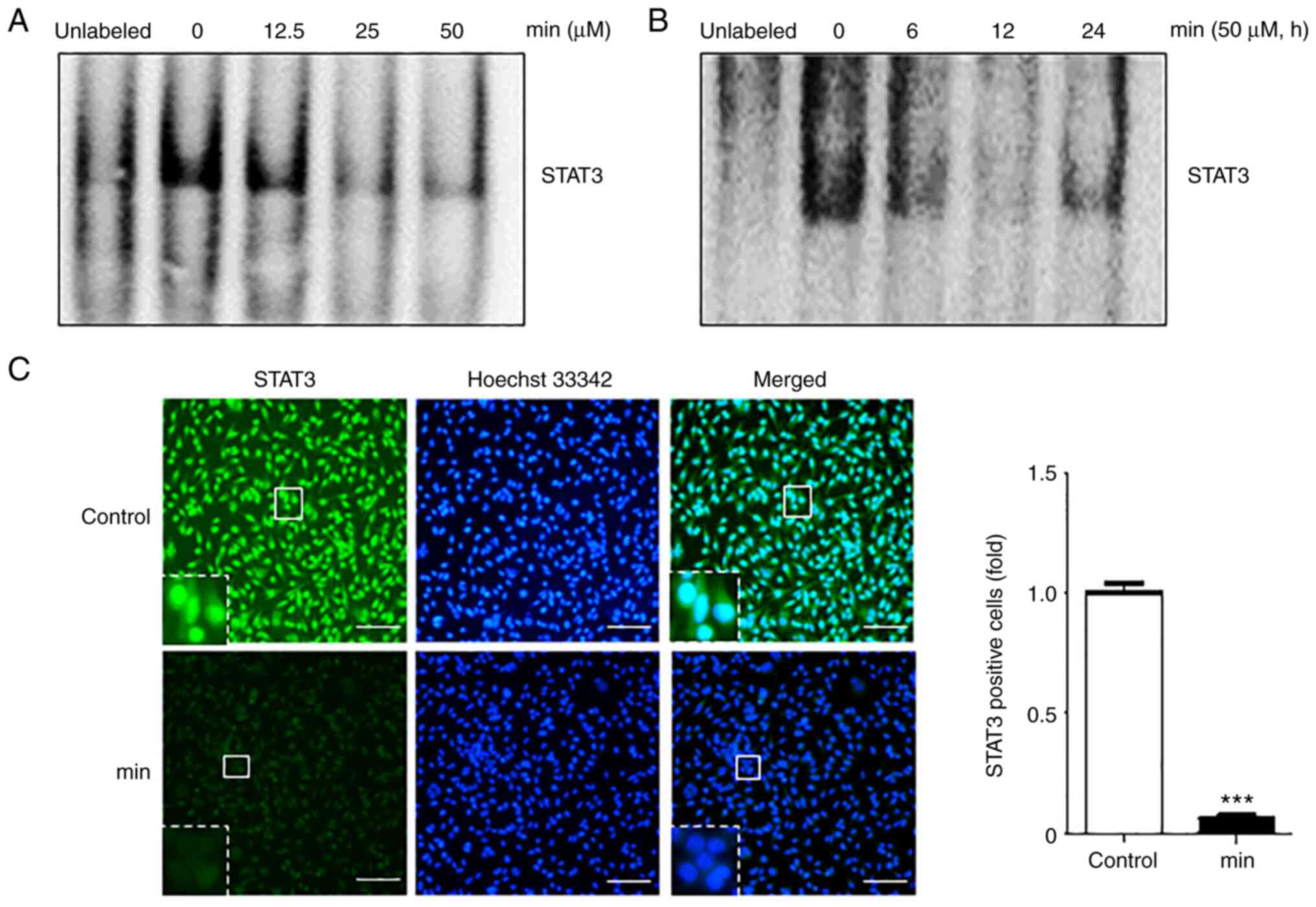
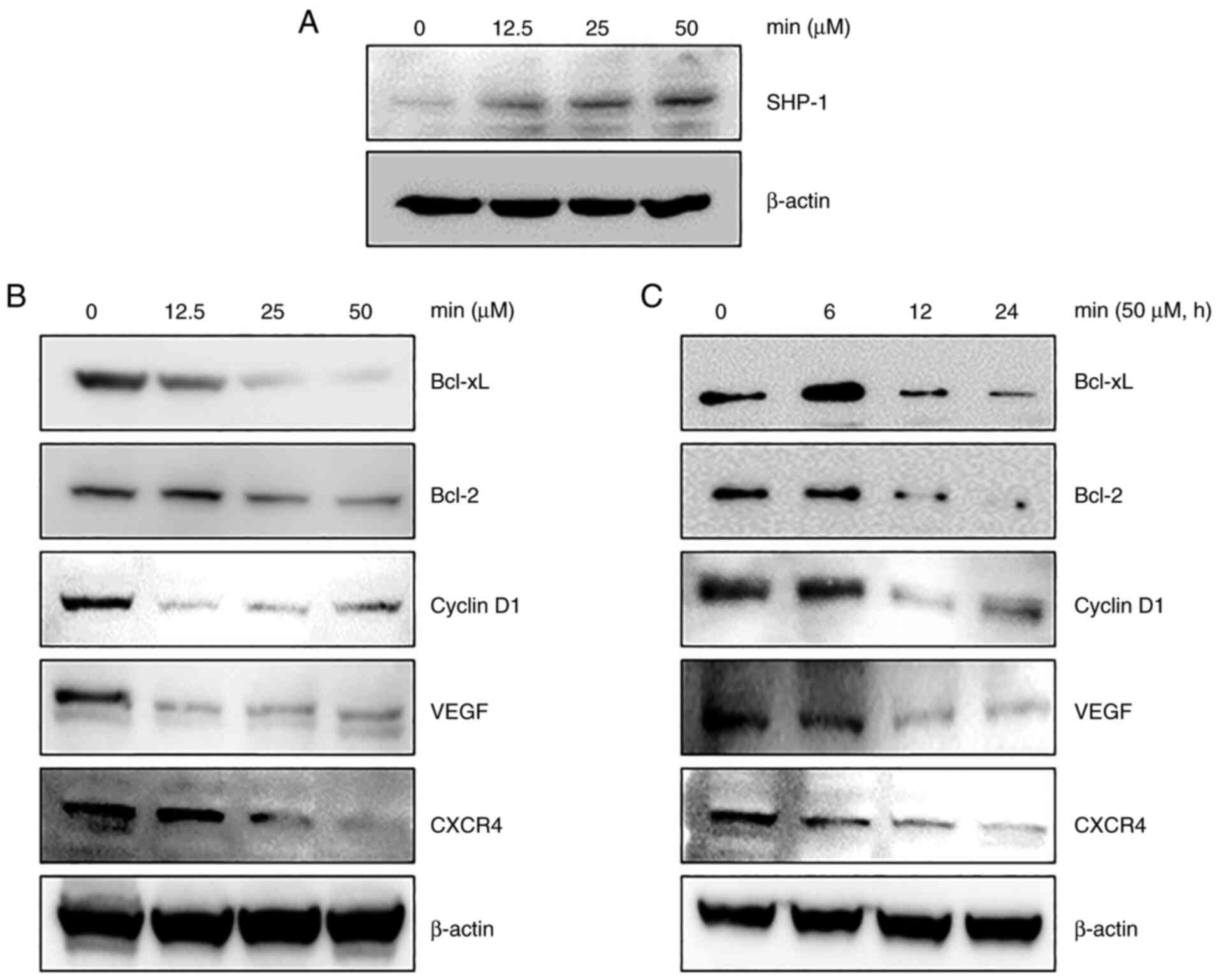
|
1
|
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:409–418. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumour stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Banerjee K and Resat H: Constitutive
activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int J Cancer.
138:2570–2578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laudisi F, Cherubini F, Monteleone G and
Stolfi C: STAT3 interactors as potential therapeutic targets for
cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 19:17872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garbers C, Aparicio-Siegmund S and
Rose-John S: The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: Recent advances
towards specific inhibition. Curr Opin Immunol. 34:75–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA,
Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Burg J, Strand S, Kiesslich R, Huber S, et al:
TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition
of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 21:491–501. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kundu J, Choi BY, Jeong CH, Kundu JK and
Chun KS: Thymoquinone induces apoptosis in human colon cancer
HCT116 cells through inactivation of STAT3 by blocking JAK2- and
Src-mediated phosphorylation of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncol
Rep. 32:821–828. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang X, Crowe PJ, Goldstein D and Yang JL:
STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in
human cancers (Review). Int J Oncol. 41:1181–1191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gu F, Dubé N, Kim JW, Cheng A,
Ibarra-Sanchez Mde J, Tremblay ML and Boisclair YR: Protein
tyrosine phosphatase 1B attenuates growth hormone-mediated
JAK2-STAT signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:3753–3762. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu CY, Tseng LM, Su JC, Chang KC, Chu PY,
Tai WT, Shiau CW and Chen KF: Novel sorafenib analogues induce
apoptosis through SHP-1 dependent STAT3 inactivation in human
breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu C, Sun M, Liu L and Zhou GW: The
function of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in cancer. Gene.
306:1–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joo MK, Park JJ, Yoo HS, Lee BJ, Chun HJ,
Lee SW and Bak YT: Epigenetic regulation and anti-tumorigenic
effects of SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP1) in
human gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:4603–4612. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kwak JH, Kim HJ, Lee KH, Kang SC and Zee
OP: Antioxidative iridoid glycosides and phenolic compounds from
Veronica peregrina. Arch Pharm Res. 32:207–213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim B, Min YH and Park B: Minecoside
modulates cell invasion via regulation of CXCR4 expression in
breast and colon cancer cells. Planta Med. 86:331–337. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park S, Shin H, Park Y, Choi I, Park B and
Lee KY: Characterization of inhibitory constituents of NO
production from Catalpa ovata using LC-MS coupled with a cell-based
assay. Bioorg Chem. 80:57–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim B, Lee KY and Park B: Crocin
suppresses constitutively active STAT3 through induction of protein
tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. J Cell Biochem. 118:3290–3298. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Masciocchi D, Gelain A, Villa S,
Meneghetti F and Barlocco D: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 (STAT3): A promising target for anticancer therapy.
Future Med Chem. 3:567–597. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim M, Morales LD, Jang IS, Cho YY and Kim
DJ: Protein tyrosine phosphatases as potential regulators of STAT3
signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 19:27082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han Y, Amin HM, Franko B, Frantz C, Shi X
and Lai R: Loss of SHP1 enhances JAK3/STAT3 signaling and decreases
proteosome degradation of JAK3 and NPM-ALK in ALK+
anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood. 108:2796–2803. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiao H, Berrada K, Yang W, Tabrizi M,
Platanias LC and Yi T: Direct association with and
dephosphorylation of Jak2 kinase by the SH2-domain-containing
protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:6985–6992.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Real PJ, Sierra A, De Juan A, Segovia JC,
Lopez-Vega JM and Fernandez-Luna JL: Resistance to chemotherapy via
Stat3-dependent overexpression of Bcl-2 in metastatic breast cancer
cells. Oncogene. 21:7611–7618. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Xu J and Xing G: Lycorine inhibits
the growth and metastasis of breast cancer through the blockage of
STAT3 signaling pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
49:771–779. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu X, Xiao Q, Bai X, Yu Z, Sun M, Zhao H,
Mi X, Wang E, Yao W, Jin F, et al: Activation of STAT3 is involved
in malignancy mediated by CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in human breast
cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2760–2768. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura
E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Johnston PA and Grandis JR: STAT3
signaling: Anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol Interv.
11:18–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burke WM, Jin X, Lin HJ, Huang M, Liu R,
Reynolds RK and Lin J: Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3
suppresses growth of human ovarian and breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 20:7925–7934. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang T, Niu G, Kortylewski M, Burdelya L,
Shain K, Zhang S, Bhattacharya R, Gabrilovich D, Heller R, Coppola
D, et al: Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by
Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat Med. 10:48–54. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ihle JN: STATs: Signal transducers and
activators of transcription. Cell. 84:331–334. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schreiner SJ, Schiavone AP and Smithgall
TE: Activation of STAT3 by the Src family kinase Hck requires a
functional SH3 domain. J Biol Chem. 277:45680–45687. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang TT, Su JC, Liu CY, Shiau CW and Chen
KF: Alteration of SHP-1/p-STAT3 signaling: A potential target for
anticancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 18:12342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Santoni M, Massari F, Del Re M, Ciccarese
C, Piva F, Principato G, Montironi R, Santini D, Danesi R, Tortora
G and Cascinu S: Investigational therapies targeting signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 for the treatment of
cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 24:809–824. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Dangerous
liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:11–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|