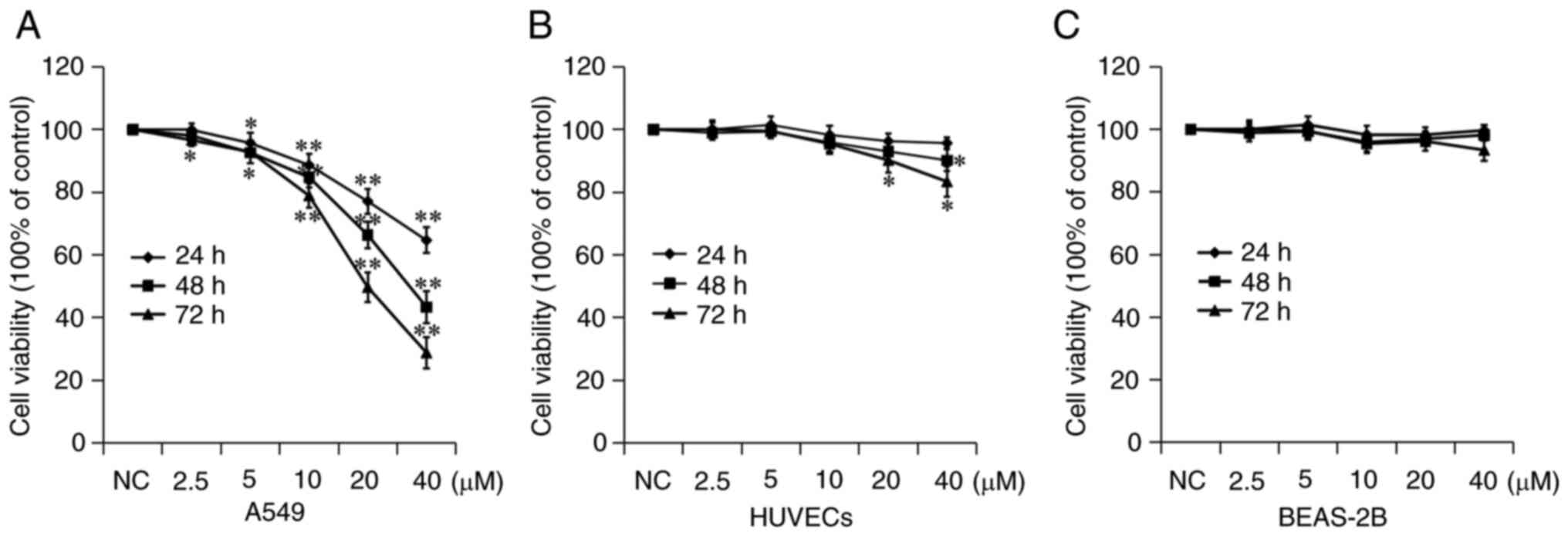
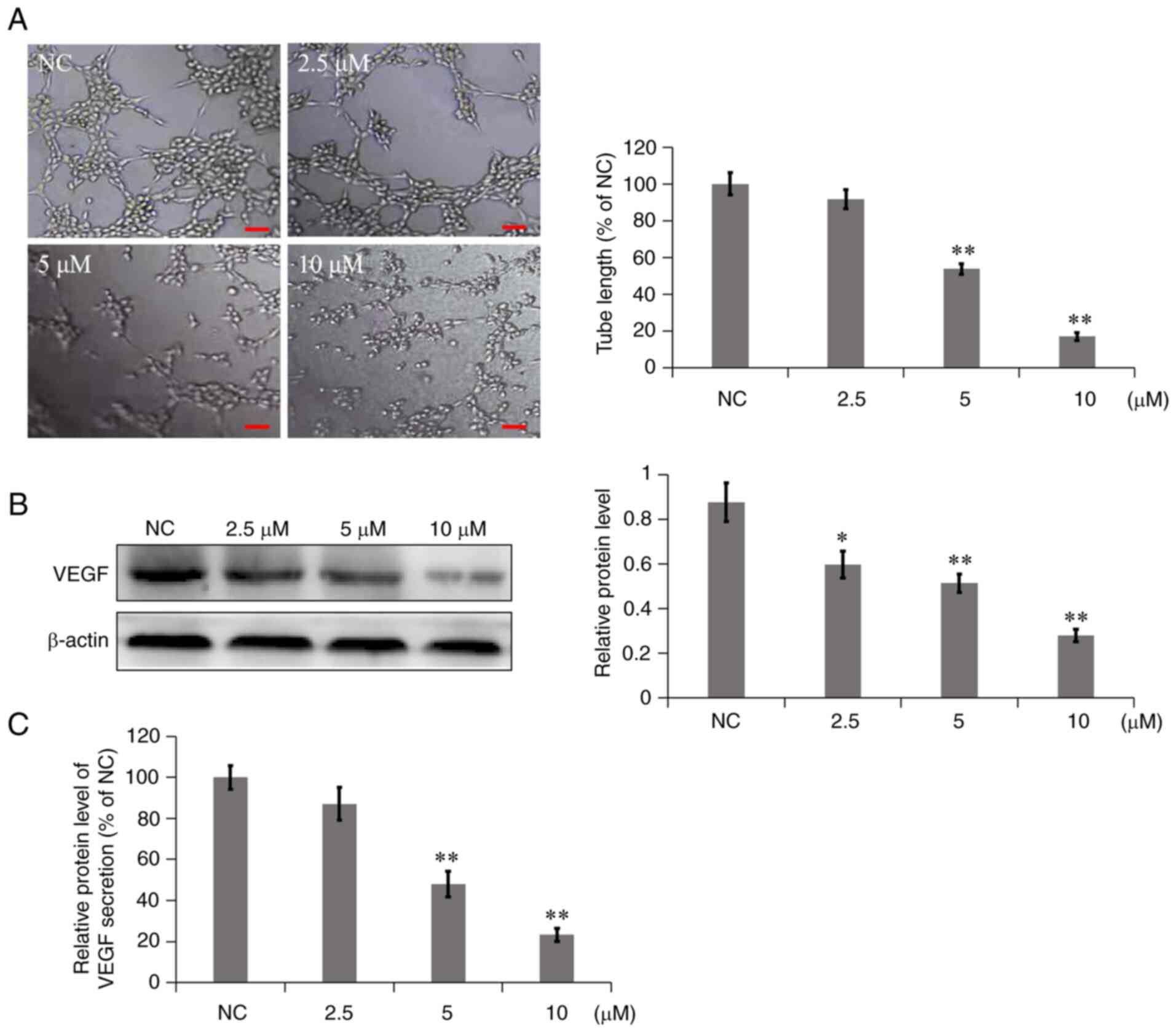
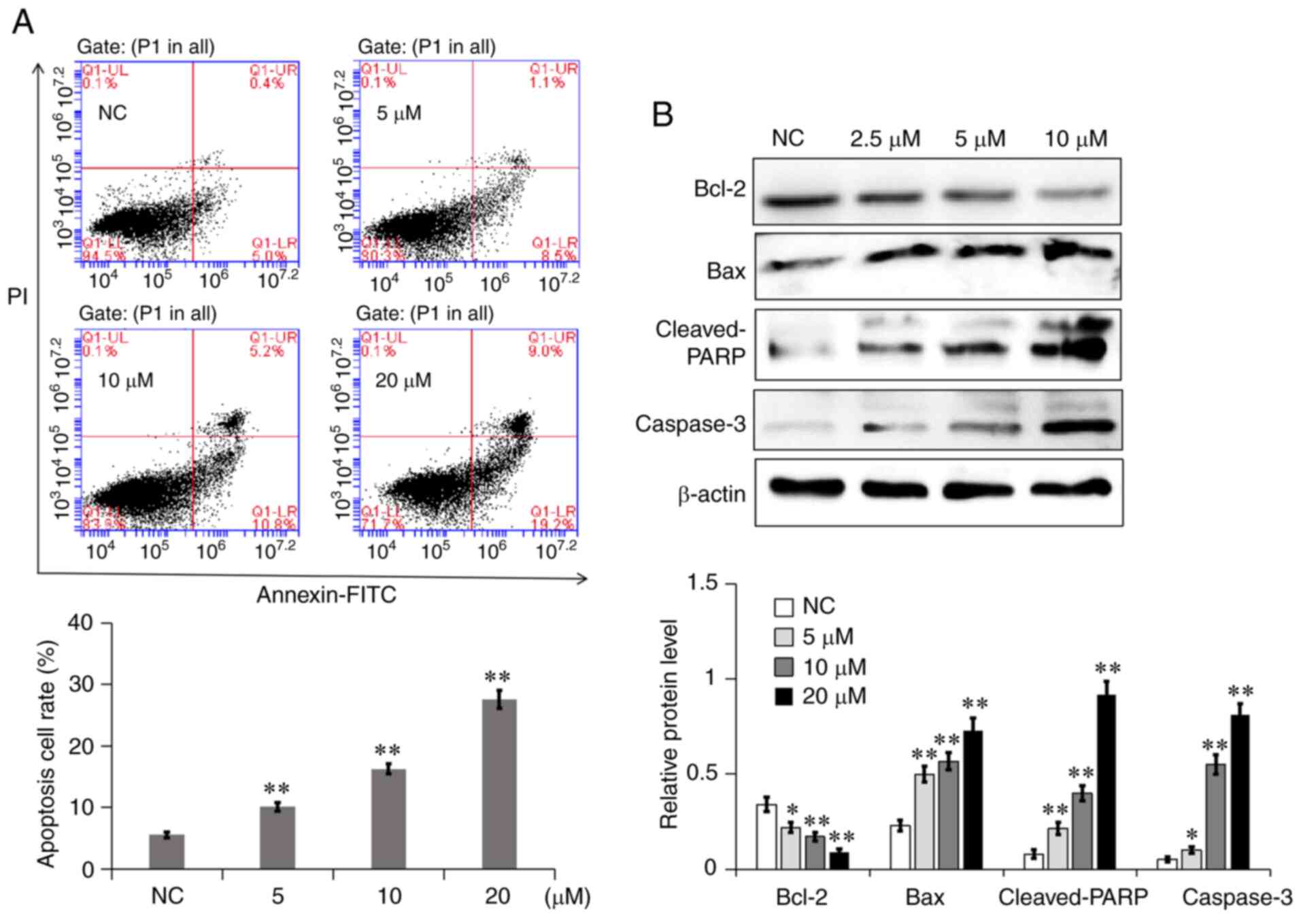
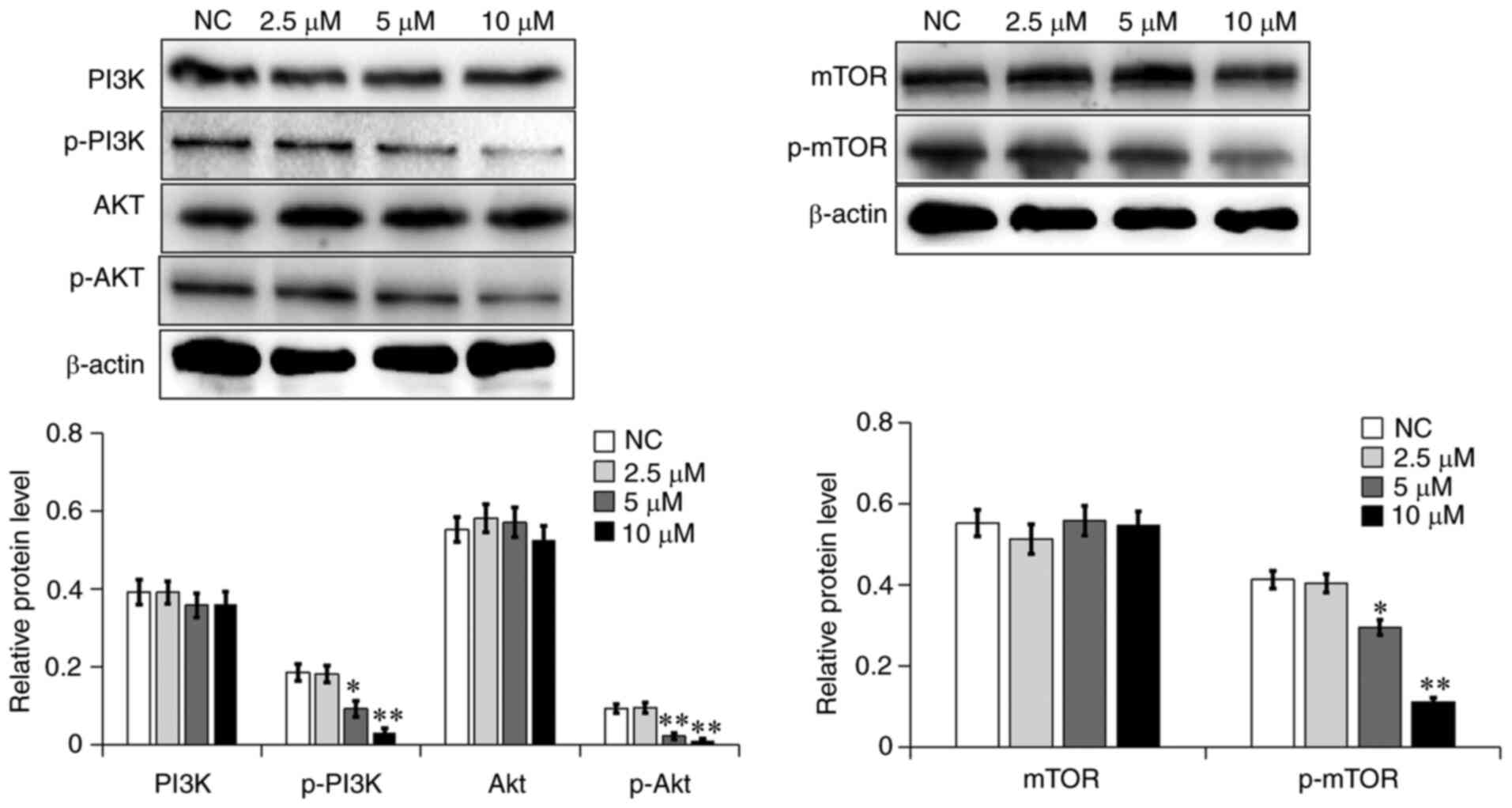
|
1
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quint LE, Tummala S, Brisson LJ, Francis
IR, Krupnick AS, Kazerooni EA, Iannettoni MD, Whyte RI and Orringer
MB: Distribution of distant metastases from newly diagnosed
non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 62:246–250. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaya J, Belinky PA and Aviram M:
Antioxidant constituents from licorice roots: Isolation, structure
elucidation and antioxidative capacity toward LDL oxidation. Free
Radic Biol Med. 23:302–313. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan SC, Chang YS, Wang JP, Chen SC and
Kuo SC: Three new flavonoids and antiallergic, anti-inflammatory
constituents from the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera. Planta Med.
64:153–158. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamamoto S, Aizu E, Jiang H, Nakadate T,
Kiyoto I, Wang JC and Kato R: The potent anti-tumor-promoting agent
isoliquiritigenin. Carcinogenesis. 12:317–323. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cuendet M, Guo J, Luo Y, Chen S, Oteham
CP, Moon RC, van Breemen RB, Marler LE and Pezzuto JM: Cancer
chemopreventive activity and metabolism of isoliquiritigenin, a
compound found in licorice. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 3:221–232.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tian T, Sun J, Wang J, Liu Y and Liu H:
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits cell proliferation and migration through
the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in A549 lung cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 16:6133–6139. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang CC, Park AY and Guan JL: In vitro
scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of
cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2:329–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Andrews N Yu LG, Zhao Q, McKean D,
Williams JF, Connor LJ, Gerasimenko OV, Hilkens J, Hirabayashi J,
Kasai K and Rhodes JM: Galectin-3 interaction with
thomsen-friedenreich disaccharide on cancer-associated MUC1 causes
increased cancer cell endothelial adhesion. J Biol Chem.
282:773–781. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–11108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herzig M, Savarese F, Novatchkova M, Semb
H and Christofori G: Tumor progression induced by the loss of
E-cadherin independent of beta-catenin/Tcf-mediated wnt signaling.
Oncogene. 26:2290–2298. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Passalidou E, Trivella M, Singh N,
Ferguson M, Hu J, Cesario A, Granone P, Nicholson AG, Goldstraw P,
Ratcliffe C, et al: Vascular phenotype in angiogenic and
non-angiogenic lung non-small cell carcinomas. Br J Cancer.
86:244–249. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu X, Zong Y, Gao Y, Sun X, Zhao H, Luo W
and Jia S: VEGF induce vasculogenic mimicry of choroidal melanoma
through the PI3k signal pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2019:39091022019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao Z, Hao Z, Xin M, Yu L, Wang L, Zhang
Y, Zhang X and Guo X: Endogenous and exogenous galectin-3 promote
the adhesion of tumor cells with low expression of MUC1 to HUVECs
through upregulation of N-cadherin and CD44. Lab Invest.
98:1642–1656. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu G, Zhang W, Bertram P, Zheng XF and
McLeod H: Pharmacogenomic profiling of the PI3K/PTEN-AKT-mTOR
pathway in common human tumors. Int J Oncol. 24:893–900.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jung SK, Lee MH, Lim DY, Kim JE, Singh P,
Lee SY, Jeong CH, Lim TG, Chen H, Chi YI, et al: Isoliquiritigenin
induces apoptosis and inhibits xenograft tumor growth of human lung
cancer cells by targeting both wild type and L858R/T790M mutant
EGFR. J Biol Chem. 289:35839–35848. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakajima S, Doi R, Toyoda E, Tsuji S, Wada
M, Koizumi M, Tulachan SS, Ito D, Kami K, Mori T, et al: N-cadherin
expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4125–4133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Merchant N, Nagaraju GP, Rajitha B,
Lammata S, Jella KK, Buchwald ZS, Lakka SS and Ali AN: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Their functional role in lung cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 38:766–780. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown GT and Murray GI: Current
mechanistic insights into the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in
tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 237:273–281. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thi MU, Trocmé C, Montmasson MP, Fanchon
E, Toussaint B and Tracqui P: Investigating metalloproteinases
MMP-2 and MMP-9 mechanosensitivity to feedback loops involved in
the regulation of in vitro angiogenesis by endogenous mechanical
stresses. Acta Biotheor. 60:21–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Makrilia N, Kollias A, Manolopoulos L and
Syrigos K: Cell adhesion molecules: Role and clinical significance
in cancer. Cancer Invest. 27:1023–1037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Q, Barclay M, Hilkens J, Guo X,
Barrow H, Rhodes JM and Yu LG: Interaction between circulating
galectin-3 and cancer-associated MUC1 enhances tumour cell
homotypic aggregation and prevents anoikis. Mol Cancer. 9:1542010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Q, Guo X, Nash GB, Stone PC, Hilkens
J, Rhodes JM and Yu LG: Circulating galectin-3 promotes metastasis
by modifying MUC1 localization on cancer cell surface. Cancer Res.
69:6799–6806. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Popper HH: Progression and metastasis of
lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 35:75–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA,
Gardner LM, Pe'er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS and Hendrix MJ: Vascular
channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro:
Vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 155:739–752. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shirakawa K, Tsuda H, Heike Y, Kato K,
Asada R, Inomata M, Sasaki H, Kasumi F, Yoshimoto M, Iwanaga T, et
al: Absence of endothelial cells, central necrosis and fibrosis are
associated with aggressive inflammatory breast cancer. Cancer Res.
61:445–451. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sood AK, Seftor EA, Fletcher MS, Gardner
LM, Heidger PM, Buller RE, Seftor RE and Hendrix MJ: Molecular
determinants of ovarian cancer plasticity. Am J Pathol.
158:1279–1288. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharma N, Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Gruman LM,
Heidger PM Jr, Cohen MB, Lubaroff DM and Hendrix MJ: Prostatic
tumor cell plasticity involves cooperative interactions of distinct
phenotypic subpopulations: Role in vasculogenic mimicry. Prostate.
50:189–201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mei J, Gao Y, Zhang L, Cai X, Qian Z,
Huang H and Huang W: VEGF-siRNA silencing induces apoptosis,
inhibits proliferation and suppresses vasculogenic mimicry in
osteosarcoma in vitro. Exp Oncol. 30:29–34. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meier P, Finch A and Evan G: Apoptosis in
development. Nature. 407:796–801. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brown R: The bcl-2 family of proteins. Br
Med Bull. 53:466–477. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Knight T, Luedtke D, Edwards H, Taub JW
and Ge Y: A delicate balance-The BCL-2 family and its role in
apoptosis, oncogenesis and cancer therapeutics. Biochem Pharmacol.
162:250–261. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Breckenridge DG and Xue D: Regulation of
mitochondrial membrane permeabilization by BCL-2 family proteins
and caspases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 16:647–652. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xia J, Dai L, Wang L and Zhu J: Ganoderic
acid DM induces autophagic apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer
cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR activity. Chem Biol Interact.
316:1089322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Z, Zhu J, Huang Y, Li W and Cheng H:
MYO18B promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Diagn Pathol. 13:852018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Krencz I, Sztankovics D, Danko T,
Sebestyen A and Khoor A: Progression and metastasis of small cell
lung carcinoma: The role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and metabolic
alterations. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:doi:
10.1007/s10555-021-10012-4. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seo BR, Min KJ, Cho IJ, Kim SC and Kwon
TK: Curcumin significantly enhances dual PI3K/Akt and mTOR
inhibitor NVP-BEZ235-induced apoptosis in human renal carcinoma
Caki cells through down-regulation of p53-dependent Bcl-2
expression and inhibition of Mcl-1 protein stability. PLoS One.
9:e955882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chien CS, Shen KH, Huang JS, Ko SC and
Shih YW: Antimetastatic potential of fisetin involves inactivation
of the PI3K/Akt and JNK signaling pathways with downregulation of
MMP-2/9 expressions in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 333:169–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhong XS, Zheng JZ, Reed E and Jiang BH:
SU5416 inhibited VEGF and HIF-1alpha expression through the
PI3K/AKT/p70S6K1 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
324:471–480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappaB: The
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou P, Wang C, Hu Z, Chen W, Qi W and Li
A: Genistein induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells by reversal of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal via a Notch1/NF-κB/slug/E-cadherin
pathway. BMC Cancer. 17:8132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li J, Lau GKK, Chen L, Dong SS, Lan HY,
Huang XR, Li Y, Luk JM, Yuan YF and Guan XY: Interleukin 17A
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via NF-κB induced
matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 expression. PLoS One.
6:e218162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shibata A, Nagaya T, Imai T, Funahashi H,
Nakao A and Seo H: Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity decreases the
VEGF mRNA expression in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 73:237–243. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|