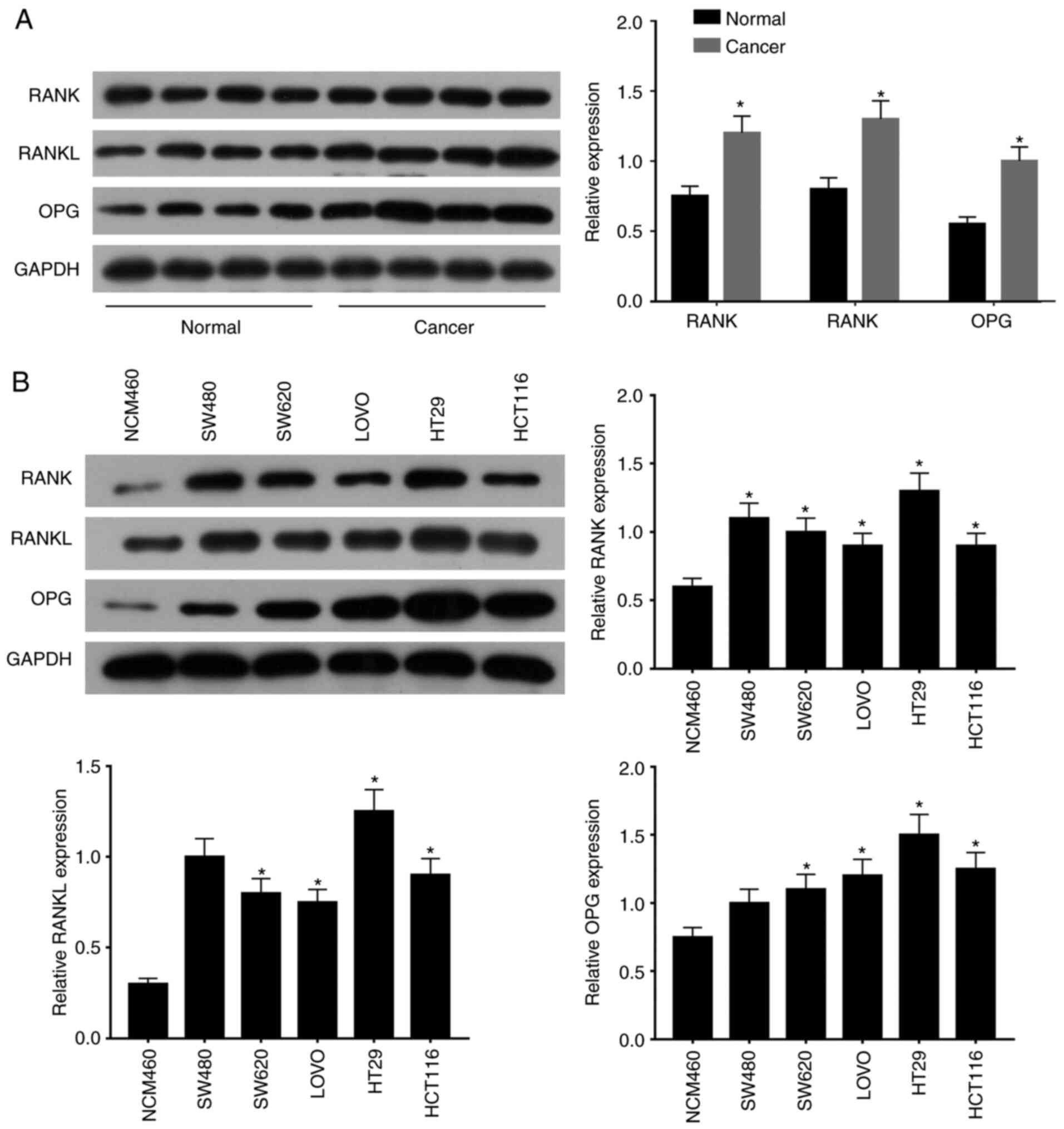
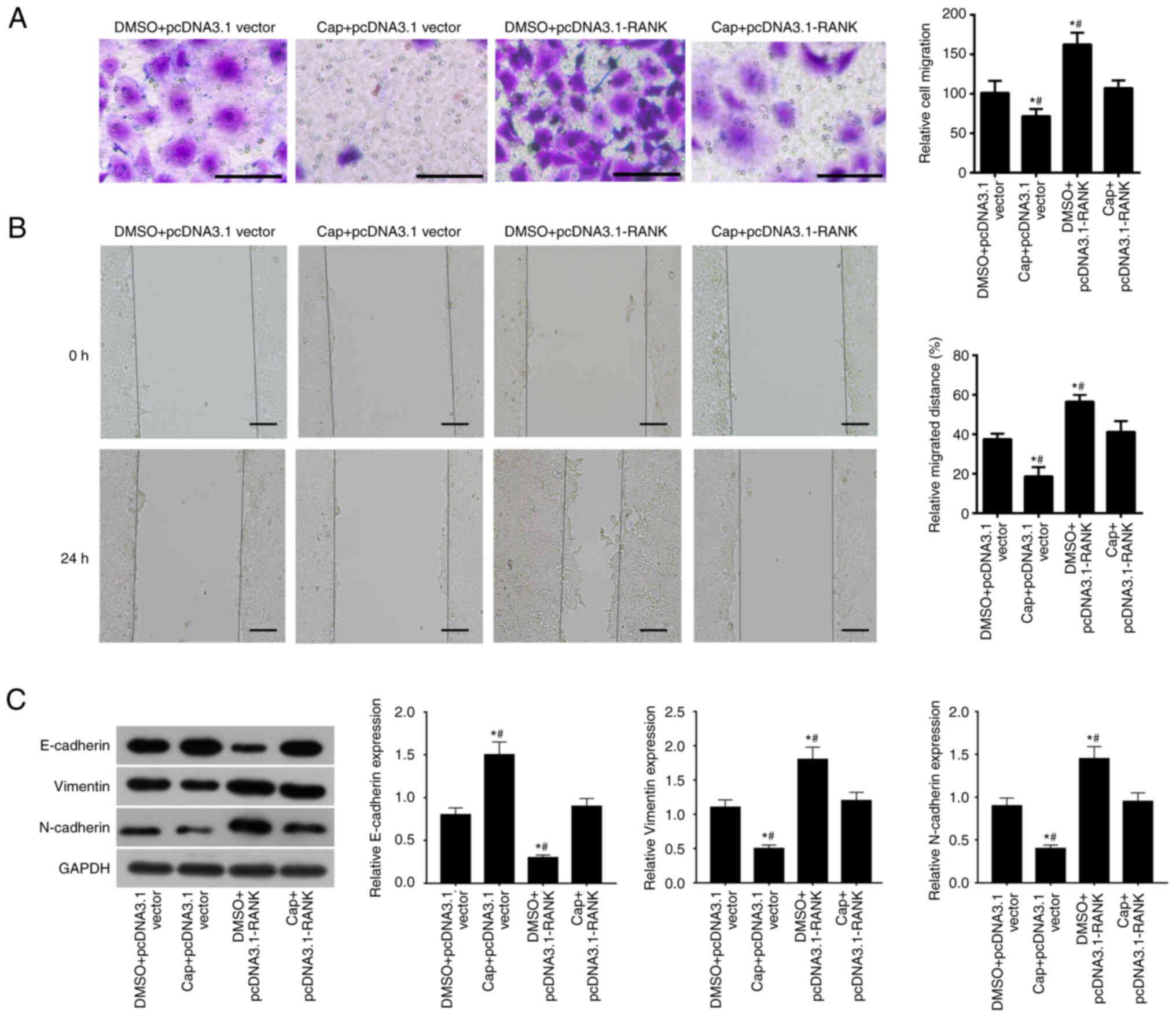
|
1
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carethers JM and Doubeni CA: Causes of
socioeconomic disparities in colorectal cancer and intervention
framework and strategies. Gastroenterology. 158:354–367. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sivamaruthi BS, Kesika P and Chaiyasut C:
The role of probiotics in colorectal cancer management. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. Feb 14–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1155/2020/3535982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Müller MF, Ibrahim AE and Arends MJ:
Molecular pathological classification of colorectal cancer.
Virchows Arch. 469:125–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Quan Y, Xu M, Cui P, Ye M, Zhuang B and
Min Z: Grainyhead-like 2 promotes tumor growth and is associated
with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Cancer. 6:342–350.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Wang L, Wang W and Guo X:
Overexpression of circular RNA hsa_circ_0001038 promotes cervical
cancer cell progression by acting as a ceRNA for miR-337-3p to
regulate cyclin-M3 and metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1
expression. Gene. 733:1442732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Falco V, Napolitano S, Roselló S,
Huerta M, Cervantes A, Ciardiello F and Troiani T: How we treat
metastatic colorectal cancer. ESMO Open. 4 (Suppl 2):e0008132020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thorat SG, Chikhale RV and Tajne MR:
Development and validation of HPLC and HPTLC methods for
therapeutic drug monitoring of capecitabine in colorectal cancer
patients. J Chromatogr Sci. 57:892–900. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JH: Chemotherapy for colorectal cancer
in the elderly. World J Gastroenterol. 21:5158–5166. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aglago EK, Huybrechts I, Murphy N,
Casagrande C, Nicolas G, Pischon T, Fedirko V, Severi G,
Boutron-Ruault MC, Fournier A, et al: Consumption of fish and
long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is associated with
reduced risk of colorectal cancer in a large european cohort. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:654–66.e6. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Cutsem E, Verslype C and Tejpar S:
Oral capecitabine: Bridging the Atlantic divide in colon cancer
treatment. Semin Oncol. 32:43–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Q, Mao Y, Meng F, Wang L, Zhang H,
Wang W and Hua D: Rs7911488 modified the efficacy of
capecitabine-based therapy in colon cancer through altering
miR-1307-3p and TYMS expression. Oncotarget. 8:74312–74319. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hirsch BR and Zafar SY: Capecitabine in
the management of colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 3:79–89.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silva I and Branco JC: Rank/Rankl/opg:
Literature review. Acta Reumatol Port. 36:209–218. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khosla S: Minireview: The OPG/RANKL/RANK
system. Endocrinology. 142:5050–5055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sisay M, Mengistu G and Edessa D: The
RANK/RANKL/OPG system in tumorigenesis and metastasis of cancer
stem cell: Potential targets for anticancer therapy. Onco Targets
Ther. 10:3801–3810. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo G, Li F, Li X, Wang ZG and Zhang B:
TNFα and RANKL promote osteoclastogenesis by upregulating RANK via
the NFκB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:6605–6611. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wood MB, Rios D and Williams IR: TNF-α
augments RANKL-dependent intestinal M cell differentiation in
enteroid cultures. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 311:C498–C507. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chu GC, Zhau HE, Wang R, Rogatko A, Feng
X, Zayzafoon M, Liu Y, Farach-Carson MC, You S, Kim J, et al: RANK-
and c-Met-mediated signal network promotes prostate cancer
metastatic colonization. Endocr Relat Cancer. 21:311–326. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Casimiro S, Mohammad KS, Pires R,
Tato-Costa J, Alho I, Teixeira R, Carvalho A, Ribeiro S, Lipton A,
Guise TA and Costa L: RANKL/RANK/MMP-1 molecular triad contributes
to the metastatic phenotype of breast and prostate cancer cells in
vitro. PLoS ONE. 8:e631532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Buckle CH, Neville-Webbe HL, Croucher PI
and Lawson MA: Targeting RANK/RANKL in the treatment of solid
tumours and myeloma. Curr Pharm Des. 16:1272–1283. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okimoto G, Zeinalzadeh A, Wenska T, Loomis
M, Nation JB, Fabre T, Tiirikainen M, Hernandez B, Chan O, Wong L
and Kwee S: Joint analysis of multiple high-dimensional data types
using sparse matrix approximations of rank-1 with applications to
ovarian and liver cancer. BioData Min. 9:242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khan MA, Sharif M, Akram T, Yasmin M and
Nayak RS: Stomach deformities recognition using rank-based deep
features selection. J Med Syst. 43:3292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Infante M, Fabi A, Cognetti F, Gorini S,
Caprio M and Fabbri A: RANKL/RANK/OPG system beyond bone
remodeling: Involvement in breast cancer and clinical perspectives.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sood SK, Balasubramanian S, Higham S,
Fernando M and Harrison B: Osteoprotegerin (OPG) and related
proteins (RANK, RANKL and TRAIL) in thyroid disease. World J Surg.
35:1984–1992. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Retraction, Antitumor and antimetastatic
activities of docetaxel are enhanced by genistein through
regulation of osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear
factor-κB (RANK)/RANK Ligand/MMP-9 signaling in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 78:54752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pritchard L, Cardle L, Quinn S and Dufton
M: Simple intrasequence difference (SID) analysis: An original
method to highlight and rank sub-structural interfaces in protein
folds. Application to the folds of bovine pancreatic trypsin
inhibitor, phospholipase A2, chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase A.
Protein Eng. 16:87–101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang Q, Wang Y, Lu Y, Zhu Q, Xie W, Tang
N, Huang L, An T, Zhang D, Yan A, et al: RANK promotes colorectal
cancer migration and invasion by activating the
Ca(2+)-calcineurin/NFATC1-ACP5 axis. Cell Death Dis. 12:3362021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao W, Chen B, Guo X, Wang R, Chang Z,
Dong Y, Song K, Wang W, Qi L, Gu Y, et al: A rank-based
transcriptional signature for predicting relapse risk of stage II
colorectal cancer identified with proper data sources. Oncotarget.
7:19060–19071. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
National Health Commission of the People's
Republic of China, . [Chinese Protocol of Diagnosis and Treatment
of Colorectal Cancer. ((2020 edition)]). Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.
58:561–585. 2020.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park DW, Ham YM, Lee YG, So R, Seo YJ and
Kang SC: Multioside, an active ingredient from adonis amurensis,
displays anti-cancer activity through autophagosome formation.
Phytomedicine. 65:1531142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choi MY, Flood K, Bernatsky S,
Ramsey-Goldman R and Clarke AE: A review on SLE and malignancy.
Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 31:373–396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wen J, Liu X, Qi Y, Niu F, Niu Z, Geng W,
Zou Z, Huang R, Wang J and Zou H: BMP3 suppresses colon
tumorigenesis via ActRIIB/SMAD2-dependent and TAK1/JNK signaling
pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:4282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li B, Zhu FC, Yu SX, Liu SJ and Li BY:
Suppression of KIF22 inhibits cell proliferation and xenograft
tumor growth in colon cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:50–57.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li F, Zhang C and Fu L: PRR14
overexpression promotes cell growth, epithelial to mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of colon cancer via the AKT pathway. PLoS
ONE. 14:e02188392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kiesel L and Kohl A: Role of the
RANK/RANKL pathway in breast cancer. Maturitas. 86:10–16. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Yoshizumi M, Ueda E,
Itoh T, Imano M, Satou T and Nishida S: RANK-RANKL interactions are
involved in cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance in multiple
myeloma cell lines. Tumour Biol. 37:9099–9110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang J, Sun X, Zhang H, Wang Y and Li Y:
MPA influences tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion
induced by RANKL through PRB involving the MAPK pathway in
endometrial cancer. Oncol Rep. 33:799–809. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yamaue H, Tanimura H, Nakamori M, Noguchi
K, Iwahashi M, Tani M, Hotta T, Murakami K and Ishimoto K: Clinical
evaluation of chemosensitivity testing for patients with colorectal
cancer using MTT assay. Dis Colon Rectum. 39:416–422. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Singh G, Graffner HO, Milsom JW and
Chaudry IH: Tauromustine is more effective than conventional
chemotherapy in the treatment of colonic tumors. Dis Colon Rectum.
36:394–399. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lam SW, Guchelaar HJ and Boven E: The role
of pharmacogenetics in capecitabine efficacy and toxicity. Cancer
Treat Rev. 50:9–22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Song D, Meng T, Xu W, Hou T, Lin Z, Yin H,
Li B, Zhou L, Wang T, Han S, et al: 5-Fluoruracil blocked giant
cell tumor progression by suppressing osteoclastogenesis through
NF-kappaB signals and blocking angiogenesis. Bone. 78:46–54. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|