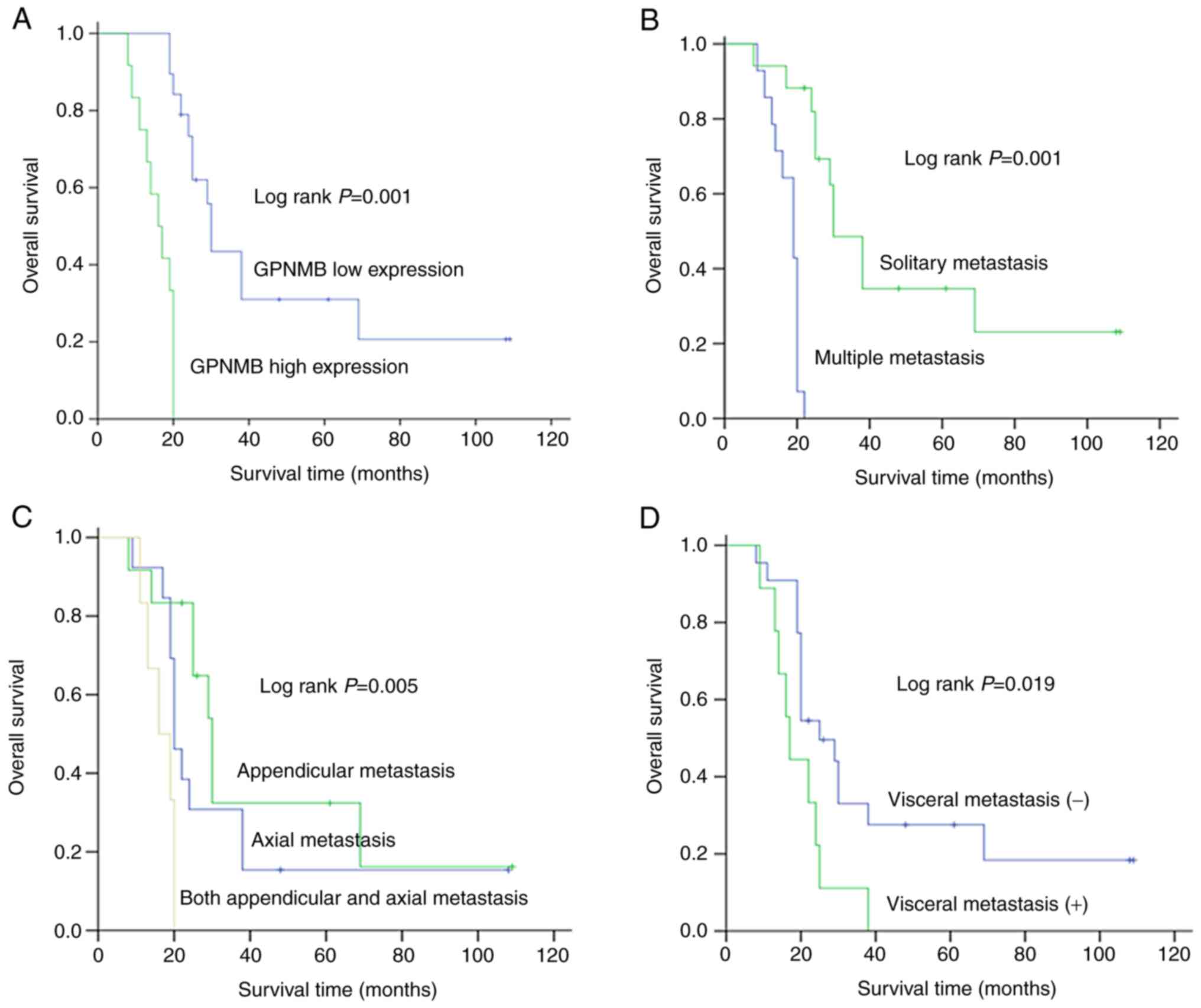
Jianpo Z, Ning L, Hai W, Haidong W and
Libo M: Expression of GPNMB, ERK, MMP3 and MMP9 in primary lesion
and bone metastasis of renal cell carcinoma and their correlation.
Cancer Res Prev Treat. 47:367–371. 2020.
|
|
23
|
Mayo JC, Hevia D, Quiros-Gonzalez I,
Rodriguez-Garcia A, Gonzalez-Menendez P, Cepas V, Gonzalez-Pola I
and Sainz RM: IGFBP3 and MAPK/ERK signaling mediates
melatonin-induced antitumor activity in prostate cancer. J Pineal
Res. Oct 13–2016.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12373.
|
|
24
|
Qin C, Liu Z, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Li H, Zhang
C, Xu T and Wang X: Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B
as a predictive prognostic factor in clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma following radical nephrectomy. Mol Med Rep. 9:851–886.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rose AA, Pepin F, Russo C, Abou Khalil JE,
Hallett M and Siegel PM: Osteoactivin promotes breast cancer
metastasis to bone. Mol Cancer Res. 5:1001–1114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rose AA and Siegel PM: Emerging
therapeutic targets in breast cancer bone metastasis. Future Oncol.
6:55–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ramani V, Teshima T, Tamura K, Chung JS,
Kobayashi M, Cruz PD Jr and Ariizumi K: Melanoma-derived soluble
DC-HIL/GPNMB promotes metastasis by excluding T-Lymphocytes from
the pre-metastatic niches. J Nvest Dermatol. 138:2443–2451. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rose AA, Grosset AA, Dong Z, Russo C,
Macdonald PA, Bertos NR, St-Pierre Y, Simantov R, Hallett M, Park
M, et al: Glycoprotein nonmetastatic B is an independent prognostic
indicator of recurrence and a novel therapeutic target in breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2147–2156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li YN, Zhang L, Li XL, Cui DJ, Zheng HD,
Yang SY and Yang WL: Glycoprotein nonmetastatic B as a prognostic
indicator in small cell lung cancer. APMIS. 122:140–146. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma RQ, Tang ZJ, Ye X, Cheng HY, Sun KK,
Chang XH and Cui H: Overexpression of GPNMB predicts an unfavorable
outcome of epithelial ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
297:1235–1244. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arosarena OA, Barr EW, Thorpe R, Yankey H,
Tarr JT and Safadi FF: Osteoactivin regulates head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma invasion by modulating matrix
metalloproteases. J Cell Physiol. 233:409–421. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bhattacharyya S, Feferman L, Sharma G and
Tobacman JK: Increased GPNMB, phospho-ERK1/2, and MMP-9 in cystic
fibrosis in association with reduced arylsulfatase B. Mol Genet
Metab. 124:168–175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Okita Y, Kimura M, Xie R, Chen C, Shen LT,
Kojima Y, Suzuki H, Muratani M, Saitoh M, Semba K, et al: The
transcription factor MAFK induces EMT and malignant progression of
triple-negative breast cancer cells through its target GPNMB. Sci
Signal. 10:eaak93972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen C, Okita Y, Watanabe Y, Abe F, Fikry
MA, Ichikawa Y, Suzuki H, Shibuya A and Kato M: Glycoprotein nmb is
exposed on the surface of dormant breast cancer cells and induces
stem cell-like properties. Cancer Res. 78:6424–6435. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kopp LM, Malempati S, Krailo M, Gao Y,
Buxton A, Weigel BJ, Hawthorne T, Crowley E, Moscow JA, Reid JM, et
al: Phase II trial of the glycoprotein non-metastatic B-targeted
antibody-drug conjugate, glembatumumab vedotin (CDX-011), in
recurrent osteosarcoma AOST1521: A report from the Children's
Oncology Group. Eur J Cancer. 121:177–183. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tray N, Adams S and Esteva FJ:
Antibody-drug conjugates in triple negative breast cancer. Future
Oncol. 14:2651–2661. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ott PA, Hamid O, Pavlick AC, Kluger H, Kim
KB, Boasberg PD, Simantov R, Crowley E, Green JA, Hawthorne T, et
al: Phase I/II study of the antibody-drug conjugate glembatumumab
vedotin in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol.
32:3659–3666. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ott PA, Pavlick AC, Johnson DB, Hart LL,
Infante JR, Luke JJ, Lutzky J, Rothschild NE, Spitler LE, Cowey CL,
et al: A phase 2 study of glembatumumab vedotin, an antibody-drug
conjugate targeting glycoprotein NMB, in patients with advanced
melanoma. Cancer. 125:1113–1123. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rose AA, Annis MG, Frederick DT, Biondini
M, Dong Z, Kwong L, Chin L, Keler T, Hawthorne T, Watson IR, et al:
MAPK pathway inhibitors sensitize BRAF-mutant melanoma to an
antibody-drug conjugate targeting GPNMB. Clin Cancer Res.
22:6088–6098. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yardley DA, Weaver R, Melisko ME, Saleh
MN, Arena FP, Forero A, Cigler T, Stopeck A, Citrin D, Oliff I, et
al: EMERGE: A randomized phase II study of the antibody-drug
conjugate glembatumumab vedotin in advanced glycoprotein
NMB-expressing breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 33:1609–1619. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bendell J, Saleh M, Rose AA, Siegel PM,
Hart L, Sirpal S, Jones S, Green J, Crowley E, Simantov R, et al:
Phase I/II study of the antibody-drug conjugate glembatumumab
vedotin in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 32:3619–3625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|